At 9:09 on September 9, 2019, Insight Chain (INB) announced that it will launch the mainnet for INB Public Blockchain at 10:10 on October 10, 2019 to complete the upgrade from testnet to mainnet. Henceforth, INB will realize a leap in the development level of mainnet for INB Public Blockchain and continue to carry out research and implementation on the technology and ecology of the Public Blockchain.
INB completed the transformation from an application chain to a Public Blockchain at the end of 2018, upgrading its positioning from "Decentralized Survey Ecology Chain" to "Infinitely Scalable Big Data Ecology Public Blockchain". There are two core objectives for INB Public Blockchain: Improve scalability and meet the requirements of business data’s storage onto blockchain for more applications on the premise of decentralization and security. Realize transaction data processing capacity of over 100,000 (100,000+TPS) per second and business data processing capacity of over 1 million (1,000,000+TPS) per second; realize business data’s structural storage onto blockchain and form an on-chain economy, making business data as reliable and unchangeable as transaction data.
INB team has applied for nearly 300 blockchain patents for technological invention, which cost nearly ten million yuan. In terms of patents, INB team has already made an overall arrangement at least 2 years ahead of the industry, and planned to protect its research and implementation of blockchain technology and industry, as well as the industries and scenarios that it may be involved in through patents. Mr. CTO Ji Jianxun is responsible for the formulation and implementation of INB patent strategy. He leads the technical team, ecological team, research team and intellectual property team to research, design and develop INB Public Blockchain and ecological application, and meanwhile complete the planning, design and implementation of patent strategy. In the meantime, Insight Chain plans to take the lead to establish a Blockchain Patent Alliance within which all enterprises will be authorized to use the patent free of charge, so as to inherit the openness and sharing spirit of block chain and to promote the sustainable development of blockchain technology and ecology.
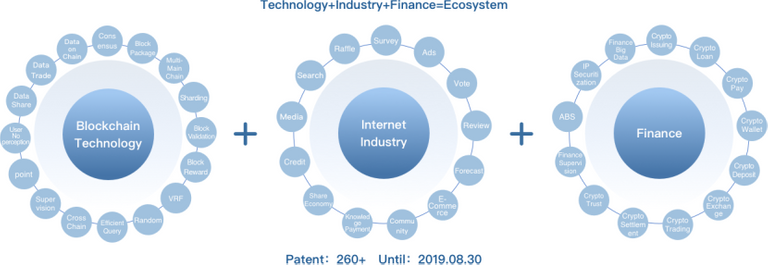
Insight Chain's vision is to enable everyone to have a credible digital account through blockchain technology and an account composed of digital currency information and data asset information, so as to build an economy involving everyone based on the digital account, in which closed loop of data flow and currency circulation will be realized, thus realizing the redistribution of economic value based on the digital account.
1 Scalability Hierarchical Model of INB Public Blockchain
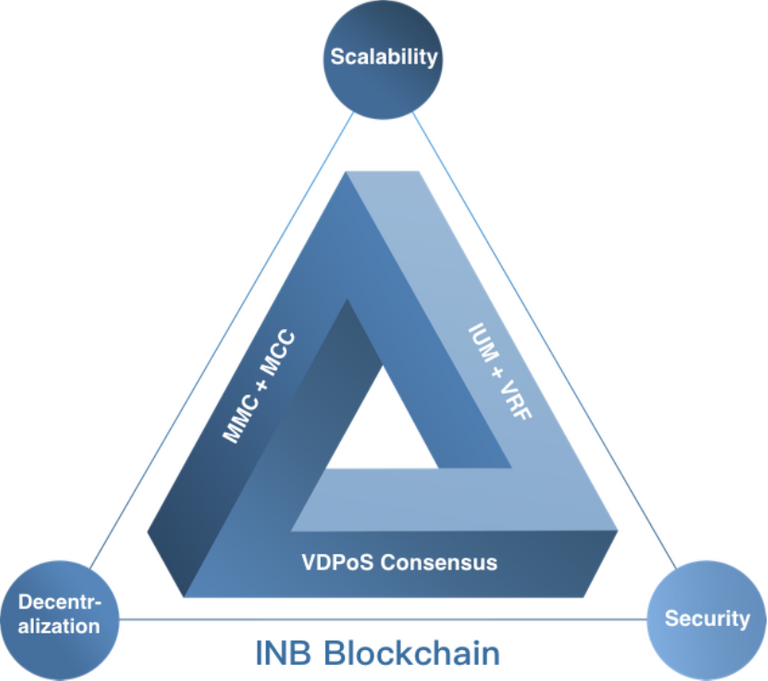
The impossible trinity problem of Public Blockchains has been a hot research topic in recent years. Many Public Blockchains have improved themselves from different aspects such as consensus, Sharding, sub-chains, etc. However, it also lead to certain problems in terms of decentralization, safety and scalability. For example, There are problems such as low TPS facing Ethereum and insufficient decentralization facing EOS. This cannot fully meet people's expectations for Public Blockchain, nor can they support large-scale application implementation. INB Public Blockchain has improved layer 0, Layer 1 and Layer 2 on the basis of its own innovation to overcome the impossible trinity of blockchain. It can be called a generalist in the field of Public Blockchain.
