Hello Everyone,
Sometimes you may have observed the sudden emergence of a black mole on your skin, “till yesterday, this part was clean, and now I have a mole here too”.
As a kid, you don’t have that many moles on your body, but as life goes on, you start to develop some moles on your body. Well, it’s not overnight, but something that you noticed overnight.

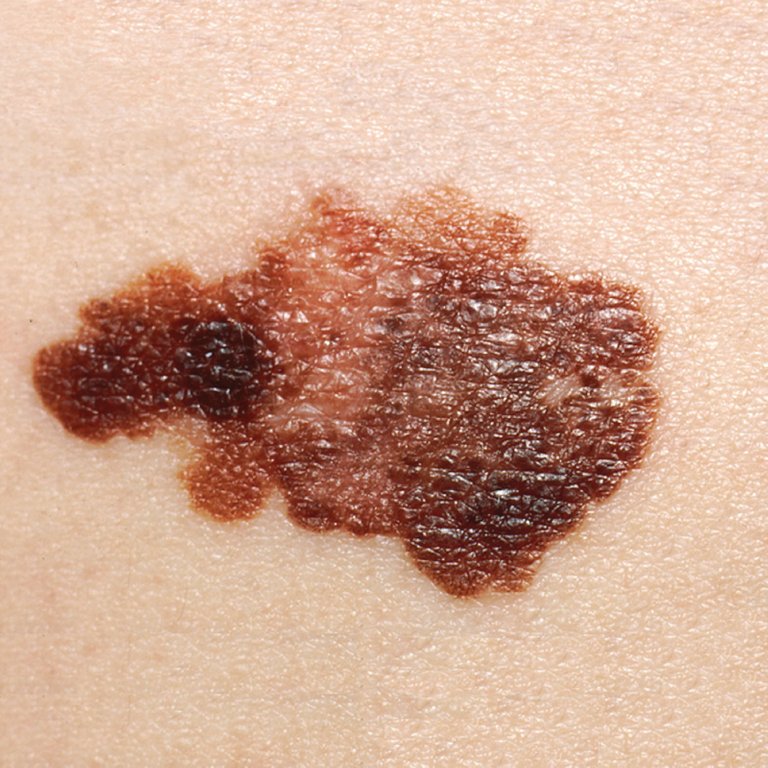
Moles are generally a common form of skin growth, which takes the shape of a tiny, dark brown patch formed by a cluster of melanocytes. Melanocytes are pigment-producing cells that give us different colors on the skin. Mole is also known as nevus (medical term) or a beauty mark. Moles can appear anywhere on your skin, and on average, every individual has around 20-40 moles on their body. These moles also have a lifetime, and the average lifetime for a mole is 50 years, they disappear, change shape, rise, and fade away, and sometimes it has hair growth. There are three types of skin moles:
- Common nevus
- Congenital nevus
- Dysplastic nevus
The common nevus is generally small growth of skin (2-3mm) colored pink, brown, or black and, most of all, with a distinct edge.
The congenital nevus is generally seen after you are born, and the chance of finding this is one in a hundred. These moles are more likely to turn into melanoma and must be examined if you suspect any sort of abnormalities in them.
On the other hand dysplastic nevus are the quite large and has irregular shape. These moles have dark-colored cores and light edges. These moles are inherited (hereditary), and people with such moles can develop more moles on their bodies as compared to normal individuals. These moles also have a chance of developing malignancy (melanoma).

Common moles, sun freckles, aging spots etc., all are considered as pigmented lesions. Even though the majority of the pigmented lesion won’t turn malignant, just in case you get too many skin lesions with non-ordinary borders or edges, you should visit a doctor. The dermatologist can see changes in lesions that seem "suspicious" through routine observation. A skin biopsy, which involves extracting a sample of the mole for close inspection under a microscope, may be necessary in response to a change in its structure. This procedure can help doctors decide whether a lesion is benign (non-cancerous), melanoma, or another kind of skin cancer.
There are some signs that are represented as ABCDEs. If you see any of these signs, have it checked by your dermatologist.
- Asymmetry: if there is an asymmetry in the shape of the mole.
- Border: if there is an irregularity in the border line of the mole.
- Color: if there is a difference of color in the same mole.
- Diameter: if the size increases more than 8mm and also increases with time.
- Elevation: if there is an elevation in a flat mole and it changes with time.
Reasons to regularly monitor your moles
Skin is the largest organ of the human body and the first protective layer as well; hence, it needs special care to keep it safe. Your skin is more prone to get cancer if you have (1) fair skin, (2) too many moles on you, and (3) hereditary history of skin cancer.
How to examine your skin mole
Skin lesions are often benign (non-cancerous). The "ugly duckling sign" or moles that grow on your skin after age 30 are the ones that should raise medical concerns since they don't resemble other moles that are already present on your body. Skin lesions are often benign (non-cancerous). If you observe any of these changes in your mole: bleeding, oozing, itching, or scale, you must see a dermatologist. Regularly check your skin for any such changes and especially take care of the areas which are exposed to the sunlight.
In case of any doubt, one should undergo a skin biopsy to uncover the truth behind the irregular behavior of the mole. If the mole is cancerous, the only option is to remove it from the patient body.

Following the normal process of pushing the older cells towards the surface where they all die and lead to a mole. Sometimes, some of the cells get their DNA damaged due to external factors. This DNA damage results in an uncontrolled growth of cells, which eventually forms a mass of cancerous cells. Apart from the external factor (UV rays from the sun), DNA damage could also be possible by some genetic factors. There are several genes that could cause melanoma, but mostly considered factor is still believed to be UV rays.
So, keep an eye on your mole and if you see any sort of changes in it, consult a dermatologist as soon as possible
References
Turkington et. al., 1965 Familial Factor in Malignant Melanoma.
Urteaga et. al., 1966 On the antiquity of melanoma.
Hope you find it interesting, see you soon with some other interesting topic.



Is it similar to birth sign on some people body?
Well birth signs are just pigmented cells but when they grow more and shows irregularities, it can lead to melanomas
Thanks for stopping by
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.
Congratulations @vinamra! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
Your next target is to reach 7000 upvotes.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPCheck out our last posts:
Yay! 🤗
Your content has been boosted with Ecency Points
Use Ecency daily to boost your growth on platform!
Support Ecency
Vote for new Proposal
Delegate HP and earn more, by @bhattg.
Thank you 😊