Hey Everyone! I know Malaria and its treatment is a very complex topic, but in this series, I will try to explain this topic as if I would explain it to a 10-year-old.
Imagine, If your senior asked you for the drug for drug-resistant malaria, as an intern, you were not able to give an answer 😁.
Now, you as an intern could not bear the sadness of not knowing the answer to this simple question. You went home after your duty and started studying Malaria, Where would you start? Of course from the Basics which is "How Does Malaria Get into the Human Body First?" only you can understand the drugs that can kill the Malarial Parasite.
 Anopheles Mosquito Source
Anopheles Mosquito SourceFrom The Basics
Well Most of us already know the malaria parasite is Plasmodium vivax. But Most of us don't know if there are many other species that cause malaria. Here are some p.falciparum, p.ovale, p.malarie, p.knowlesi.
Now, how do these small creatures get into the human body?
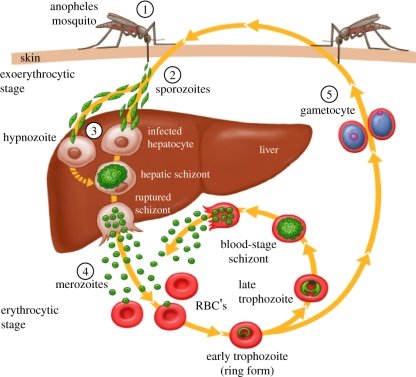
It all starts with the "bloodsucking buzz clowns". Let's Call him Marty the Mosquito. He is not an average mosquito. He is buzzing around and lands on a human hand for a tasty "Blood meal". But, he is not just after a drink, he is also carrying the Malarial Parasites in his tini tiny bag Pack. When is sips your Blood, he lets his parasites into your bloodstream. After that, his work here is done, and flies off. 😒
Now, you are infected but will the symptoms start as soon as these parasites are in your bloodstream? No.
These parasites need a home to stay and multiply so they just stay in blood for around 10 mins only. Eventually, they make their way to the Liver, where the actual Party Starts. They either choose to sleep in the liver cells or Multiply. If they choose to sleep, they will remain dormant for 7-28 days. But eventually, they will multiply. The number will be so high that they will have no room left inside the Liver cell or Hepatocytes. So, They Come out now and go into your bloodstream.
Remember, They always need a home, This time they will choose Red Blood Cells (RBC) as their home. As we know there is very little room inside RBC, and it can't bear the overpopulation of these parasites so RBC brusts and All the infective Parasites are in your blood now.
Malaria Life Cycle Source
This is where all the symptoms of Malaria start. Only after the Lysis of RBC.
Now, there are two paths for These Parasites, Either it can affect another healthy RBC and Multiply again or change into gamates.
These Gamates are taken by Marty the Mosquito in his Next Blood Meal and go on infecting another Person.
Some Medical Terms if you are Interested😅
First Pasasites from Mosquito: Sporozoites
Dormant Stage in Liver: Hypnoziotes
Multiplying In Liver: Schizont
In RBC: Tropoziotes or Gametocytes.
Satges:
When First Comes in the Liver: Pre- Erythrocytic Stage
Dormant in Liver: Exo- Erythrocytic Stage.
In RBC: Erythrocytic Stage
After forming Gamates: Gametocytic Stage
Congratulations, Now you all know the basics of the life cycle of a malaria parasite. Let's talk treatment now.
Malarial Treatment
If you understand the lifecycle, it will be a piece of cake to understand the treatment. let's start
After Marty the mosquito bit you, the first thing the parasite did was go into the liver within 10 mins(Pre-erythrocytic Stage), and then it either remained dormant(Exo-Erythrocytic Stage) or Multiplied then it went to RBC(Erythrocytic Stage) and produced symptoms after the lysis and made gamates.
Scientists have made such a drug that can inhibit all the stages except IN RBC which is an erythrocytic stage. This Drug is called "Primaquine". This Drug can literally kill the gamatecytic stage with a single dose. Imagine that 😎 But should be given continuously for 2 weeks to kill dormant parasites in the Liver.
So, what did we learn from this? Primaquine can kill gametocytes, which means Marty the mosquito won't get any gametocytes in his next meal thus the transmission is also stopped. Also, This drug attacked the cause of malaria which is the pre-erythrocytic stage.
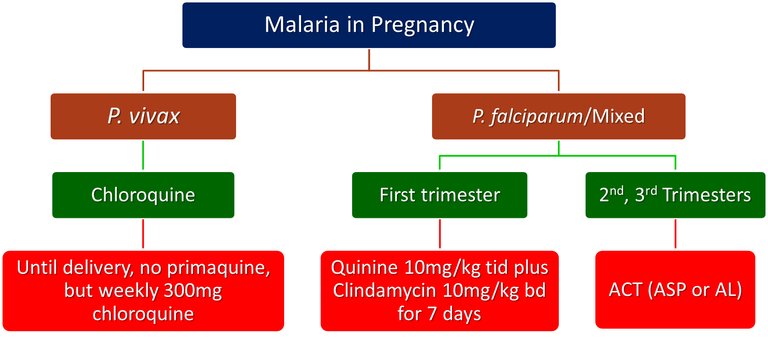
Knowing about side effects is also equally important. Primaquine can cause hemolysis (Breakdown of RBCs), only in Patients with G6pd deficiency (will explain in another article about g6pd). Therefore it should never be used in infants and pregnancies, because they are G6pd Deficient.
