
Open egg showing different parts, including the white, where a large amount of ovalbumin is found
Huevo abierto mostrando diversas partes entre ellas la clara, lugar donde se encuentra gran cantidad de la ovoalbúmina
Biological functionality of proteins
Proteins are of fundamental importance in the structure and dynamics of biological systems, and exert an immense variety of functions in them:
Funcionalidad biológica de las proteínas
Las proteínas tienen una importancia fundamental en la estructura y la dinámica de los sistemas biológicos, y ejercen en los mismos una inmensa variedad de funciones:
⊛ 1- Structural Functions. Proteins are part of cell membranes; of connective tissues (elastins, collagens); of silk (fibroin); of epidermal formations, such as: hairs, nails, scales or horns; all of them constituted by keratin.
⊛ 1- Funciones Estructurales. Las proteínas forman parte de las membranas celulares; de los tejidos conectivos (elastinas, colágenos); de la seda (fibroína); de las formaciones epidérmicas, como: pelos, uñas, escamas o cuernos; todos ellos constituidos por queratina.
⊛ 2- Transport of substances in the organism, to which they are reversibly bound, as is the case of hemoglobin, which has four heme groups with their respective iron atoms, to which O2 is bound, which is thus transported to the cells; muscle Myoglobin, with a heme group; albumin, which transports fatty acids; and lipoproteins.
⊛ 2- Transporte de sustancias en el organismo, a las cuales se unen reversiblemente, como lo es el caso de la hemoglobina, que posee cuatro grupos hemo con sus respectivos átomos de hierro, a los que se liga el O2, que es transportado así hasta las células; la Mioglobina del músculo, con un grupo hemo; la albúmina, que transporta ácidos grasos y las lipoproteínas.
⊛ 3- Defense of the organism against foreign substances. Role played by Immunoglobulins, or in the face of blood loss, providing coagulation mechanisms (thrombin, fibrinogen).
⊛ 3- Defensa del organismo frente a sustancias extrañas. Papel que desempeñan las Inmunoglobulinas, o ante la pérdida de sangre, proporcionando los mecanismos de coagulación (trombina, fibrinógeno).
⊛ 4- Movement, such as dynein of cilia and flagella or actin and myosin of muscles.
⊛ 4- Movimiento, como la dineína de cilios y flagelos o la actina y miosina de los músculos.
⊛ 5- Transmission of chemical messages, as is the case with polypeptide hormones, e.g. insulin or glucagon.
⊛ 5- Transmisión de mensajes químicos, como sucede con las hormonas polipeptídicas, por ejemplo la insulina o el glucagón.
⊛ 6- Storage and reserve, as in the case of Ovalbumin
and Lactalbumin.
⊛ 6- Almacenamiento y reserva, es el caso de la Ovoalbúmina y Lactoalbúmina.
⊛ 7- Toxins, such as those produced by many microorganisms, including those that cause diphtheria and cholera.
⊛ 8- Catalysis, function performed by enzymes.
⊛ 7- Toxinas, como las elaboradas por muchos microorganismos, entre ellos los que producen la difteria y el cólera.
⊛ 8- Catálisis, función que ejercen las enzimas.
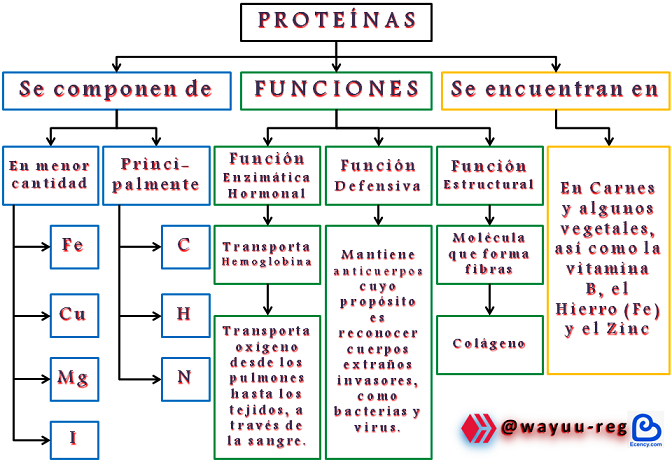
These protein molecules are made up of amino acids, unified by peptide bonds, and depending on the genetic code of the individual, the order and arrangement of the amino acid in the polypeptide or protein chain is established. Its composition is based on particles of carbon (C), oxygen (O), hydrogen (H), nitrogen (N), which store all the genetic information and transmit the inheritance of living organisms; in addition, most of them have sulfur (S) and phosphorus (P).
