OBESITY
Obesity is a chronic disease characterized by the storage of excess adipose tissue in the body, accompanied by metabolic alterations, which predispose to the presentation of disorders that deteriorate the state of health. Its etiology is multifactorial, related to biological, sociocultural and psychological factors.
The fundamental cause of overweight and obesity is an energy imbalance between calories consumed and calories expended. Globally, the following has occurred: an increase in the intake of high-calorie foods that are rich in fat; and a decline in physical activity due to the increasingly sedentary nature of many forms of work, new modes of transportation, and increasing urbanization.
How can you tell if you are already obese, or overweight? You can be guided by calculating your Body Mass Index:
BMI Weight (in kilograms) divided by height squared (in meters).
For example :
80 kilograms / (1.75 mts)2 ----------- 80 / 3.0625 ------- BMI: 26.12
The result obtained is taken to the following table:
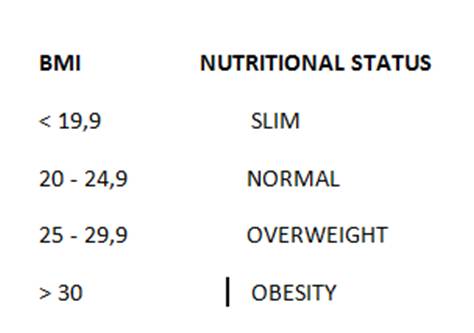
You would be in the overweight range.
If you are in the Obesity range it is necessary to know in which degree of Obesity you are:
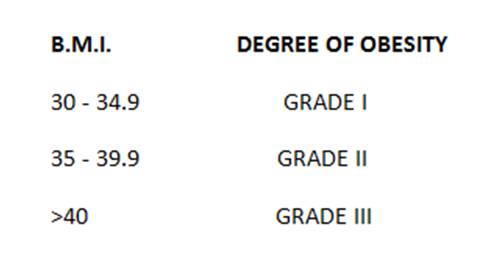
A high BMI is an important risk factor for non-communicable diseases, such as the following: cardiovascular diseases (mainly heart disease and stroke); diabetes; musculoskeletal disorders (especially osteoarthritis, a very disabling degenerative joint disease).
As my specialty is Gynecology and Obstetrics, we will talk a little about Obesity in Pregnant Women.
Obesity and overweight, prior to pregnancy as well as excessive weight gain during pregnancy are negative factors that involve increased risks during pregnancy and complications for both the woman and the fetus.
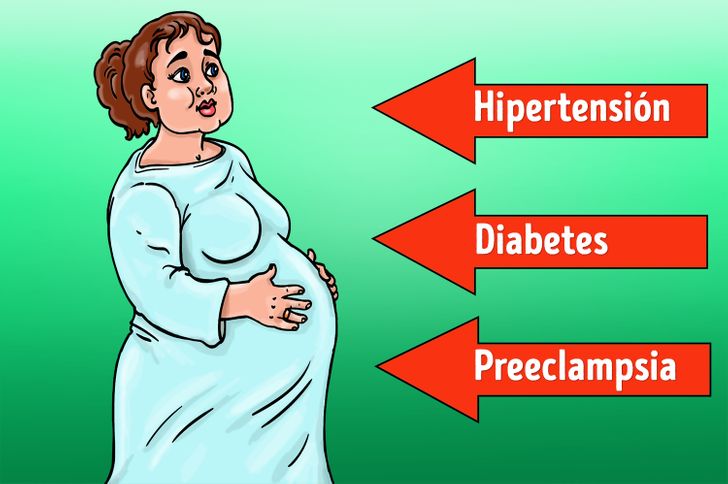
Obesity is associated with lower fertility and longer time to conceive, and pregnancies complicated by obesity are related to gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, preterm delivery, instrumental delivery or cesarean section, infections and postpartum hemorrhage; in addition, there is an increased risk of congenital malformations in their children, large fetuses, shoulder dystocia and fetal death.
It is not necessary to eat for two; avoid foods high in fat and sugar and keep in mind that nutritional needs increase from the 2nd trimester onwards.
If you start your pregnancy and you are thin, or have a BMI less than 18.5 the recommended range for weight gain throughout gestation is between 12.5 to 18 kilograms. If you have a Normal Weight, a BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 you can gain in a range of 11.5 to 16 kilograms. On the other hand, if you are already overweight, things change, because you should gain less weight during your pregnancy, because if you are overweight (BMI of 25 to 29.9) you would gain from 7 to 11.5 kilograms and finally in the Obesity range it is recommended that you only gain a range of 5 to a maximum of 9 kilograms.
The calculation of calories that you should ingest daily also varies according to your initial body weight. If you are already obese it is recommended 20 kcal per kilogram of weight/day. If you are overweight it is an estimated 25 kcal/kgr weight/day. If your weight is normal you can consume a little more kcal daily, about 30 kcal/kgr weight/day. And if you are very thin, your BMI is <20 kg/mts2 you can consume an average of 40 kcal/kgr weight/day. In short, the lower the weight, the higher the daily calorie intake needed.
