Hello my dear STEM enthusiasts. Are you the guy who can’t feel the morning without a freshly brewed coffee and you love the smell of your freshly prepared coffee. Ain’t you? And do you love pancakes? If the savoring aroma makes you cozy, well mostly a special class of organic compounds called ‘amines’ are responsible for the fragrance of your coffee to the taste of those lovely pancakes. This tiny molecules are behind the curtain of many other daily life things that gives you pleasure in some or other way. These amines are basic in nature. For simple reason, the basicity could be accounted for the lone pair of electrons they carry in their molecular structure. Yes, they do not actually have a negative charge to show the basic character. They are neutral compounds but basic in nature.

The saturated amines, could also be called as aliphatic amines in a more advanced way, are more basic than ammonia. I’m pretty sure you know what ammonia is! Yes, the fertilizer that is seen used in agriculture. As I have mentioned aliphatic amines, so let me further discuss the three types of amines with regards to the number of alkyl group attached to the N atom. There are three different aliphatic amines and how could I forget the parent ammonia compound. I will discuss and elaborate their basicity order in this blog and we will eventually get them arranged in an increasing or decreasing order at the end. Remember, there will be some twists to the order, so relax and you’ll understand everything by the end of the blog.
The pKb values of aliphatic amines lie in the range 3.0 to 4.22 while that of ammonia is 4.75. The lower the pKb value the higher is its basic nature. So from that we can easily conclude that all the three classes of aliphatic amines are more basic than ammonia. The reason is mainly the electron donating nature of the alkyl groups attached in them. As a result, the electron density around the N atom increases and they can donate the lone pair of electrons more easily than ammonia, resulting in the increase of their basic nature. I hope you do remember the Lewis acid-base concept. Just to be sure, an acid is an electron pair acceptor and the base is an electron pair donor.
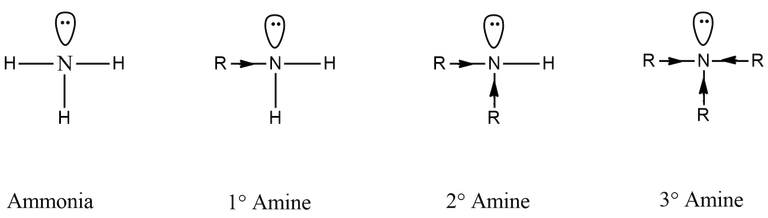
As more the R groups in the aliphatic amines, the better the donation ability and hence the stronger the base is. So by following this rule, the order of basicity should potentially be like this,
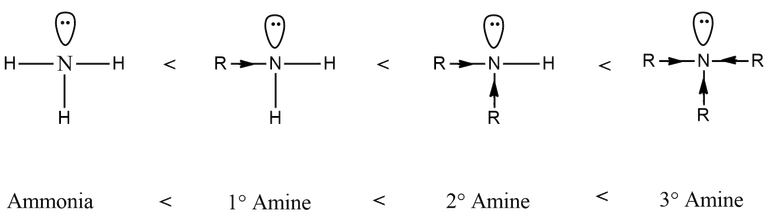
So, we got the answer, right? Well actually No! The twist begins.
It has been found experimentally that a 2° amine is more basic than 1° and 3° amines in an aqueous solution. But why? Let me explain. Your friend Mr. ChemFam is here to help you (wink).
The reason why the order is actually changed could be explain by the following reasons.
- Inductive effect (+I) of the alkyl group.
- Extent of H-bonding with water molecules.
- Steric effects of the alkyl group.
I will discuss each of them now.
+I effect
As the number of alkyl groups attached directly to the N atom increases, the extent of donor ability increases. Similarly the dispersal of positive charge on the ammonium cation by the +I effect of the alkyl group increases accordingly. Thus, on the basis of +I factor alone, the basicity of amines should decrease in the order:

Solvation effect
The stability of the ammonium cation due to H-bonding depends upon the number of H atoms present on the N atom. Obviously greater the the number of H atoms on the N atom, more stable is the ammonium cation. Thus the ammonium cation derived from a 1° amine is the most stable since it has three H atoms which can form H bonds with H2O. The ammonium cation derived from the 2° amine is less stable since it has 2 H atoms while of the 3° amine is the least stable since it has only 1 H atom which can form H-bond with H2O.
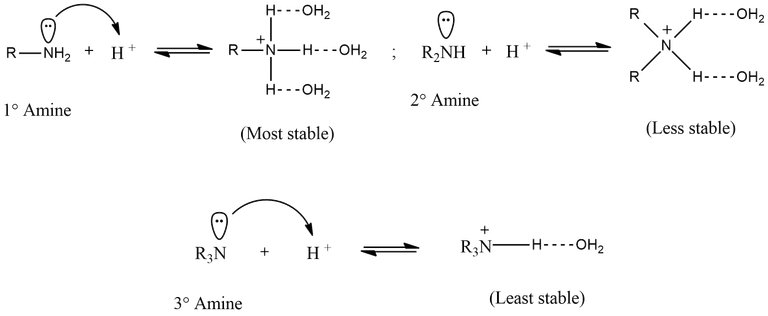
This is in regard with the fact that, the more water molecule get associate with H atom of amines to form H-bonds, the more energy of that compound is going to get released and thereby the stability will increase. Thus, the stability order with respect to the solvation effect follows the order:

