ELDER ABUSE
Hello hivers! Today I’ll be talking on elder abuse or abuse of the elderly, first of, let’s look at some statistical facts on the topic:
~It is estimated that about 1 in 6 people 60 years and above has experienced some form of abuse in community settings during the past year.
~Some studies estimate about 1 to 2 million cases of elder abuse in America but the number is largely unknown because majority of cases are not reported. For every 1 case that is reported, 5 go unreported
~Approximately 90% of all elder abuse and neglect occur at the hands of a family member or a relative.
~Both men and women are perpetrators of elder abuse, majority are their adult children or spouses.
~Most elder abuse victims are dependent on their abuser for their most basic needs
~Incidence of Elder abuse is high in nursing homes and long-term care facilities
~The commonest form of elder abuse is financial exploitation, closely followed by physical abuse, neglect, and emotional abuse.
~Elder abuse usually leads to serious physical injuries and long-term psychological consequences including morbidity and mortality.
What then is Elder Abuse?
According to the World Health Organisation, elder abuse is “A single or repeated act, or lack of appropriate action, occurring within any relationship where there is an expectation of trust which causes harm or distress to an older person” An older person being one who is 60years or older
Types or Forms of Elder Abuse
Abuse of the elderly can occur in one or more of the following ways and this includes;
- Physical Abuse: this usually involves inflicting injury or pain to the elderly or could also be in form of physical coercion or restraint. Physical abuse can be in form of assault, battery, prolonged or continual deprivation of food or water, or medications, use of physical restraints for punishment, pushing, shoving, slapping (more common in the helpless]
- Sexual Abuse: Any sort of non-consensual sexual contact. Such contacts may be physical sexual acts or showing an elderly pornographic materials, incest, rape etc
- Neglect: Failure to provide necessary physical or mental care to an elderly person. Such as failure to assist in personal hygiene, failure to provide food, clothing or shelter, failure to provide medical care, or to protect from health and safety hazards or to prevent malnutrition or dehydration. Note that it also includes self-neglect one of the most common forms of abuse occurring in community settings. Neglect is also failing to provide, or deliberately withholding necessities such as hearing aid, eyeglasses, walker, cane, wheelchair, medications, food, help in bathing, clean clothes or failure to provide appropriate physical precautions
- Psychological / Emotional Abuse: this involves engaging in activities that will lead to mental anguish such as threats of deprivation or harm, verbal aggression and name calling, insults, false accusations, denigration, intimidation and failure to permit access to social contacts.
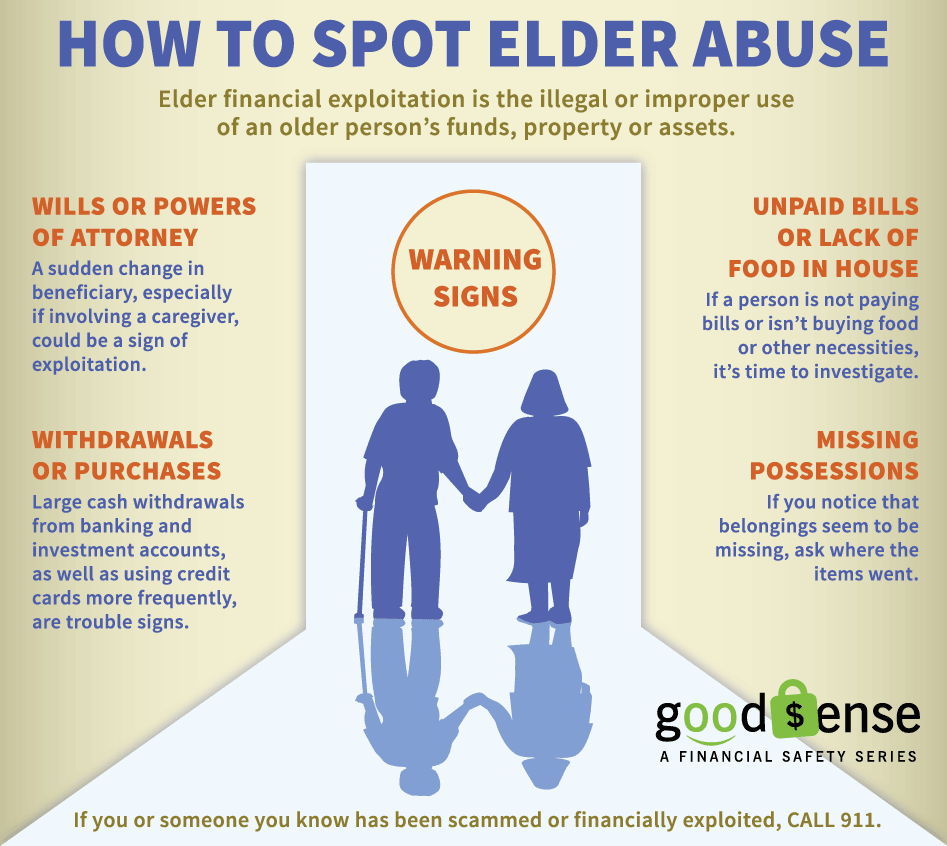
- Financial abuse: The illegal or unauthorized taking or using of an elder's funds, property or assets by an individual or entity. Theft of money, possessions, keeping the elder for their social security check, getting power of financial attorney, preying on the elder’s gullibility, helplessness, or ignorance
- Others: such as threats or intimidation, isolation ( ie intentionally preventing or restraining an elder from receiving mail, telephone calls or visitors), witchcraft accusation and stigmatization, abuse by systems such as health clinics, pension offices and even the government.
