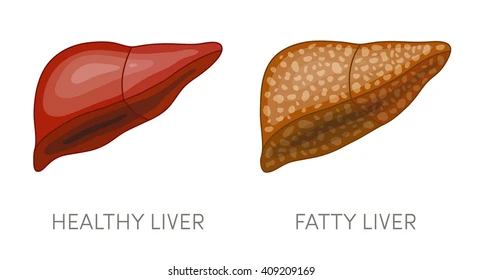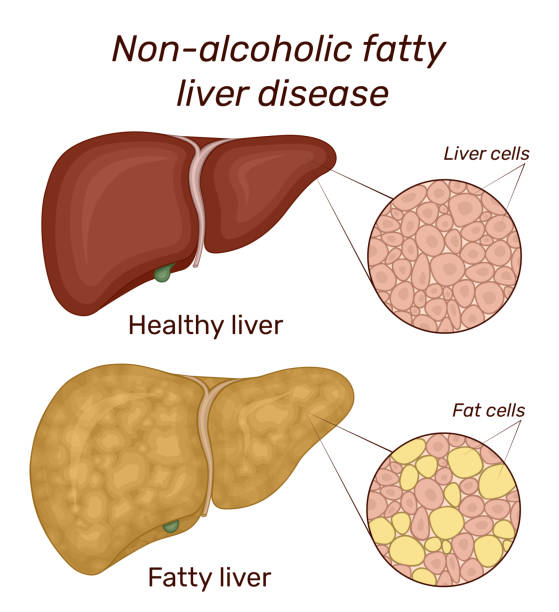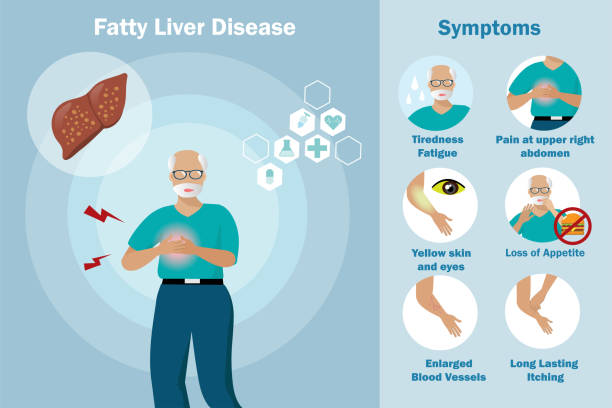
Good Morning! my all reader and my lovely friend.How are you all? Today I will discuss about Fatty liver disease. Fatty liver disease is a serious and growing health concern that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a condition in which fat builds up in the liver, leading to inflammation, scarring, and other long-term health risks. Although the cause of fatty liver disease is still largely unknown, there are several factors that can increase a person's risk of developing the condition, such as obesity, diabetes, or excessive alcohol intake. The symptoms of fatty liver disease can range from mild to severe and can include fatigue, abdominal pain, and jaundice. Fortunately, there are a variety of treatment options that can help manage the condition, such as lifestyle modifications, medications, and supplements. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments for fatty liver disease, you can better protect your health and avoid the serious complications associated with the condition.
What is fatty liver disease?
Fatty liver disease is a type of liver disorder that occurs when too much fat is stored in the liver. It is the result of fat build-up in the liver cells, causing inflammation. This can lead to the following complications: Liver damage can be caused by several factors, including obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol, high triglycerides, autoimmune hepatitis, excessive alcohol intake, a poor diet, and a family history of fatty liver disease. Fatty liver disease is different than nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), although they are often associated with each other. NAFLD is the build-up of fat in the liver that is not caused by alcohol. While NAFLD is not a serious condition, it can progress to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). NASH is a type of fatty liver disease that can lead to scarring and fibrosis of the liver.source
There are several risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing fatty liver disease. Some of the most common risk factors include obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol, high triglycerides, autoimmune hepatitis, excessive alcohol intake, and a family history of fatty liver disease. While the exact cause of fatty liver disease is unknown, experts believe that insulin resistance induced by obesity is linked to the development of the condition. Insulin resistance occurs when the cells in the body become resistant to the effects of insulin, which is a hormone that helps the body process carbohydrates and proteins from food. Insulin resistance can cause an excess of glucose (sugar) to build up in the bloodstream, leading to pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes. In addition, insulin resistance is thought to cause fat to accumulate in the liver and contribute to fatty liver disease.
Symptoms of fatty liver disease
Fatty liver disease is typically asymptomatic, meaning there are no noticeable symptoms. However, the condition can progress to more serious complications if left untreated, including scarring and fibrosis of the liver. If the disease is detected and treated early, the prognosis is usually good. Some of the more common symptoms of fatty liver disease include fatigue, abdominal pain, and jaundice. Fatigue is a common symptom experienced by those with fatty liver disease, especially during the acute phase of the condition. It can be caused by the buildup of toxins in the liver and an increase in ammonia in the bloodstream, which is a byproduct of protein breakdown. Other symptoms that can occur during the acute phase of fatty liver disease include appetite loss, nausea, weight loss, and muscle aches and pains. During the chronic phase of fatty liver disease, fatigue and other symptoms may subside, but symptoms of hypertriglyceridemia, such as abdominal pain and jaundice, may appear.