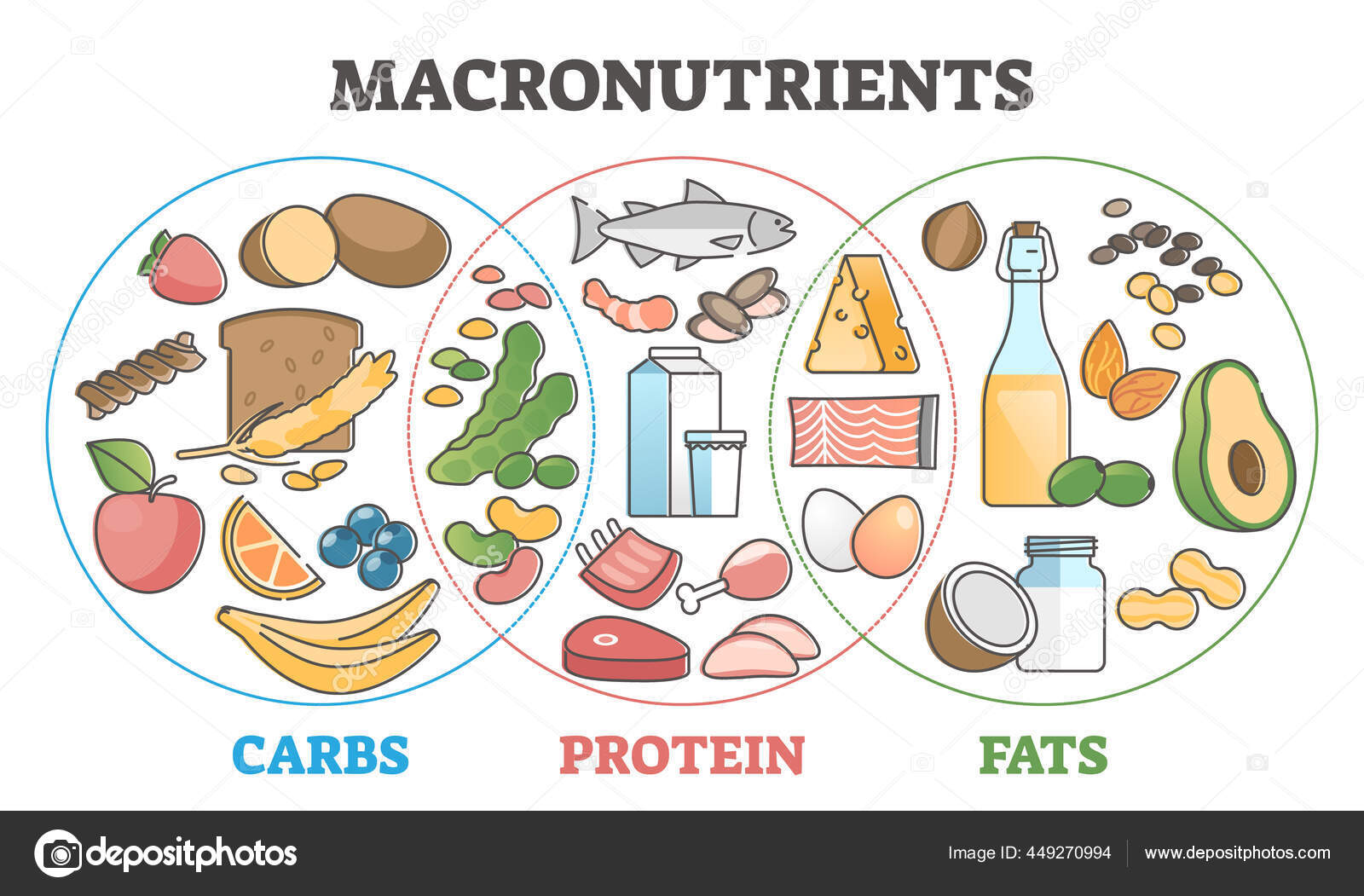
Your macronutrient intake should be distributed as follows: 15 to 20% protein, 20 to 35% fat, and 45 to 45% carbohydrates. You must have your three food groups, and not the false belief that you should totally eliminate fats, what should be decreased is the intake of saturated fats to less than 10% of the total daily calories; and increase the intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Optimal control of obesity should begin before pregnancy is achieved. Obese women who manage to lose even a small amount of weight before pregnancy may have better obstetric outcomes, and weight loss, dietary modification, exercise and behavioral change during pregnancy should be encouraged. It is not recommended to prescribe medications for weight control at the time of conception or during pregnancy, due to safety and possible adverse effects. So my dear readers, take care of yourself and control your diet and weight.

LA OBESIDAD
La obesidad es una enfermedad crónica caracterizada por el almacenamiento en exceso de tejido adiposo en el organismo, acompañada de alteraciones metabólicas, que predisponen a la presentación de trastornos que deterioran el estado de salud. Su etiología es multifactorial, relacionada a factores biológicos, socioculturales y psicológicos.
La causa fundamental del sobrepeso y la obesidad es un desequilibrio energético entre calorías consumidas y gastadas. A nivel mundial ha ocurrido lo siguiente: un aumento en la ingesta de alimentos de alto contenido calórico que son ricos en grasa; y un descenso en la actividad física debido a la naturaleza cada vez más sedentaria de muchas formas de trabajo, los nuevos modos de transporte y la creciente urbanización.