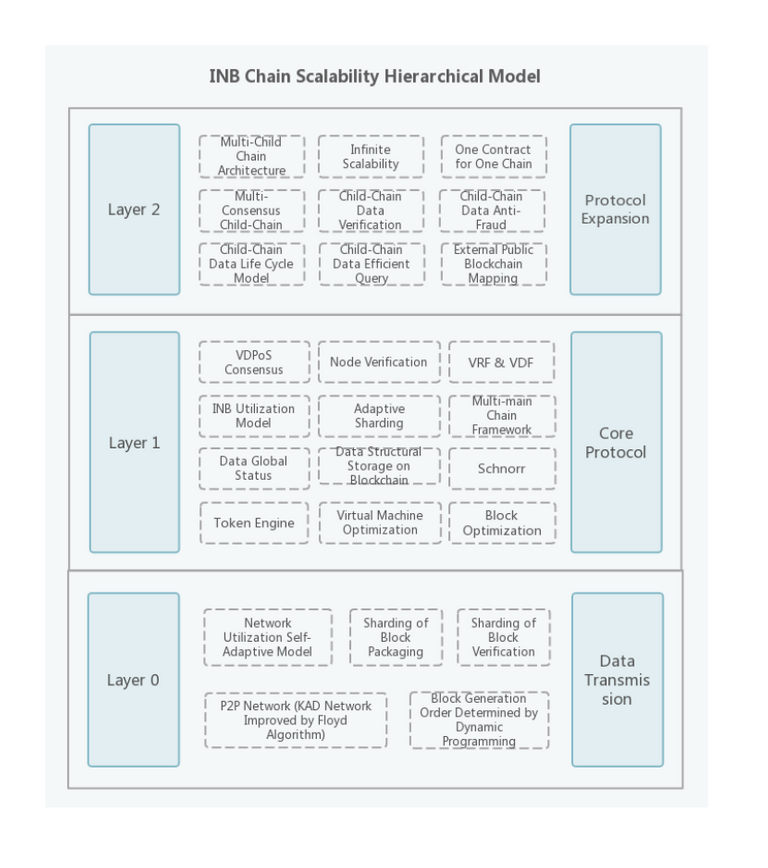
2 Innovation of Layer 0 (Data Transmission)
There are two thoughts on the improvement of INB Public Blockchain on Layer 0 (Data Transmission): To reduce the content and frequency of data transmission and to improve the network topology.
Firstly, the adaptive model of network utilization. INB Public Blockchain will measure the network utilization of the whole Public Blockchain through technical means, so as to automatically control the number of various segments and transmission conditions of the Public Blockchain to maximize the use of the network.
Secondly, the sharding of blocks. A sharding method of block packaging and verification will be applied in INB Public Blockchain. If the data volume of each block is large, the packaging, verification and network transmission of blocks will be time consuming. To avoid this, each block will be fragmented by VRF random lottery mechanism and sent to different nodes for packaging and verification, so as to maximize the utilization rate of nodes and network, and reduce the processing time. Meanwhile, this random lottery mechanism will be verified by other nodes to prevent cheating.
