Graphic created using canva.com
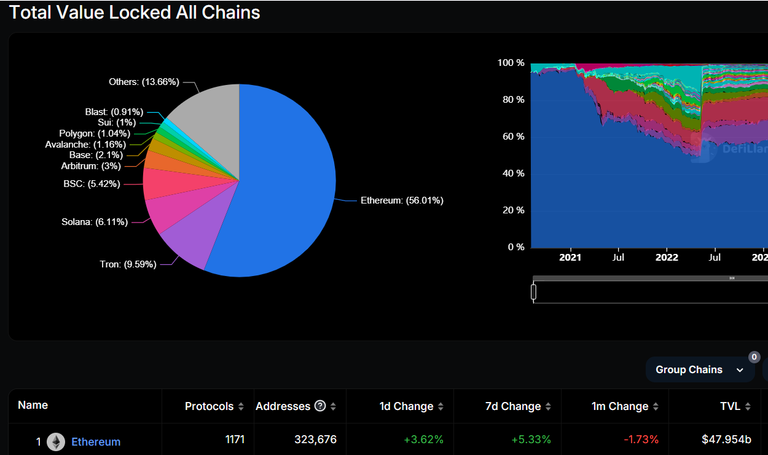
Despite its known scalability challenges, Ethereum has consistently maintained its position as the dominant Layer 1 (L1) blockchain. Despite the rise of several competing L1 blockchains, Ethereum continues to power the largest number of decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contract protocols, boasting a total value locked (TVL) of $44.856 billion, according to DefiLlama.
Why Ethereum's Scalability Issues Haven't Stopped Its Growth?
Ethereum’s early limitations, particularly in scalability, were seen as opportunities by other L1 blockchains that marketed themselves as "Ethereum killers." These competitors aimed to offer superior transaction throughput and lower costs, hoping to lure dApps and users away from Ethereum. But despite frequent congestion and high transaction fees during peak usage times, Ethereum's decentralized and secure architecture kept it at the forefront of the blockchain ecosystem.
Ethereum’s lack of scalability was often highlighted, but what couldn’t be replicated by emerging L1 blockchains was the strong developer and user community that had formed around Ethereum.
Early DeFi giants like Uniswap, Aave, and Curve were built on Ethereum and accumulated substantial liquidity, solidifying their place in the ecosystem.
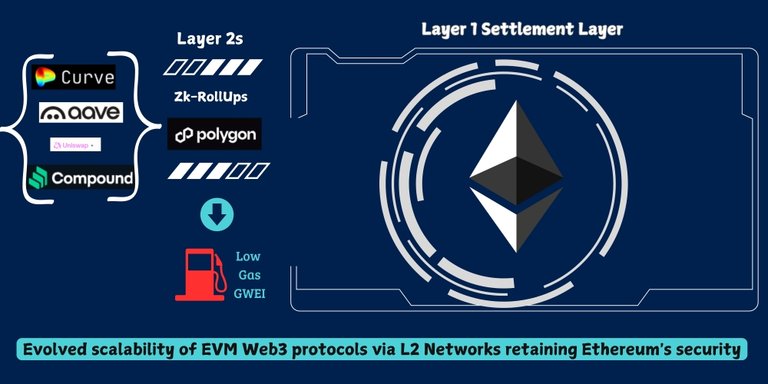
Rather than migrating to new L1 blockchains, these protocols also launched on Layer 2 (L2) Networks that were successful in being an alternate scalable platform, secured by Ethereum Blockchain.
Layer 2 Blockchains: Easing Ethereum’s Scalability Woes
Instead of being replaced, Ethereum was augmented by L2 blockchains like Polygon, Arbitrum, and Optimism. These networks were designed to handle the execution of transactions off-chain, while still relying on Ethereum for final settlement and security.
This L2 architecture allowed Ethereum to focus on data storage and security, while the computational burden of executing transactions was offloaded to these L2s.