There is no definitive test for diagnose fatty liver disease, and diagnosis is often made based on the signs, symptoms, and risk factors associated with the condition. A doctor may order blood tests to determine the presence of liver enzymes, which are molecules produced by the liver that are released into the bloodstream. In addition, a doctor may order a biopsy of the liver to detect signs of fatty liver disease, such as scarring, fibrosis, and cell damage. During the biopsy, the doctor will remove a tiny piece of the liver and send it to a lab for analysis. A liver ultrasound may also be performed to detect any signs of fatty liver disease.source
Treatments for fatty liver disease
There are several treatments for fatty liver disease, including lifestyle modifications, medications, and supplements. Treatment options depend on the severity of the condition, the presence of complications such as scarring and fibrosis, and the presence of comorbidities. Therefore, it is important to monitor the progression of fatty liver disease and address any complications as early as possible. Fatty liver disease can be managed and treated through lifestyle modifications. These include eating a healthy diet low in sugar and refined carbohydrates, increasing physical activity, getting enough sleep, and reducing stress. In addition, it is important to avoid excessive alcohol intake, as this can worsen the condition. While medications are not considered a treatment for fatty liver disease, they can be used to manage complications and reduce the risk of progression. For example, blood pressure-lowering medications can help lower blood pressure and triglyceride-lowering medications can reduce triglyceride levels in the blood. Other treatments for fatty liver disease include nutritional supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids and coenzyme Q10.
There are several lifestyle modifications that can help manage fatty liver disease and prevent complications. First, it is important to avoid excessive alcohol intake, as this can worsen the condition. Excessive alcohol intake can also increase the risk of liver damage, regardless of whether or not the person has fatty liver disease. In addition, it is crucial to eat a healthy diet low in sugar and refined carbohydrates. Loading up on sugary and processed foods can increase inflammation and lead to weight gain, which can worsen the condition. Finally, it is important to get enough sleep and reduce stress to prevent further liver damage. Fatty liver disease can also be treated with medication, such as blood pressure-lowering medications and triglyceride-lowering medications.source
Blood pressure-lowering medications
- Blood pressure-lowering medications, such as beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and ARBs, can help reduce the risk of progression and complications of fatty liver disease.
- Triglyceride-lowering medications - Triglyceride-lowering medications, such as fibrates and statins, can help reduce liver damage and inflammation associated with fatty liver disease.
Supplements for fatty liver disease
There are several nutritional supplements that can help manage fatty liver disease and prevent complications. These include omega-3 fatty acids, coenzyme Q10, vitamin E, and vitamin C. Omega-3 fatty acids were first prescribed to patients with fatty liver disease in the 1970s and 1980s. They work by reducing blood triglyceride levels and improving blood flow to the liver. Coenzyme Q10 is a powerful antioxidant that is produced naturally by the body. It can also be obtained through diet and supplements. Vitamin E is an immune system booster and can help protect the liver and reduce inflammation. Vitamin C is also an antioxidant that can protect the liver from oxidative damage and harmful toxins.
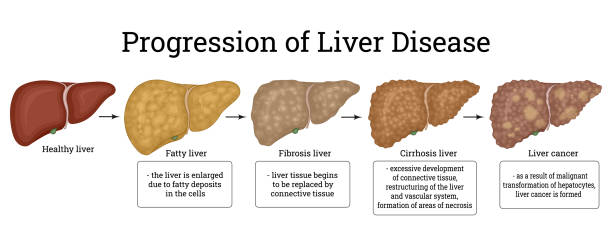
Prevention of fatty liver disease
The best way to prevent fatty liver disease is to maintain a healthy lifestyle and avoid excessive alcohol intake. It is important to eat a healthy diet low in sugar and refined carbohydrates and to get enough sleep. In addition, it is helpful to reduce stress and exercise regularly. If you have had fatty liver disease or are at high risk for the condition, it is important to follow a healthy lifestyle and be aware of potential complications. Fatty liver disease is a serious condition that can lead to scarring and fibrosis of the liver if left untreated. Fortunately, there are a variety of treatments and lifestyle modifications that can help manage the condition, so it's important to get tested for fatty liver disease and follow the doctor's recommendations.
Reference:
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15831-fatty-liver-disease#:~:text=Fatty%20liver%20disease%20is%20a,liver%20disease%20with%20lifestyle%20changes.
https://www.healthline.com/health/fatty-liver
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/non-alcoholic-fatty-liver-disease/
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/nonalcoholic-fatty-liver-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20354567