When your body is unable to absorb glucose (sugar) into your cells and utilise it as fuel. As a result, your bloodstream begins to accumulate additional sugar.
Environmental, genetic as well as socioeconomic factors have roles to play in the manifestation of this disorder. These factors will determine the type of diabetes one will have.
This ranges from type 1, type 2, through to hyperglycaemia in pregnancy.
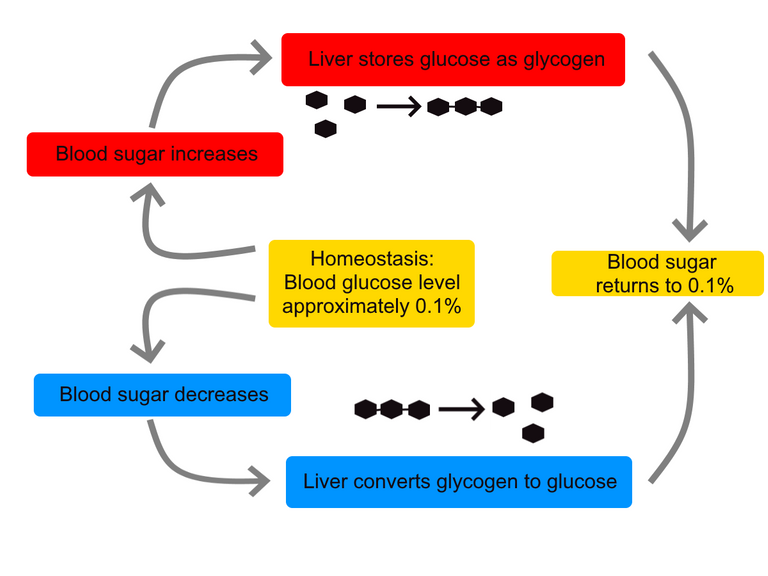
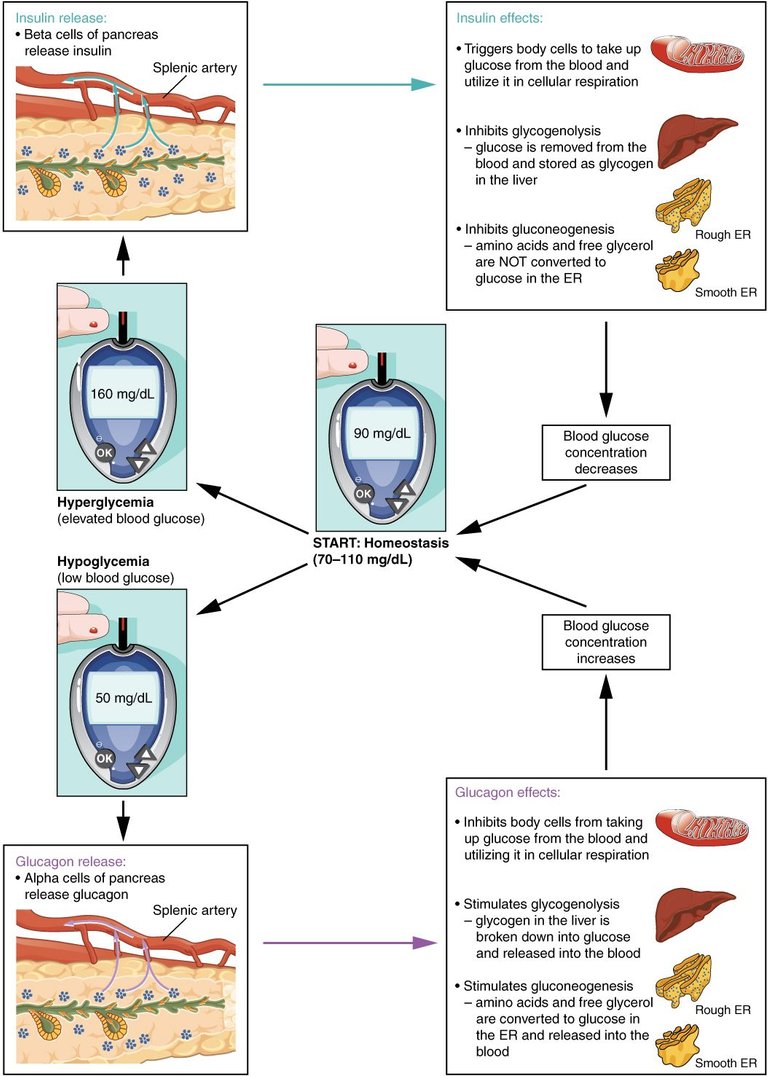
Following a meal, glucose is absorbed from the intestine and enters the blood. The rise in the blood glucose level stimulates the secretion of insulin by beta cells of Langerhans of pancreas. The uptake of glucose by most extrahepatic tissues, except brain is dependent on insulin. Moreover, insulin helps in the storage of glucose as glycogen or its conversion to fat.
Normally, 2 to 2½hours after a meal, the blood glucose levels falls to near fasting levels.
By Christinelmiller - Own work, CC0
It may go down further; but this is prevented by processes that contribute glucose to the blood.
For another 3 hours, hepatic glycogenolysis will take care of the blood sugar level. Thereafter, gluconeogenesis will take charge of the situation.
By OpenStax College - Anatomy & Physiology, Connexions Web site. CC BY 3.0,
Your body's tissues and organs may sustain severe harm if your blood glucose level is high for an extended length of time. Over time, some issues may pose a threat to life.
cardiovascular conditions such as atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, heart attack, and chest pain (narrowing of the arteries).
Heart attacks and strokes are two- to three-fold more likely to occur in adults with diabetes.
Numbness and tingling brought on by nerve injury (neuropathy) that begins at the toes or fingers and spread.
This increases the chance of foot ulcers, infection and eventual need for limb amputation.
A significant contributor to blindness, diabetic retinopathy results from cumulative long-term harm to the retina's tiny blood vessels. Diabetes causes over a million individuals to go blind.
Kidney damage (nephropathy) that can lead to kidney failure or the need for dialysis or transplant.
It has been demonstrated that changes in lifestyle can postpone or stop the onset of type 2 diabetes. In order to help prevent type 2 diabetes and its complications, people should:
Reach and maintain a healthy body weight;
Engage in regular, moderate-intensity physical activity for at least 30 minutes on most days;
To control weight, one must increase exercise, consume a nutritious diet free of sugar and saturated fats; and Refrain from using tobacco because it raises the risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Testing for blood glucose is a relatively cheap method of achieving an early diagnosis.
Diabetes is treated with a healthy diet, regular exercise, reducing blood sugar levels, and other known risk factors for blood vessel damage. It's crucial to stop smoking if you want to prevent difficulties.
Blood glucose management, especially for type 1 diabetes. Insulin is necessary for those with type 1 diabetes, and while oral medications can be used to treat type 2 diabetes, insulin may also be necessary;
Blood pressure management
foot treatment
REFERENCE
Cleveland clinic
Pubmed
WHO