Estas moléculas proteicas que son formadas por aminoácidos, unificándose mediante enlaces peptídicos, dependiendo del código genético del individuo se establece el orden y disposición del aminoácido en la cadena polipeptídica o proteínica. Su composición se basa en partículas de carbono (C), oxígeno (O), hidrógeno (H), nitrógeno (N), que almacenan toda la información genética y transmiten la herencia de los organismos vivos; además, en su mayoría, posee azufre (S) y fósforo (P).
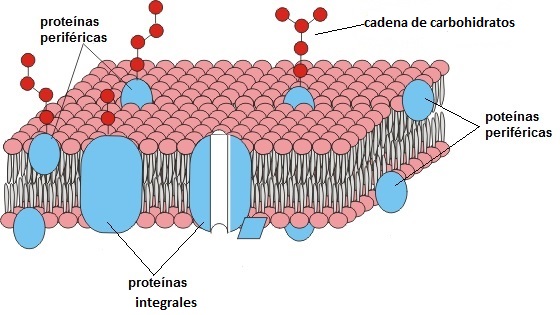
Being present in all the cells of the organism, proteins participate in practically all the biochemical processes of the body. One of these processes and thanks to the volume of nitrogen, they perform the function of growth; also, they basically intervene in the synthesis and maintenance of various tissues, also in various components such as hemoglobin, gastric juices, hormones and vitamins; in enzymes they act as a biological catalyst, stimulating the biochemical reactions of metabolism, increasing the speed with which these reactions occur. Through the bloodstream, they transport gases such as carbon dioxide and oxygen. They play a very important role in maintaining plasma Oncotic Pressure and acid-base balance, functioning as "shock absorbers".
Estando presentes en todas las células del organismo, las proteínas participan, prácticamente, en todos los procesos bioquímicos del cuerpo. Uno de estos procesos y gracias al volumen de nitrógeno, realizan la función del crecimiento; también, interviene básicamente en la síntesis y mantenimiento de varios tejidos, además en diversos componentes como en la hemoglobina, los jugos gástricos, en las hormonas y vitaminas; en las enzimas se porta como un catalizador biológico, estimulando las reacciones bioquímicas del metabolismo, haciendo aumentar la velocidad con la cual se producen estas reacciones. A través del torrente sanguíneo, transportan gases como el dióxido de carbono y el oxígeno. Ejecutan una función muy importante para mantener la Presión Oncótica del plasma y el equilibrio ácido-base, funcionando a modo de “amortiguadores”.
Another type of proteins are the Antibodies, which perform the natural defensive function against external agents that can cause infections in the organism; Collagen is essential for the resistance of the supporting tissues; there are also two proteins, Myosin and Actin, which among many other functions make the movement of muscles possible.
Otro tipo de proteínas son los Anticuerpos, ejercen la función defensiva natural en contra de los agentes externos que pueden causar infecciones al organismo; el Colágeno, es imprensindible para la resistencia de los tejidos de sostén; existen también dos proteínas, Miosina y Actina, que entre muchas otras funciones posibilitan el movimiento de los músculos.
Depending on their configuration, there are globular proteins, such as globins, and fibrous proteins, such as keratin.
In general, proteins are classified according to their chemical components and their shape; in the latter, there are fibrous, globular and mixed (fibrillar and globular) proteins. They possess two main properties, stability and solubility, which allow the correct performance and existence of their functions. This indicates that stability must be given in the storage medium or when they develop their function, where most aqueous proteins elaborate a hydrophobic nucleus, which is packed making the protein replacement and which relates its sufficiently long half-life without generating alterations in the organism. On the other hand, solubility is located so that the bonds are stable, each protein must maintain its temperature and pH in an optimal state (if the pH or temperature increases, solubility is lost). There are other secondary properties, depending on its chemical characteristic: specificity, where its function is concrete and specific, which differs from other molecules; pH buffering, depending on whether it loses or gains electrons, it behaves as basic or acidic, causing the pH of the tissue to maintain the appropriate level. Another property is the electrolytic capacity, where negative poles are transferred to positive poles and vice versa.
Según su configuración, hay proteínas globulares, como las globinas, y fibrosas, como la queratina.
Por lo general, las proteínas se clasifican en función de sus componentes químicos y de su forma; en esta última, hay proteínas fibrosas, globulares y mixtas (fibrilar y globular). Poseedoras de dos propiedades primordiales, la estabilidad y la solubilidad, las cuales permiten el correcto desempeño y la existencia de sus funciones. Esto indica que la estabilidad debe estar dada en el medio de almacenamiento o cuando desarrollan su función, en donde la mayoría de proteínas acuosas elaboran un núcleo hidrofóbico, el cual se empaqueta haciendo el recambio proteico y que relaciona su vida media suficientemente larga sin generar alteraciones en el organismo. Por otro lado, se ubica a la solubilidad para que los enlaces sean estables, cada proteína debe mantener su temperatura y su pH en estado óptimo (si el pH o la temperatura aumentan se pierde la solubilidad). Existen otras propiedades secundarias, dependiendo de su característica química: la especificidad, en donde su función es concreta y específica, que difiere de las demás moléculas; la amortiguación de pH, en función de perder o ganar electrones, se comporta como básicos o como ácido, haciendo que el pH del tejido mantenga el nivel adecuado. Otra propiedad es la capacidad electrolítica, en donde se trasladan los polos negativos a los positivos y viceversa.
One of the most notable causes of illness or death is the deficiency of proteins in the organism; this lack of proteins can cause mental retardation or alterations in the cognitive capacity of the individual (low intellect). Deficiency can be detected in patients convalescing from surgery, trauma or diseases such as Kwashiorkor. People who are prone to diet to get rid of several kilos of weight, end up manifesting a protein deficit due to poor nutrition and self-medication; certain external factors of the deficit are: wars, famines, overpopulation, inflationary indexes, where all of them contribute to increase the rate of malnutrition of the entire affected population.
Una de las causas más notables de enfermedad o muerte es la deficiencia de proteínas en el organismo; esta falta de proteínas puede originar retardo mental o alteraciones en la capacidad cognitiva del individuo (bajo intelecto). Se puede detectar deficiencia en pacientes convalecientes por cirugía, traumas o enfermedades como Kwashiorkor. Las personas que son propensas a hacer dietas para librarse de varios kilos de peso, terminan manifestando un déficit proteico debido a su mal nutrición y automedicación; ciertos factores externos del déficit son: las guerras, las hambrunas, sobrepoblación, indicies inflacionarios, en donde todos ellos contribuyen a incrementar la tasa de mal nutrición de toda la población afectada.
Just as proteins help to build muscle mass, excessive consumption can cause calcium depletion in the body, which in the long term could lead to the loss of bone mass. Another negative cause is the frequent allergic reactions that some foods produce in certain individuals. Their occurrence is due to the structure or composition of the protein, which is slightly different; where some release a reaction from the immune system, while others do not cause hypersensitivity reactions, remaining safe in their consumption. Some proteins that certainly produce allergies are: Casein (milk), gluten (wheat and other grains); proteins found in peanuts, shellfish or seafood.