Graphic created using canva.com
The result? Users could access the same dApps they trusted—such as Uniswap, Aave, and Curve—on L2 networks, enjoying significantly lower gas fees and faster transaction speeds. These L2 solutions helped Ethereum scale without compromising its security or decentralization, allowing Ethereum-based dApps to grow in both user base and liquidity.
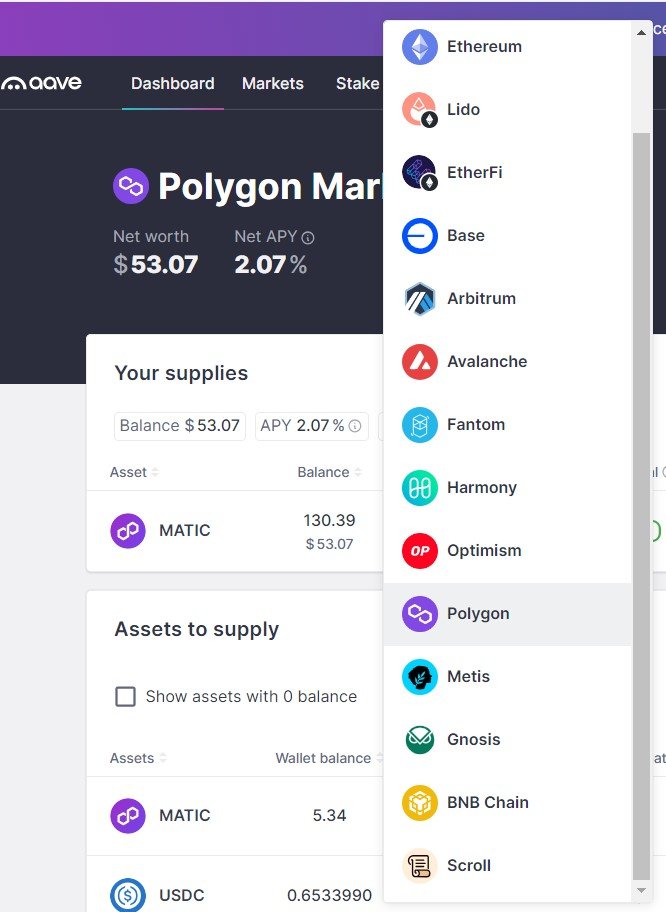
Aave Protocol on Ethereum L2 Networks — Polygon, Arbutrum, Optimism, Metis, Scroll…
L1 Blockchains link to Ethereum building Scalable Web3 dApps on L2 Networks
Numerous EVM-based L2 networks have emerged, designed to help other L1 blockchains integrate with Ethereum more effectively. Developers can utilize Ethereum’s tools, programming languages, and libraries to launch their Web3 dApps on these L2 platforms.
Users can seamlessly interact with these dApps using their Ethereum-compatible Metamask wallets.

Graphic created using canva.com
Today, any L1 blockchain can join the Ethereum ecosystem by developing its own zkEVM virtual machine, enhancing connectivity and scalability.
The Role of zk-Rollups in Ethereum’s Scaling Journey
As Ethereum continues to evolve, zk-Rollups have emerged as a leading L2 solution. Zero-knowledge rollups (zk-Rollups) offer a way to bundle transactions off-chain and submit a proof of their validity to Ethereum, drastically reducing the data and computational load on the Ethereum mainnet.
These zk-Rollups use cryptographic validity proofs (zk-proofs), which allow the Ethereum network to verify the correctness of transactions without having to process all the transaction data. By doing this, zk-Rollups make it possible for Ethereum to settle large numbers of transactions quickly and efficiently, enhancing scalability without sacrificing security.

Graphic created using canva.com
The Role of Data Storage in L2 Scalability
While L2s have unlocked new levels of scalability for Ethereum, their design decisions around data storage remain crucial. Most L2s still use Ethereum for data storage, which guarantees security but incurs higher fees. Storing data off-chain, on the other hand, can boost scalability but at the expense of security.
Each L2 has to balance these trade-offs carefully.
For example, Polygon POS offers a decentralized validator setup, ensuring secure data validation without overburdening Ethereum’s network. This balance between on-chain and off-chain storage plays a critical role in shaping the scalability of L2 solutions.
##Tackling Fragmented Liquidity and Shared State Challenges
One of the challenges with L2 solutions is the fragmentation of liquidity. Each L2 blockchain operates independently, and although they all settle on Ethereum, users cannot directly move funds or share liquidity between different L2 chains without reverting to Ethereum as an intermediary.
This fragmentation not only limits liquidity but also hinders capital efficiency across the ecosystem. In a world where seamless movement of liquidity and shared state between chains is essential, a more unified approach is needed.
Towards a Unified L2 Ecosystem: Polygon's Agg Layer and Beyond
Efforts are underway to address these interoperability issues. One promising development is Polygon’s Agg Layer, which aims to create an aggregated group of blockchains within the Polygon ecosystem. This infrastructure will allow different L2 blockchains to interact securely and with low latency, even before transactions are finalized on Ethereum.
By enabling direct communication and transaction settlement between L2s, the Agg Layer would eliminate the need for users to bridge assets back to Ethereum, enhancing the overall user experience and improving capital efficiency. This represents a significant step towards a more cohesive and scalable Ethereum ecosystem.

https://polygon.technology/blog/aggregated-blockchains-a-new-thesis
The Future of Scalable Web3 Protocols
As these technologies evolve, we can expect EVM-based L2 networks to become increasingly interoperable and composable. This means that users will be able to interact with dApps across different L2 networks within the larger Ethereum ecosystem, facilitating seamless transactions and unlocking new use cases.
The vision of a modular, interconnected Ethereum ecosystem is becoming a reality, where sovereign Web3 protocols can scale independently while leveraging Ethereum’s security. As these L2 networks become more efficient and interconnected, Ethereum’s role as the foundational Layer 1 blockchain in the Web3 space will only strengthen.
Thank you for reading!
Disclaimer - I also post articles in the following platforms. All images if not attributed are my own created images. If readers find similar content in the platforms mentioned below, it's because I created the content and have the rights to publish it in other platforms.
Hive — https://ecency.com/hive-150329/@mintymilecan
Publish0x — https://www.publish0x.com/@greenchic
Medium - https://medium.com/@kikctikcy
t2World - https://app.t2.world/u/0x13235be5596047f935fe3ec502237f27259f2715
Posted Using InLeo Alpha
Posted Using InLeo Alpha
Posted Using InLeo Alpha
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.