Let's discuss everything chemically basic and with that, I mean the opposite of an acid which means substances that have a high affinity for hydrogen (are good at bonding with hydrogen ion). So if you have herd of strong acids before, then it is great that you know that there are strong base or super base. Just as you have the idea that acids can be very dangerous, so is it with bases because they can be just as dangerous as acids.
Have you had a taste of a basic substance before? Bases have bitter taste and when felt against the skin, they have a slippery feeling like soap and that's why they are used as soap. Bases like Sodium hydroxide are combined with fatty acids or animal fat to produce sodium salts which helps water lift grease from the skin but I am not saying that you should wash your hands with bases directly because just like acids, they can burn and just like strong acids burn, strong bases also burn and as of today, the strongest base to be discovered is the Ortho-diethynylbenzene dianion.
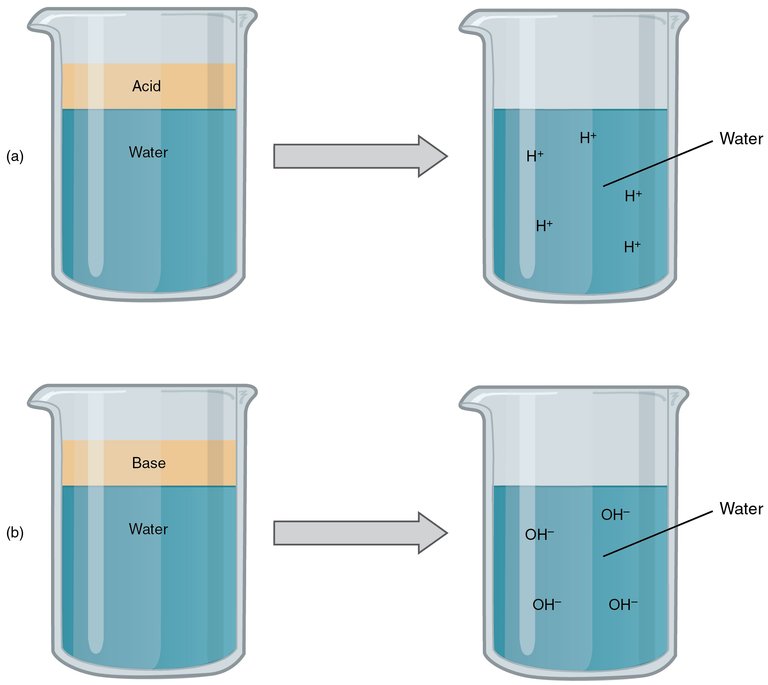
To identify a base or an acid or the strength and weakness of a base or an acid, we use the pH scale which measures from 0 to 14 and it explains how a substance reacts when it mixes with water. If a pH is 7, it means that it splits to an equal number of negatively charged hydroxide ion and positively charged hydrogen ion but when there is an imbalance, then it can either be an acid or a base.
If a compound is basic, it is more likely to bond to the hydrogen ions so there are more hydroxide ion. For every 1 number upwards in the pH scale means there is a tenth of hydrogen ion in the solution which means if a substance is having a pH of 8, then it has 1 hydrogen ion for every 10 hydroxide ions. If we are to look at substances like drain cleaner which is extremely basic at pH of 14, it would mean that there is only 1 hydrogen ion for every 10 million hydroxide ions.
If substance have a pH above 14, then they can rip hydrogen ions from the water molecule (deprotonation) and these types of substances are referred to as super base because at this point, the pH scale doesn't really work again rather the proton affinity (amount of energy released when it bonds with hydrogen) of the substance is used to measure its strength. The higher the proton affinity, the stronger the base and Ortho-diethynylbenzen dianion has an affinity of 440 kilocalories per mole.
Currently, scientists are looking for a use for Ortho-diethynylbenzen dianion and hopefully we find. Ortho-diethynylbenzen dianion isn't the only super base available and scientists have been able to find uses for a lot of super base like sodium hydride which is used as a drying agent to dry chemical in the lab since super base react quickly with water. It has also been looked into as a way of storage for hydrogen which can be used as fuel.
For Further Reading
https://www.softschools.com/formulas/chemistry/sodium_hydride
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2016/sc/c6sc01726f
https://www.chemistryexplained.com/Ru-Sp/Soap.html
https://www.ks.uiuc.edu/Training/SumSchool/materials/sources/tutorials/05-qm-tutorial/part2.html
https://rushim.ru/books/mechanizms/superbases-for-organic-synthesis.pdf

Congratulations @paulade! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
Your next target is to reach 3500 upvotes.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPCheck out our last posts:
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.