Respiratory acidosis is a condition that occurs when the lungs fail to remove enough carbon dioxide from the body, leading to an increase in the acidity of the blood. This condition is typically caused by a respiratory problem such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, pneumonia, or chest injuries.
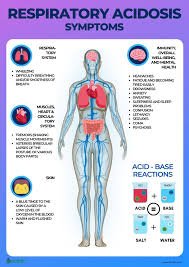
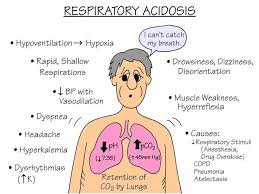
Carbon dioxide is produced as a byproduct of cellular metabolism and is removed from the body through the lungs. When there is an issue with the lungs or breathing, such as in respiratory acidosis, carbon dioxide builds up in the bloodstream, leading to an increase in acidity. This can cause a range of symptoms, including headache, confusion, drowsiness, and even coma.
Treatment for respiratory acidosis depends on the underlying cause of the condition. For example, if the condition is caused by a lung infection such as pneumonia, treatment will involve antibiotics to clear the infection. If the condition is caused by a chronic lung condition such as COPD, treatment may involve medications to help manage symptoms and improve lung function.
In some cases, oxygen therapy may be necessary to help increase oxygen levels in the bloodstream and reduce the buildup of carbon dioxide. In severe cases of respiratory acidosis, mechanical ventilation may be necessary to help the patient breathe.
Prevention of respiratory acidosis involves managing the underlying conditions that can cause the condition. This may involve quitting smoking, managing asthma or COPD symptoms, and seeking treatment for respiratory infections promptly.
Respiratory acidosis is a condition caused by a failure of the lungs to remove enough carbon dioxide from the body. This can lead to a range of symptoms and can be caused by a variety of underlying conditions. Treatment depends on the underlying cause of the condition and may involve medications, oxygen therapy, or mechanical ventilation. Prevention involves managing the underlying conditions that can cause the condition.
Respiratory acidosis can also occur due to external factors such as high altitudes, which can cause a decrease in oxygen levels in the air and make breathing more difficult. In addition, certain medications can also contribute to respiratory acidosis, such as sedatives and opioids, which can depress the respiratory system and cause breathing difficulties.
In some cases, respiratory acidosis can also occur as a result of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), a severe lung condition that can be caused by infections, trauma, or other factors. ARDS can cause the lungs to fill with fluid, making it difficult to breathe and leading to respiratory acidosis.
If left untreated, respiratory acidosis can lead to more serious complications, such as organ failure and even death. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of respiratory acidosis, especially if you have an underlying respiratory condition.
The diagnosis of respiratory acidosis is typically made through blood tests to measure the acidity and carbon dioxide levels in the bloodstream. Other tests, such as chest X-rays or pulmonary function tests, may also be performed to determine the underlying cause of the condition.
There are some lifestyle changes that can help manage the condition. These may include quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding exposure to air pollutants and other environmental toxins.
Respiratory acidosis is a condition that can be caused by a variety of factors, including respiratory conditions, medications, and external factors. It can lead to a range of symptoms and can be serious if left untreated. Treatment depends on the underlying cause of the condition and may involve medications, oxygen therapy, or mechanical ventilation. Lifestyle changes can also help manage the condition and prevent further complications. .
The treatment of respiratory acidosis primarily depends on the underlying cause. In mild cases, the body can often correct the imbalance naturally once the underlying condition is treated or resolved. However, in more severe cases, medical intervention may be required.
One of the primary goals of treatment is to increase oxygen levels in the bloodstream and reduce the buildup of carbon dioxide. This can be achieved through oxygen therapy, which involves delivering oxygen through a mask or nasal cannula. Oxygen therapy can help improve breathing and reduce the symptoms of respiratory acidosis.
In some cases, mechanical ventilation may be necessary to help the patient breathe. This may involve using a machine to deliver oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the bloodstream. Mechanical ventilation is typically reserved for severe cases of respiratory acidosis, such as those that result from ARDS or other respiratory failure.
Managing the underlying conditions that can cause respiratory acidosis is also important. This may involve taking medications to manage symptoms of asthma or COPD, treating respiratory infections promptly, and avoiding exposure to air pollutants and other environmental toxins.
The treatment of respiratory acidosis involves addressing the underlying cause of the condition and managing symptoms. Oxygen therapy and mechanical ventilation may be necessary in severe cases, while lifestyle changes can help manage the condition and prevent further complications. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of respiratory acidosis, especially if you have an underlying respiratory condition.
References :
https://www.healthline.com/health/respiratory-acidosis
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/313110

Quite an intricate writeup, very enlightening, i would advise that you use bigger images and center them to align better with the passages to make the read even more fun and interesting though. it was a pleasurable read, thanks for your time