Finally, the optimization of the network topology. It includes two aspects: Determining the block generation order by dynamic programming and improving Kademlia network by Floyd algorithm, which will be discussed in detail below.
Dynamic Programming Determines Block Generation Order
Before each round of block generation, the order of super node sharding of the block generation must be determined in advance to synchronize the block data as quickly as possible. This problem can be described as: Knowing the distance between any two nodes to find out how to traverse the shortest path of all nodes from one node, that is, the TSP problem (Traveling Salesman Problem). INB Public Blockchain introduces dynamic programming algorithm to solve the TSP problem.
Floyd Algorithm Improves Kademlia Network
In the INB Public Blockchain, it is mainly composed of super nodes, verification nodes and other nodes. These nodes form a Kademlia (KAD) network. All nodes store information such as the location of other super nodes. Different from the traditional KAD, the INB Public Blockchain stores the distance information of any two nodes, and introduces Floyd algorithm to improve the efficiency of data transmission between nodes. Floyd algorithm is then used to select the shortest path from one node to other nodes for communication, thus improving the network efficiency.
3 Innovation of Layer 1 (Core Protocol)
There are some thoughts on the improvement of INB Public Blockchain in Layer 1 (Core Protocol): Consensus algorithm, sharding, business data’s structural storage onto blockchain, adding world state, virtual machine optimization and introduction of Schnorr signature algorithm.
(a)VDPoS Consensus Algorithm (First in the World)
INB Public Blockchain proposes a new consensus algorithm: VDPoS (Validated DPoS) algorithm, which is an organic combination of DPoS + BFT + Node Verification. Voting in DPoS algorithm solves the problem that a larger amount of PoW algorithm resources are consumed uselessly, and also INB's mortgage and punishment mechanisms are applied to limit the nodes to do wrong things to a great extent. After the block is generated, BFT algorithm is firstly used to carry out fast verification inside the super node. At the same time, the super node uses VRF algorithm to find a plurality of random verification nodes. The verification nodes also use BFT algorithm to carry out asynchronous verification on the block data, so as to prevent the super node and the verification node from doing wrong thing jointly thus greatly improving the degree of decentration and safety of the Public Blockchain.
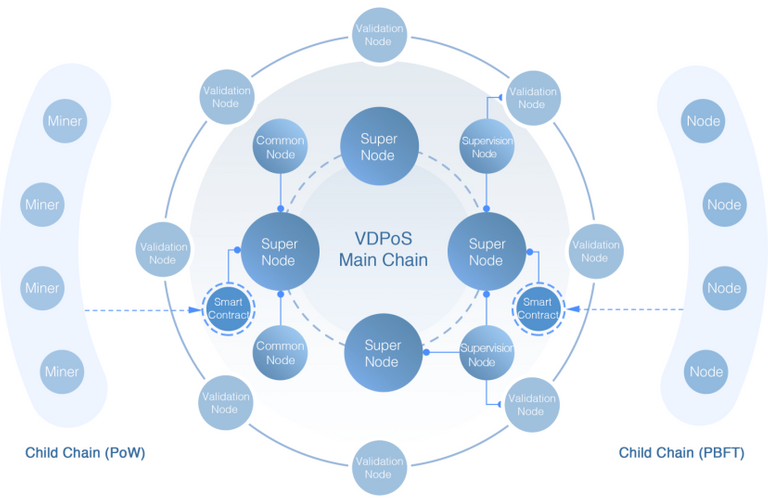
Using VRF to Select Verification Nodes
The full name of VRF is Verifiable Random Function. VRF is widely used in blockchain due to its randomness and random verifiability. INB Public Blockchain uses VRF random lottery mechanism to select some verification nodes from all verification nodes to verify the block, which not only ensures the randomness of verification node selection but also prevents super nodes and verification nodes from jointly doing wrong things. INB Public Blockchain has many innovations in the implementation and application of VRF, and has applied for a patent for it.
Meanwhile, DPoS consensus has also optimized the blocks, such as increasing the block size limit, reducing the block generation time and block confirmation time.