Como puedes saber si ya eres obeso, o tienes sobrepeso? Te puedes guiar calculando tu Índice de Masa corporal:
IMC Peso (en kilogramos) dividido entre la talla al cuadrado (en metros)
Por ejemplo :
80 kilos / (1,75 mts)2 ----------- 80 / 3,0625 ------- IMC: 26,12
El resultado obtenido se lleva a la siguiente tabla:
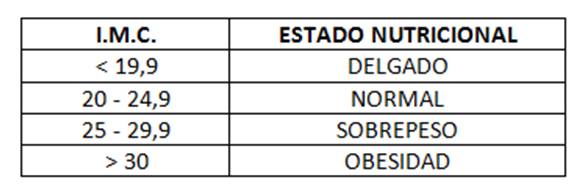
Estarías en el rango de sobrepeso.
Si entras en el rango de Obesidad es necesario conocer en qué grado de Obesidad te encuentras:
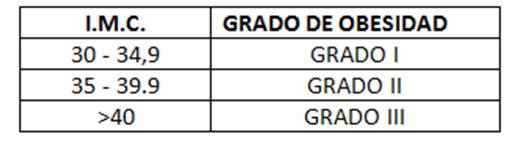
Un IMC elevado es un importante factor de riesgo de enfermedades no transmisibles, como las siguientes: las enfermedades cardiovasculares (principalmente las cardiopatías y los accidentes cerebro vasculares); la diabetes; los trastornos del aparato locomotor (en especial la osteoartritis, una enfermedad degenerativa de las articulaciones muy discapacitante)
Como mi especialidad es la Ginecología y Obstetricia conversaremos un poco de la Obesidad en la mujer Embarazada.
La Obesidad y el sobrepeso, previo al embarazo así como la ganancia excesiva de peso durante la gestación son factores negativos que implican un aumento de los riesgos durante la gestación y complicaciones tanto para la mujer como para el feto.
La obesidad se asocia con menor fertilidad y mayor tiempo para concebir, y los embarazos complicados con obesidad se relacionan con la diabetes gestacional, preeclampsia, parto pretérmino, partos instrumentados o cesáreas, infecciones y hemorragia posparto; además, existe mayor riesgo de malformaciones congénitas en sus hijos, fetos grandes, distocia de hombros y muerte fetal
No es necesario comer por dos; hay que evitar los alimentos con alto contenido en grasa y azúcar y hay que tener en cuenta que las necesidades nutricionales aumentan a partir del 2º trimestre.
Si empiezas tu embarazo y eres delgada, o tienes un IMC menor de 18,5 el rango recomendado para ganancia de peso en toda la gestación es entre 12,5 a 18 kilogramos. Si tienes un Peso Normal, un IMC entre 18,5 y 24,9 podrás aumentar en un rango de 11,5 a 16 kilos. En cambio si ya tienes sobrepeso la cosa cambia, porque debes aumentar menos peso durante tu embarazo, pues con sobrepeso (IMC de 25 a 29,9) aumentarías de 7 a 11,5 kilogramos y finalmente en el rango de Obesidad es recomendable que solo aumentes un rango de 5 a máximo 9 kilogramos.
EL calculo de calorias que debes ingerir diariamente tambien varia según tu peso corporal inicial. Si ya eres obesa lo recomendable son 20 kcal por kilogramo de peso/dia. SI tienes sobrepeso es un estimado de 25 kcal/kgr peso/dia. Si tu peso es normal puedes consumir un poco mas de kcal diarieamente, unas 30 kcal/kgr peso /dia. Y si eres muy delgada, tu IMC es <20 kg/mts2 puedes consumir un promedio de 40 kcal/kgr peso/dia. En fin, a menor peso, mayor el aporte de calorías necesarias diariamente.
Tu ingesta de macronutrientes debe estar distribuida de la siguiente manera: 15 a 20% de proteinas, 20 a 35% de grasas, y 45 a 45% de carbohidratos. Debes tener tus tres grupos alimenticios, y no la falsa creencia que debes eliminar por total las grasas, lo que se debe disminuir es la ingesta de grasas saturadas a menos de 10% del total de calorias diarias; y aumentar la ingesta de acidos grasos poliinsaturados.
Un control óptimo de la obesidad debería empezar antes de lograr un embarazo. Las mujeres obesas que logran disminuir aunque sea un poco de su peso antes del embarazo pueden tener mejores resultados obstétricos, y se debe promover perder peso, modificar la dieta, ejercicio y cambio de conducta durante la gestación. No se recomienda indicar medicamentos para el control del peso en el momento de la concepción o en el embarazo, por seguridad y posibles adversos efectos. Así que mis estimadas lectoras, a cuidarse y controlar la alimentación y el peso.



Congratulations @drginecoweb! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s):
Your next target is to reach 50 posts.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPTo support your work, I also upvoted your post!
Check out the last post from @hivebuzz:
Support the HiveBuzz project. Vote for our proposal!