Así como las proteínas ayudan a formar masa muscular, el consumo excesivo puede causar menoscabo en el calcio del organismo, lo que originaría a largo plazo, la pérdida de masa ósea. Otra causal negativa, son las frecuentes reacciones alérgicas que producen algunos alimentos a ciertos individuos. Su ocurrencia es debido a la estructura o composición de la proteína, la cual es ligeramente diferente; en donde, algunas liberan una reacción desde el sistema inmune, mientras otras no editan reacciones de hipersensibilidad, permaneciendo seguras en su consumo. Algunas proteínas que ciertamente producen alergias son: Caseína (leche), gluten (trigo y otros granos); proteínas que se encuentran en el maní, en mariscos o alimentos marinos.
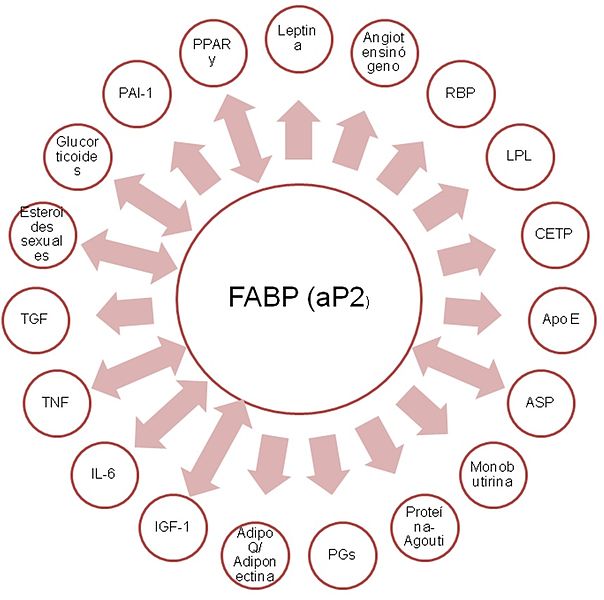
“Molecules produced by adipocytes, which act as endocrine, paracrine or autocrine signals, are shown Among the various proteins secreted by adipocytes we find Hormones, cytokines and other molecules involved in metabolic, neuroendocrine, immune and cardiovascular regulatory processes. Abbreviations: ASP, acylation-stimulating protein; Apo E, apolipoprotein E; Adipo Q, adipocyte complement-related protein; CETP, cholesterol ester translocator protein; FABP, fatty acid-binding protein; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor; IL-6, interleukin 6; LPL, lipoprotein lipase; PAI-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1; PG, protaglandin; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator activator receptor gamma; RBP, retinol-binding protein; Rs, receptors; TGF β, transforming growth factor beta; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor alpha. One-way arrows indicate endocrine effects and two-way arrows indicate autocrine and paracrine effects”
“Se muestran las moléculas producidas por los adipocitos, que actúan como señales endocrinas, paracrinas o autocrinas Entre las diversas proteínas secretadas por los adipocitos encontramos Hormonas, citocinas y otras moléculas implicadas en procesos de regulación metabólica, neuroendocrina, inmunológica y cardiovascular. Abreviaturas: ASP, proteína estimuladora de acilación; Apo E, apolipoproteína E; Adipo Q, proteína del adipocito relacionada al complemento; CETP, proteína translocadora de ésteres de colesterol; FABP, proteína que se une a ácidos grasos; IGF-1, factor de crecimiento similar a insulina; IL-6, interleucina 6; LPL, lipasa de lipopro- teínas; PAI-1, inhibidor del activador del plasminógeno tipo 1; PG, protaglandina; PPARγ, receptor gamma para el activador del proliferador del peroxisoma; RBP, proteína que se une a retinol; Rs, receptores; TGF β, Factor de crecimiento transformante beta; TNFα, Factor de necrosis tumoral alfa. Las flechas de un solo sentido indican efectos endocrinos y las de doble sentido efectos autocrinos y paracrinos”
Thank you very much
for your kind attention !
Remember that to donate blood
is to save many lives...
¡ Muchísimas gracias
por su amable atención !
Y recuerde que donar sangre
es salvar muchas vidas…

BIBLIOGRAPHIC QUERIES ⊛ CONSULTAS BIBLIOGRÁFICAS
⊛ Protein (Proteína)
⊛ What are proteins?
(¿Qué son las proteínas?)
⊛ What are Proteins and what are they for?
(¿Qué son las Proteínas y para qué sirven?)
⊛ Manual of nutrition and dietetics
(Manual de nutrición y dietética)
⊛ Diet and Nutrition: Essential Amino Acids
(Dieta y Nutrición: Aminoácidos Esenciales)
All images in this publication are in the public domain (CC0) and were edited with Paint and PowerPoint as PNG images
The GIF image, with personal photos, was edited with the online application Picasion.com
The Hive.blog Logo (CC0) and Ecency Logo was used
The translation was made by DeepL
I would be very pleased to receive your valuable comments and constructive suggestions on the topic presented, as they will be considerable for the improvement of future publications
T H A N K Y O U !
Todas las imágenes de esta publicación son de dominio público (CC0), fueron editadas con la aplicación Paint y PowerPoint como imagen PNG
La imagen GIF, con fotografías personales, fue editada con la aplicación en línea Picasion.com
Se utilizó el Logo de Hive.blog (CC0) y Ecency Logo
La traducción fue realizada por DeepL
Me sentiría muy complacida en recibir su valioso comentario y constructivas sugerencias acerca del tema presentado, ya que serán considerables para el mejoramiento de las futuras publicaciones
¡ G R A C I A S !

Congratulations @wayuu-reg! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
Your next target is to reach 4000 upvotes.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPCheck out our last posts:
Support the HiveBuzz project. Vote for our proposal!
You have shared a great, simplified but quite comprehensive guide to the important functions that proteins play in our bodies.
It is here when you finish to understand why it is necessary to eat proteins, because they can not be missing in diets. And it is here where you see very well why a person who does not consume protein ends up having a weak immune system, among other things.
Good job.
Muchísimas gracias Doctor @apineda por su valioso comentario que enrriquece mi artículo.
The importance of protein can not be underated. It has so much importance beyond our imagination
Muy buenas proteínas las que presentas por acá... Saludos!
You have prepared a very nice article. Are you a nurse? I wondered about the details of what you do, do you know all this information?
Si lo desea, puede pasar a leer mi artículo de presentación en Hive.blog y gracias por comentar en mi artículo.
Saludos @ipexito
Feel free to stop by and read my introduction article on Hive.blog and thanks for commenting on my article.
Greetings @ipexito
Me agradó la explicación de la funcionalidad biológica de las proteínas que expone desglosadas en 8 funciones diferentes, haciendo es más entendible para el lector que no está familiarizado con las Ciencias Naturales. El gráfico támbién está bien estructurado y muy entendible. Gracias @wayuu-reg
I liked the explanation of the biological functionality of proteins broken down into 8 different functions, making it more understandable for the reader who is not familiar with Natural Sciences. The graphic is also well structured and very understandable. Thanks @wayuu-reg
Thanks for the info 🙏
!discovery 35
Thanks for the lesson. :) !PIZZA
!PIZZA
I gifted $PIZZA slices here:
@jilt(2/5) tipped @wayuu-reg (x1)
Send $PIZZA tips in Discord via tip.cc!
Su post ha sido valorado por @ramonycajal
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.
The rewards earned on this comment will go directly to the people( @alummno ) sharing the post on Twitter as long as they are registered with @poshtoken. Sign up at https://hiveposh.com.