(b)Sharding of VDPoS Consensus (First in the World)
INB Public Blockchain conducts automatic sharding for super nodes according to the resource utilization rate of the Public Blockchain. Each sharding is equivalent to a separate super node, which is called super node sharding. Select one sharding from 21 super nodes separately to form a main chain, thus forming a parallelly operating architecture of multiple main chains.
In the INB Public Blockchain, it is assumed that the block generation time of each main chain is 2 seconds, and the block generation time of multiple main chains has a time gap of "2s/number of sharding". In 2 seconds, the super node sharding of each main chain will generate block once, forming a multi-main chain continuously generating block mechanism, and the shardings that generates blocks within the 2 seconds are not on the same super node, thus maximizing the utilization of network and super node resources. For example, in the case of 20 shardings per super node, the entire main chain will generate block every 0.1 seconds, which is 20 times higher than the TPS by traditional DPoS algorithm and greatly reduces the waiting time. The schematic diagram is as follows. Under the existing conditions, the main chain adopting this mechanism will realize transaction data processing capacity of over 100,000+ TPS per second, and will gradually improve with the improvement of node and network capabilities.
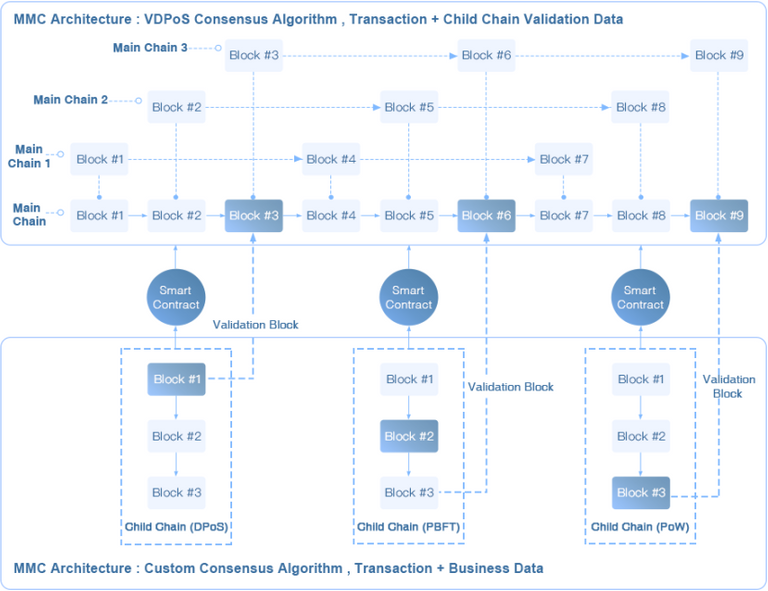
Utilization Model of Public Blockchain
In order to measure the resource utilization of the whole Public Blockchain, INB Public Blockchain proposes the concept of Public Blockchain utilization model: INB Utilization Model, abbreviated as IUM, which includes CPU and memory resources of super nodes and network resources. As the operation efficiency of the whole Public Blockchain is positively related to IU, when IU is very small, Public Blockchain resources should be fully utilized to improve scalability. Based on this concept, INB Public Blockchain proposes that the number of Sharding of super node and the height interval of child-chain verification blocks should be automatically adjusted according to the size of IU, so as to make full use of the resources of the whole Public Blockchain to improve TPS.
(a)Business Data’s Structural Storage onto Blockchain (First in the World)
The structural storage onto blockchain is one of the major advantages of INB Public Blockchain, which is different from traditional Public Blockchain projects that only store the data content onto blockchain while leaving the data attributes and processes. So the traditional way cannot truly guarantee the credibility of the data. Moreover, the data stored onto blockchain is not structured and cannot express the information such as the association between data and the association between attributes and data. In INB Public Blockchain, it enables business data’s structural storage onto blockchain so that the business data can be self-interpreted through the chain itself without a third-party application to interpret unstructured data, thus truly realizing the credibility of data and ensuring the value transmission of data. The structured business data is stored on the chain using Trie which improves access efficiency.