Everything I explained till now was about Plasmodium Vivax. There is a parasite that is more dangerous than vivax, called P. falciparum. This one is notorious and highly infective and causes severe and complicated malaria. What's Complicated Malaria? When the parasites reach your brain, things get complicated, hence the name "Complicated Malaria". There are different sets of Drugs for P. falciparum which we will look at later.
Malaria Treatment Source
Now, what about the erythrocytic stage or RBC stage, after all, it is the one that produces all the clinical Symptoms. If we treat this stage, all the clinical symptoms will be gone.
Drugs for Erythrocytic Stages only:
| Fast Acting | Slow Acting |
|---|---|
| Mefloquine | Sulfadoxine |
| Atovaquone | Pyrimethamine |
| Chloroquine | Proguanil |
| Halofantrine | Doxycycline |
| Artemisinins | Clindamycin |
| Qunine |
Some Peculiar Characteristics of Specific Drugs:
Mefloquine: Longest Acting in Fast Acting Group, But this one can cause neuropsychiatric disorders like depression therefore it is contraindicated in persons with neuropsy disorders.
Chloroquine: Actually it's not just a single drug, it's a group that has these 3 drugs:
- Chloroquine
- Amodiaquine
- Piperaquine
This group particularly Chloroquine is now the Drug of Choice for Drug Sensitive Malaria. Also, It has not shown any negative effects in pregnancy till now, therefore considered safe for pregnancy and Children too. We have seen one peculiar Side effect of this drug called " Bulls Eye Maculopathy", By the name you can tell, something is going wrong in the eye. Actually, this side effect takes several years to develop, but you only give malarial drugs for a few weeks, therefore you won't see this side effect in Malarial treatment. But in which Conditions you used Chloroquine for years though?
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- DLE
- Lepra Reaction
Artemisinins: Scientists extracted this from Artemisia annua, sweet wormwood, a Chinese herbal plant. This group consists of drugs like Artesunate and Artemether. Fastest and shortest-acting drug and used for Drug-Resistant Malaria.
But there is a problem, as they are the fastest and shortest, Imagine there were 1000 malarial parasites in the blood and this drug killed 900 of them and the effect decreased as it is the shortest. Those 100 parasites left in the blood will multiply after some time and Person gets sick again. This is called "Recrudescence" or incomplete treatment. Those 100 left parasites must also be killed to prevent this. Therefore we never give this drug alone, it is always given in combination with a long-acting drug.
And that's Artmesenin Based Combination Therapy(ACT).
Example: Artesunate + Sulfadoxine or Artesunate+ Pyrimethamine
Let's Revise:
| Parasite | Normal | Pregnancy |
|---|---|---|
| P.vivax | Chloroquine | Chloroquine |
| P.falciparum | ACT | Quinine |
What about Complicated Malaria?
Remember we talked about when a parasite reaches the brain, that's where things get complicated and that's complicated malaria. Symptoms like Seizures, abnormal behavior, impairment of consciousness and coma can be seen in this stage.
As the person is not conscious, we will have to give the drug intravenously, therefore the drug is:
I/V Artesunate which must be given for at least 24 hours even if the patient wakes up and then ACT whenever a person can take oral drugs.
Imagine you are going to a malaria-prone Area, Of course, you wouldn't want to get malaria Parasites by Marty the Mosquito. What to do now? Is there any way that you can prevent getting Malaria in those high-risk areas?
Of course, there is 😁
It depends on how long you are going to stay in that area, If it is less than 6 weeks we will call it short-term, and If it's more than Long-term
Here's the Prophylaxis Treatment:
| Short Term (<6 Weeks) | Long Term (>6 Weeks) |
|---|---|
| Doxycycline (Daily) 2 days before going and continue 4 weeks after leaving | Mefloquine (once a week) Start 2 weeks before going and Continue up to 4 weeks after leaving |
Final words
In conclusion, we've taken a simple journey into the world of malaria, breaking down its complexities in understandable ways, much like explaining it to a kid. We've learned about the names of different types of malaria parasites, how they enter the human body through mosquito bites, and the basics of malaria treatment, including the superhero drugs, Primaquine, and Chloroquine.
But remember, there's still more to explore about malaria, including its complicated forms and different treatments for various stages. So, stay curious and keep learning!
References:
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/221134-overview
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6617065/
https://www.nature.com/subjects/malaria/srep
https://www.cdc.gov/malaria/travelers/drugs.html
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.
Congratulations @idoctor! You received a personal badge!
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
Check out our last posts: