Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) have become a major health concern in recent years. They are spread through various types of sexual contact and can cause a range of health problems. It is important to understand What STDs is and know the different types of STDs and their symptoms so you can make informed decisions about your sexual health.
This article however, will provide you with all the necessary information to understand STDs, its symptoms, and the different treatment options available. You will learn about how to prevent the spread of STDs, as well as how to seek appropriate medical care if needed. With this guide, you can ensure that you stay informed and take the necessary steps to keep yourself and your partner safe.
SOURSE:
First and foremost it is best to know What are STDs, and also understand the types of STDs that people can contact.
STDs, or sexually transmitted diseases, are infections that are transmitted through sexual contact. Some of the most common STDs include chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, herpes, and human papillomavirus (HPV). There are many other STDs that are much less common. STDs are distinguished from other health conditions that are transmitted through sexual contact, such as bacterial infections and yeast infections, by their ability to be transmitted from one person to another during sexual contact. While some STDs have few or no symptoms, others may cause a wide range of symptoms, including itching, burning, sores, pain when urinating, and pain during sexual intercourse. This can make it challenging to know if you have an STD.
If you are sexually active, it is important to get tested for STDs on a regular basis—as often as once a year, depending on your sexual practices. If you have more than one sexual partner, are not in a mutually monogamous relationship (where neither you nor your partner are having sex with anyone else), or have recently changed sexual partners, you should get tested for STDs more frequently.
Types of STDs
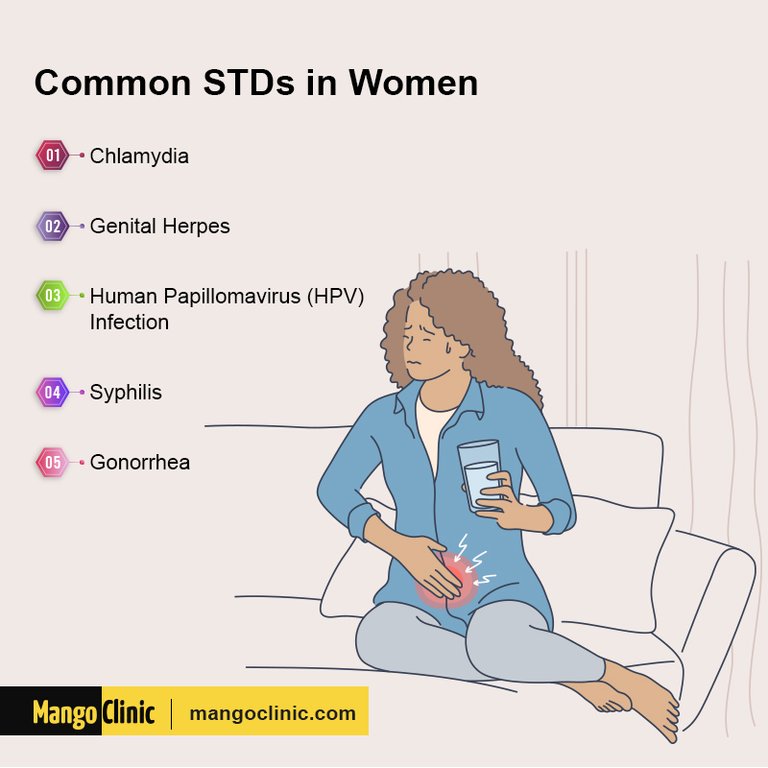
There are many different types of sexually transmitted diseases, including bacterial infections, viral infections, and parasitic infections. Here are some of the most common STDs:
Bacterial Infections: Bacterial infections are caused by bacteria such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. Bacterial infections are treatable with antibiotics, but they can damage the body if left untreated. Bacterial infections can lead to long-term health problems, including infertility.
Viral infections: Viral infections include human papillomavirus (HPV), herpes, and hepatitis B and C. There are no cure for viral infections, though symptoms can be treated. Viral infections can lead to long-term consequences, including cancer.
Parasitic Infections: Parasitic infections include trichomoniasis and pubic lice. Parasitic infections are treated with prescription medications.
SOURSE:
The symptoms of sexually transmitted diseases can vary widely, depending on the type of infection and the body part that is infected. This can make it particularly challenging to identify and treat an STD. The most common symptoms of an STD are: Painful urination: Urinary tract infections, bacterial infections, and gonorrhea can all cause painful urination. These infections are treatable, so it is important to see a doctor if you experience this symptom.
Discharge from the genitals: This can be a sign of a bacterial infection, trichomoniasis (a parasitic infection), or various other STDs.
Flu-like symptoms: While many STDs don’t cause any symptoms, the ones that do tend to cause flu-like symptoms, such as a fever, headaches, and muscle aches. -
Itching: Bacterial infections, viral infections, and pubic lice can all cause itching in the genitals (or elsewhere).
Raised rash: Certain viral infections, such as herpes and shingles, can cause a rash in the genital area.
Genital sores: Bacterial infections, viral infections, and parasitic infections can all cause sores in the genital area.
Swelling in the lymph nodes: There are many bacterial infections that can cause the lymph nodes to swell, including chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. Lymph nodes are soft tissue that are found throughout the body. They help fight infections by trapping bacteria and viruses and producing antibodies. When the lymph nodes are swollen, it means that there is an infection in the area.

SOURSE:
Possible Treatment Options for STDs
Most sexually transmitted diseases can be treated with antibiotics. If you have symptoms that suggest an STD, it is important to visit a doctor so you can get tested and treated as soon as possible. If you have an STD, you can pass it on to your partner(s) even if you don’t have any symptoms. It is also possible to have an STD without any symptoms (although this is less common). If you discover that you have an STD, it is important to tell your partner(s) so they can get tested and treated as well. It is also important to change your sexual practices so you can avoid getting another STD in the future. While STDs can be treated, they cannot be cured. This means that if you get an STD once, you can get it again—and you can also pass it on to others.
Preventing the Spread of STDs
The best way to prevent the spread of sexually transmitted diseases is to practice safe sex. This includes using condoms, or other barrier methods, whenever you have sex (including oral sex), as well as avoiding sex if you have open cuts or sores on your genitals. Even if you are in a long-term, monogamous relationship, condoms can help prevent the spread of STDs.
It is important to remember that condoms do not protect against all STDs—they are most effective against bacterial infections, such as chlamydia and gonorrhea. Condoms are less effective at preventing the spread of viral infections, such as HPV. Condoms can break, so it is important to keep in mind that no form of birth control is 100 percent effective.
In addition to using barrier methods, you can also reduce your risk of contracting STDs by getting tested regularly, being in a mutually monogamous relationship (where neither partner is having sex with anyone else), and avoiding sexual contact when you have an open wound or sore on your genitals.
I also suggest Seeking of Medical attention and Care. If you have symptoms that suggest an STD, it is important to get tested. Your doctor will likely ask you about your sexual practices and may ask you to take a blood or urine test to determine if you have an STD. It is important to get tested, even if you don’t have any symptoms, because you may not experience any symptoms in the early stages of an STD.
If you are diagnosed with an STD, your doctor will likely prescribe antibiotics. It is important to finish the entire course dosage of antibiotics prescribed by qualified Doctor , even if you feel better, to make sure you get rid of the infection completely. It is also important to tell your partner(s) so they can get tested and treated. If you don’t, you could infect your partner(s) and they could, in turn, infect others and that is how it will keep spreading on and on.
Conclusively, sexually transmitted diseases are infections that are transmitted through sexual contact. Most STDs don’t have any symptoms, so it is important to get tested regularly, regardless of your sexual practices. You can protect yourself from the spread of STDs by using barrier methods, such as condoms, and avoiding sexual contact when you have an open wound or sore.

SOURSE:
Of course sometimes I tell people when it comes to medical advice as regards STDs, it’s very important you learn majors for safe sex, if you think you have not learn how to protect yourself, then its better you avoid it totally, hence the spreading of the diseases will affect the society at large. Lastly, whenever you find out you’ve got one please, get treated.
STD's are very serious issues that needs to be treated as such, it's best to stay safe out there.
exactly. thank you for reading