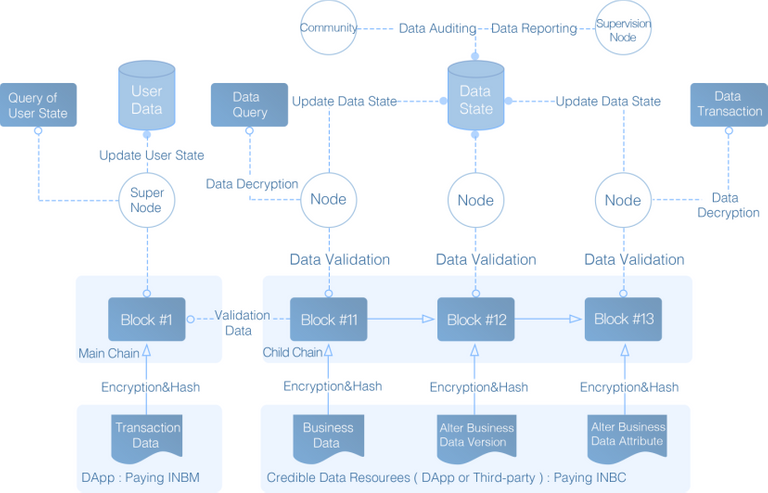
(b)World Status: Balance, Data, Token and Voting (First in the World)
The traditional Public Blockchain uses smart contracts to store all the world status except the balance. For example, the Token state of Ethereum is stored in the smart contract of Token. A big problem with this storage method is that the change of Token balance of each user will lead to rewriting of all user balance data. When the number of users is large, the chain cannot bear the amount of data rewritten each time. INB Public Blockchain uses Trie structure to store balance status, data status, Token status and voting status. Changes in each status will only cause data rewriting of Trie node where the status is located, greatly improving storage efficiency and saving storage space.
INB Transaction Engine
INB Public Blockchain proposes another way to greatly reduce the consumption of node resources: Separate the smart contract of Token in the traditional Public Blockchain from the smart contract business and execute it in a concise script language, called INB Transaction Engine (ITE). In Ethereum, a large proportion of smart contracts are the issuance contracts of Tokens, and at least half of the transactions are ETH and Token transactions, which consume a lot of system resources by starting the virtual machine to call the smart contracts. However, with INB transaction engine to execute, it will greatly reduce the resource consumption and save a lot of system resources and time during token transactions and verification.
(c)Optimization of Virtual Machines
INB Public Blockchain will support Turing-complete smart contract. It will support smart contract through a new virtual machine, called INB Virtual Machine (IVM). IVM will be implemented using WebAssembly (WASM), which means developers can use any familiar programming language to develop smart contract which will have better performance.
In addition, INB will optimize the storage structure of IVM to improve the execution and storage efficiency of virtual machines. For example, the Trie structure will be used to store the data in variables such as the Map of the virtual machine, and each Key in the Map will be stored as a node of the Trie, and so, compared to previous structure, it is not necessary to refresh the node data corresponding to the entire Map when each data in the Map changed, thus greatly improving the execution and storage efficiency of the virtual machine.
(d)Schnorr Signature Algorithm
In order to improve the efficiency of the INB Public Blockchain, save storage space and support the multi-signature function, the INB Public Blockchain introduces Schnorr signature algorithm to improve some problems existing in the traditional ECDSA signature.
Performance: It can greatly reduce the cost of signature verification. For traditional single signature transactions, Schnorr is much more efficient than ECDSA. For multi-signature transaction, compared to multiple verifications as required before, it only needs to be verified once by using aggregation signature, which greatly improves the verification speed of signatures;
Transaction size: Schnorr aggregates multiple signatures into one signature, which can greatly reduce the space occupation of multiple signatures and significantly reduce the bandwidth consumed for network transmission;
Privacy: Schnorr aggregation signature can improve the privacy of data on the chain. To the verifier, the aggregation signature looks like the ordinary Schnorr signature, and it is impossible to distinguish whether this transaction is an ordinary transaction or a multi-signature transaction. Besides, the public key and signature of the users participating in the transaction will not be exposed.
4Innovation of Layer 2 (Protocol Extension)
There are three main thoughts on the improvement of INB Public Blockchain in Layer 2 (Protocol Extension): Introduction of multi-child-chain architecture, efficient query of data cross the chain and on the chain.
