
1.Lightning is a giant spark of electricity.
It happens when tiny droplets of water and ice swirl around inside a storm cloud. This makes the cloud develop a strong electrical charge. Eventually, a spark jumps between the base of the cloud and the ground. This allows electricity to flow, releasing the electrical charge. We see the spark as a flash or 'bolt' of lightning.
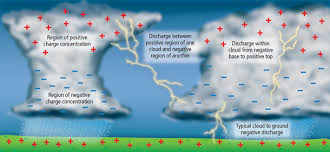
V During a thunderstorm, negative electrical charge builds up at the base of a cloud, while the ground has a positive charge. A lightning spark jumps between them to release the charge. V
2.Thunder and lightning go together.
In fact, thunder is the sound of lightning. When a lightning bolt jumps through the air, it is very hot. It can reach a temperature of 30,000°C. It heats the air around it very quickly. Heat makes air expand (get bigger). It expands so suddenly that it pushes against the air around it, and creates a shock wave. The wave travels through the air and our ears detect it as a loud boom.
3.Long ago, people used to think lightning was a punishment sent by their gods.
However, from the 1500s, scientists began learning about electricity and how it worked. Around 1750, US scientist Benjamin Franklin found that lightning was a kind of electricity. He invented the lightning conductor to protect buildings from lightning damage. It is a metal pole that can be fixed to tall buildings from lightning damage. If lightning strikes, the electrical charge runs down the pole and down a metal wire, then flows safely into the ground.
V You can clearly see the lightning conductor on the spire of this cathedral in Liverpool, UK. V

4.It is quite rare for lightning to strike people, and most of those who are struck, survive.
However, lightning does kill over 2000 people around the world each year.
5.Lightning can make glass.
Glass is made by heating up sand. When lightning strikes in a sandy desert or on a sandy beach, this happens naturally. At the place where the lightning hit the ground, it creates a tube-like tunnel of glass in the sand. These natural glass tubes are called fulgurites.
V Fulgarites occur when lightning strikes sand. The high temperature makes the sand melt. It eventually cools into hollow tubes. V


光线是电力的巨大火花。
当水和冰的微小水滴在暴风云中旋转时就会发生。这使得云开发出强大的电荷。最终,火花在云的底部和地面之间跳跃。这允许电流流动,释放电荷。我们看到火花闪闪发光,或闪电闪电。
V在雷暴期间,负电荷在云底建立,而地面正电。闪电在它们之间跳跃以释放电荷。 V

雷电一起走。
其实雷声是闪电的声音。当一个闪电跳过空气时,它很热。它可以达到30,000°C的温度。它很快地加热了周围的空气。热使空气膨胀(变大)。它突然膨胀,推动它周围的空气,并产生冲击波。波浪通过空气传播,我们的耳朵发现它是一个大声的繁荣。
以前,人们习惯于思考闪电是他们神的惩罚。
然而,从15世纪15年代起,科学家就开始了解电力及其工作原理。 1750年左右,美国科学家本杰明·富兰克林发现雷电是一种电力。他发明了避雷针,以防止建筑物遭受雷击伤害。它是一个金属杆,可以固定在高层建筑物上,避免雷击。如果雷击,电荷会沿着极点向下运动,然后将金属线放下,然后安全地流入地面。
V你可以清楚地看到在英国利物浦这座大教堂的尖塔上的闪电指挥。 V

闪电是非常罕见的罢工人,大多数人都被击毙,生存下来。
然而,闪电确实每年杀死世界各地的2000多人。
光线可以做玻璃。
玻璃是通过加热砂制成的。当沙漠或沙滩上发生雷击时,会发生这种情况。在闪电撞到地面的地方,它在沙子中形成了管状的玻璃隧道。这些天然玻璃管称为fulgurites。
V闪闪发生在沙尘暴时。高温使沙子融化。它最终冷却成中空管。 V

Great explanations about the