Causes of Elder Abuse
This often occurs in combination. It could be domestic (ie among relatives at home ) or institutional (ie among workers in nursing homes)
1)Domestic causes: could be due to a number of factors including:
i)Physical dependency
ii)Caregiver stress: frustration, lack of finances, lack of employment
iii)Family violence pattern: Abused children become abusive adults who then abuse own children and also their parents
iv)Pathological abusers due to drug and alcohol abuse or mental illness
v)Cultural and societal norms
2)Institutional causes:
i) Inadequate training of staff on how to handle the elderly
ii)Insufficient staff
iii)insufficient resources
Risk factors associated with elder abuse
- Victim Factors
- Caregiver Factors
- Environmental / System Factors
1} Victim factors: this includes
~Insufficient income to live independently
~Increasing dependency
~Cognitive impairment, especially if recent
~Behavioural problems: shouting, incontinence, wandering, paranoia, stubborn
~Dementia – less able to protect self
~Elder gets abusive, violent, socially inappropriate
~Poor health especially if elder requires much care
~Social isolation of both the care giver and the elder
2} Caregivers factor: this includes
~History of violence, or victim of abuse
~Substance abuse
~External stressors
3} Environmental factors
~Victim and perpetrator in shared living situation
~Financial and other dependence on caregiver
~Perpetrator financially dependent on the elder
Warning signs of Elder Abuse
~Abuser Often speaks for elder
~Abuser isolates elder
~Abuser controls mail, visits and phone calls
~Elder appears helpless, confused, hesitant to speak freely
~Elder has insufficient food and basic necessities
~Elder exhibits poor hygiene
~Untreated medical conditions
~Visible injuries
~Change in sleep, appetite or behavior
~Unkempt appearance,emaciated or bloated, dirty or inappropriate clothing, unshaven face and uncombed hair, unusual body odor
Diagnosis
~Signs of physical injury
~Conflicting and/or vague histories from the patient and caregiver
~History inappropriate to degree of injury
~Denial
~Long delay between injury and presentation
~History of being “accident prone”
~Look for STI, genital injuries, depression and withdrawal.
Physical findings
~Welts, laceration, fractures
~Excess drugs / unexplained lethargy
~Burns, Bruises
~Frequent falls
Barriers to reporting elder abuse
~Uncertainty about the validity of the diagnosis
~Lack of training in recognizing abuse
~Discomfort in confronting the alleged perpetrator
~Fear that the abuser will retaliate against the victim
~Unawareness of procedures for reporting
~Disinclination to be involved in the legal System.
~Hesitancy to “label” the victim or the abuser
~Perception that the proof of abuse is inadequate
~Lack of professional protocols for elder Abuse
Intervention
a)Talk to victim privately
b)If danger suspected, admit person with a “medical diagnosis”
c)Counsel the caregiver
-provide information about patient’s condition
-meet needs of caregiver (relieve stress)
-talk to caregiver about how to respond to patient’s behavioural problems
-respite or alternative care if burden too great for caregiver
-help the caregiver maximise the elderly individual’s abilities.
Prevention
i)Avoid isolation
ii)Stay social/active – volunteer, see friends
iii)Avoid living with a person with a history of abuse or violence
iv)Beware of family members with financial motivations or with substance abuse issues
v)Consider respite services to relieve caregivers
vi)Have friends and relatives remain involved and observant
vii)Consider Counseling
viii)Communicate
ix)Have relatives and friends visit at various times of the day – unannounced
Recommendations
- A course on aging should be part of the general studies (compulsory) courses in the university to increase the awareness of elder abuse
- Universities should encourage research in the study of the aged.
- Seniors citizens should be involved in some intergenerational extracurriculum activities with the youths.
References
1.https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/elder-abuse
2.https://www.who.int/violence_injury_prevention/violence/global_campaign/en/chap5.pdf?ua=1