(a)Multi-Child-Chain Architecture
INB Public Blockchain uses a hybrid architecture of Multi-Main Chain + Multi-Child Chain (MMC+MCC for short), which is the first Public Blockchain in the world to use this hybrid architecture. According to the resource utilization of the whole Public Blockchain, it automatically conducts sharding of the super nodes, form a multi-main chain parallel block generation mode. It takes full advantage of the network resources and the super node resources, which greatly improved the block generation speed and the vertical scalability of the Public Blockchain. Meanwhile, multiple child-chains can be launched on the main chain according to the usage of the application to support more DApp business data’s storage onto blockchain and increase the horizontal scalability of the Public Blockchain.
The proposal for launching child-chain is started by DApp or the community. And appropriate consensus algorithms are selected too. The child-chain can adopt the consensus mechanism of BFT-type alliance chain or Public Blockchain consensus mechanisms such as PoW, PoS, DPoS, etc. Different consensus algorithms can be selected according to different DApp's different requirements for the efficiency of data’s storage onto blockchain, safety, etc. The main chain does not restrict the consensus mechanisms of the child-chain. The proposal for launching child-chain is voted by the super node. After voting through the proposal, the Public Blockchain will automatically start a child-chain smart contract to manage the child-chain, and then wait for the child-chain nodes that meet the requirements to join so as to launch the child-chain.
The complete data of the child-chain is saved on the nodes of the child-chain, and in order to ensure safety and credibility, the child-chain will save the verification information of the data to the main chain for verification of the child-chain data. After the child-chain generates a certain number of blocks, the root of the Merkel Tree corresponding to the partial blocks will be saved on the block of the main chain to ensure the safety and credibility of the child-chain. The block on the corresponding child-chain is called the verification block.
(b)Cross-Chain (Interaction of External Public Blockchains)
For cross-chain with other Public Blockchains, the INB Public Blockchain uses the solution of status channel. The INB Public Blockchain provides a series of native state channel smart contracts, each smart contract corresponds to a Public Blockchain and the mapping of corresponding coins on the Public Blockchain. For example, for BTC, the INB Public Blockchain will provide a BTC cross-chain status channel smart contract, an account to receive BTC and IBTC tokens, wherein the IBTC tokens are 1:1 mappings of BTC in the INB Public Blockchain. After the user deposits the BTC into the account receiving the BTC, the smart contract will automatically allocate the same amount of IBTC token to the user. The transaction of the IBTC token represents the real BTC transaction. When the user wants to get back the BTC, just return the IBTC to the smart contract, and the smart contract will automatically transfer the BTC on the account to the account designated by the user.
(c)Efficient Query about On-chain Data
Due to the huge amount of business data, INB Public Blockchain will use caching mechanism, NoSQL and other methods to provide a faster way to query data on the chain, which can truly meet the demand of internet applications dealing with 100-million-level data.
There are many innovative points in INB Public Blockchain. This article is only a brief introduction of it due to space limitations. There will be a series of articles to do in-depth interpretation and show everyone a real representative of the era of Public Blockchain 3.0.
It is believed that after the launching of mainnet which has high scalability and the ability to store business data onto blockchain, INB Public Blockchain will improve the overall technical level of the field of Public Blockchain and greatly promote the implementation of "Blockchain +". We will see an era of numerous blockchain applications contending for attention. Many killer applications will then gradually emerge and contribute to bringing blockchain technology to common people.
For more information, please refer to the official website of Insight Chain (INB): http://www.insightchain.io, and download the Insight Chain (INB) Technical White Paper: http://file.inbhome.com/inb/INB_technical_whitepaper_v1-CN.pdf.
Contact Us
WeChat Official Account: InsightChain
Official Website: http://www.insightchain.io
BiYong (Chinese Community): http://0.plus/InsightChain_CN
BiYong (Global Community): http://0.plus/InsightChain
Sina Weibo: @InsightChain
https://weibo.com/u/6394744395
Twitter: @Insight Chain
https://twitter.com/InsightChain
Facebook: @InsightChain
https://www.facebook.com/InsightChain-339432310287132/
Medium: https://medium.com/@insightchain
Steemit: https://steemulant.com/@insightchain