Steric Effect
Overcrowding of the alkyl groups around the N atom of amine hinders the attack of proton (H+) on the lone pair of amine and decreases the basic strength. The more bulky it gets, the less space is available for attack of an incoming proton. Thus, due to steric effect, the order should be as:

From the discussion above, we may conclude that it is a combination of +I effect of the alkyl groups, H-bonding and steric effect which determines the stability of the ammonium cations in solution. All these three factors are in favor for the increasing basicity of 2° amines and hence 2° amines are the strongest base among other aliphatic amines. If the alkyl group is small, i.e., CH3 (methyl) then there is no steric hindrance/overcrowding to H-bonding. In other words, the stability due to H-bonding predominates over the stability due to +I effect of CH3 group and hence 1° amine, i.e., CH3NH2 is a stronger base than 3° amine i.e., CH3)3N. In other words, the overall decreasing basic strength of methylamine is :

If, however an alkyl group bigger than CH3 group, i.e., ethyl, propyl etc. there will be some steric hindrance to H-bonding. As a result, stability due to +I effect predominates over the stability due to H-bonding and hence 3° amines become more basic than 1° amines. Thus, the overall basic strength of ethylamine follows the following order:

I really hope that I was able to completely cover the topic and answered the questions that may arise when arranging the basic order of aliphatic amines. Exploring their basicity not only sheds light on their behavior in chemical reactions but also unveils the intricacies of molecular interactions.
Until next time, Keep STEMtastic!

All the images used in this blog are my original work and belongs to me unless and otherwise separately mentioned
Software used:
The chemical reactions and diagrams are drawn using ChemDraw software.
If you like my work and would like to support me, you can do so by joining my fanbase by clicking this link
Exploring The Thengal Kachari Heritage Museum
How to Avoid Scams and Rug-Pulls
Hive Power Up Day March and Tracking My Goals
Witnessing Magnificent Goonch Catfish of the Brahmaputra River
Understanding Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions: Exploring SN1 and SN2 | ChemFam #90|
A Walk Through a Tea Estate of Assam: Lost in Tranquility
Understanding Basic Principle and Theory of Mass Spectrometry | ChemFam #89 |
Poor cellular network in rural areas
Blood Substitutes: A Quest for Artificial Blood | ChemFam #88 |
Properties of Haloalkanes and Methods of Preparation of Haloalkanes | ChemFam #87 |
Understanding the Simple Harmonic Oscillator in Quantum Mechanics | ChemFam #86 |
Understanding Degeneracy in Quantum Chemistry: Exploring 1D, 2D and 3D Box Models | ChemFam #85 |
Introduction to Zero Point Energy and its Cases in Particle in a Box | ChemFam #84 |
Quantum Confinement : Particle in a 2D box and 3D box | ChemFam #83 |
Molecular Chirality: A Mirror Image Perspective | ChemFam #82|
Exploring Time-Independent Schrödinger's Wave Equation and Particle in a 1D Box | ChemFam #80 |
The Role of Gamma Function in Quantum Mechanics | ChemFam #79 |
Postulates of Quantum Mechanics and Normalization of Wavefunction |ChemFam #78|
Understanding Commutator Relations and Exploring Eigenfunctions in Quantum Mechanics |ChemFam #77|
How to find Expression of an Operator and Commutation Relations |ChemFam #76|
PS The thumbnail image is being created by me using canva.com
Games I play on Hive
| Games I play on Hive | Game description |
|---|---|
| Terracore | Terracore is an Idle mining game based on Hive blockchain |
| Rise of the Pixels | ROTP is a Web3 browser game about game development on Hive |



Posted Using InLeo Alpha
Posted Using InLeo Alpha


!hiqvote
The rewards earned on this comment will go directly to the people ( splash-of-angs63 ) sharing the post on LeoThreads,LikeTu,dBuzz.https://inleo.io/threads/splash-of-angs63/re-splash-of-angs63-pyx2n4wj
Discord Server.This post has been manually curated by @bhattg from Indiaunited community. Join us on our
Do you know that you can earn a passive income by delegating to @indiaunited. We share more than 100 % of the curation rewards with the delegators in the form of IUC tokens. HP delegators and IUC token holders also get upto 20% additional vote weight.
Here are some handy links for delegations: 100HP, 250HP, 500HP, 1000HP.
100% of the rewards from this comment goes to the curator for their manual curation efforts. Please encourage the curator @bhattg by upvoting this comment and support the community by voting the posts made by @indiaunited..
This post received an extra 1.06% vote for delegating HP / holding IUC tokens.
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.
@splash-of-angs63, the HiQ Smart Bot has recognized your request (1/3) and will start the voting trail.
In addition, @splash-of-angs63 gets !COFFEE from @hiq.redaktion.
Discord. And don't forget to vote HiQs fucking Witness! 😻For further questions, check out https://hiq-hive.com or join our