
Simple inline commands for Windows to make things really easy.
We all know that Linux is heavy on command line usage as compared to Microsoft Windows. Nevertheless, there are a few tools that require Microsoft’s Command Prompt to diagnose and resolve computer problems. Since there are many commands to work with, we will focus on the ones that you may find useful for troubleshooting.
Listing the Tasks
A screenshot showing results for tasklist command.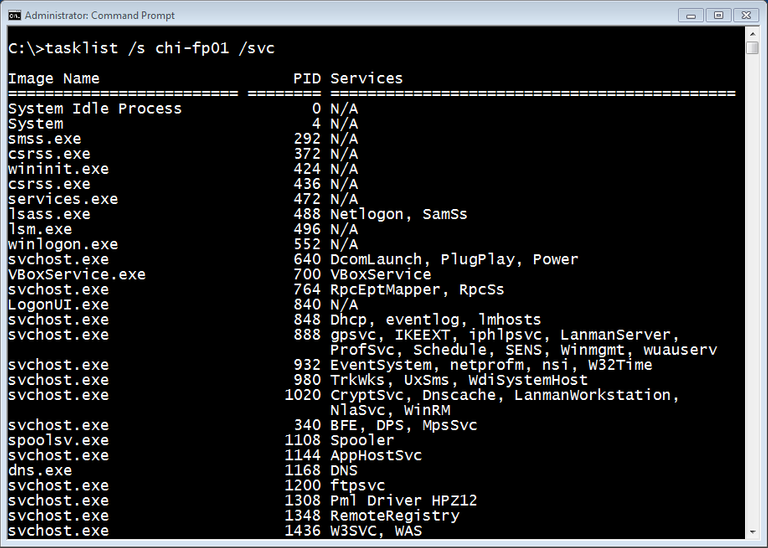
The tasklist command was created by the developers to get information about the tasks Windows is running on your system. The tasklist –m command helps identify all the tasks that are using EXE or DLL modules. The tasklist –svc command helps identify the services that are being used by the tasks.
Killing the Tasks
Command Prompt displaying Task Kill command guide.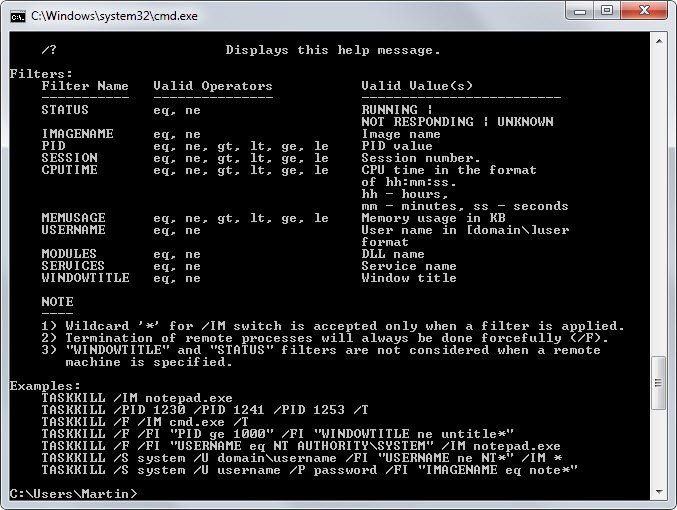
The taskkill command was created by the developers to kill a process or a task that is currently in use by the operating system.
The taskkill –im command allows the users to stop or kill a program. The taskkill –pid command is used to end programs using their Process ID, which can be obtained using the tasklist command; it helps terminate specific task that is being utilized by the software.
Configuring Internet Protocol
The ipconfig command displaying results.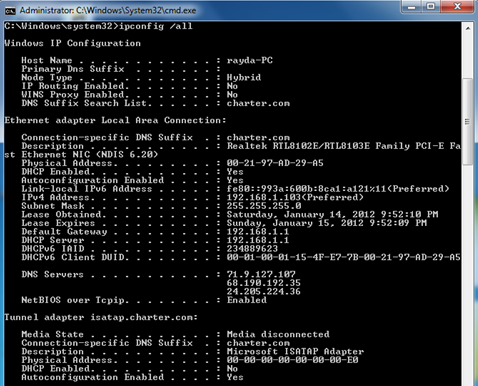
The ipconfig command is used either to view IP addresses associated with the machine or to modify them. If you want to check your Windows complete IP configuration, you will type ipconfig /all. To get a new IP address, you would have to first type ipconfig /release, which will allow Windows to remove the old IP. Then you can use ipconfig /renew so that your Wi-Fi can get a new IP address. The ipconfig /flushdns command allows users to remove the old cache DNS results, which the Windows saves for later uses.
Pinging Your Connection
A screenshot of Command Prompt showing results for the ping command.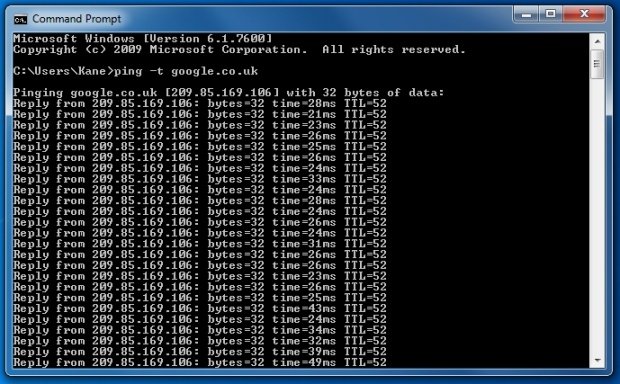
A ping is used to verify IP/TCP to the host. In order to check and use it, you need to type ping google.com bear in mind that this command will only work if your Internet Control Message Protocol traffic is allowed to pass. However, if your systems firewall is blocking it, then it will fail to ping.
DNS Checking
A screenshot showing results for the nslookup command for BBC’s website.https://www.petri.com/forums/filedata/fetch?id=463166
The nslookup is a useful tool for troubleshooting DNS problems, such as host name resolution. This tool works best when you are having problems related to legacy DNS records. In order to use this tool, you should type nslookup dc2.test.com, where dc2.test.com is the name of the host you are having problems with.
Driver Searching
A screenshot of driverquery command showing results for the installed drivers.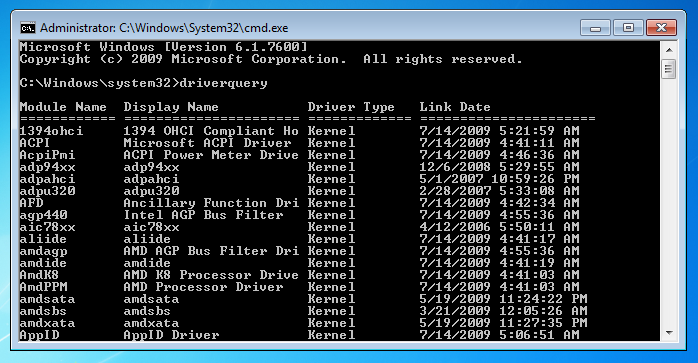
The driverquery is a simple command line tool that provides you with a detailed list of drivers installed on your computer systems. If you want specific information about your drivers, you can change the command to driverquery –v; this is going to display the verbose output results about your driver. You can also use driverquery –si; this is going to show you signed information related to your drivers.
Verification of Signed Files
Command sigverif written in Command Prompt resulting the File Signature Verification GUI window.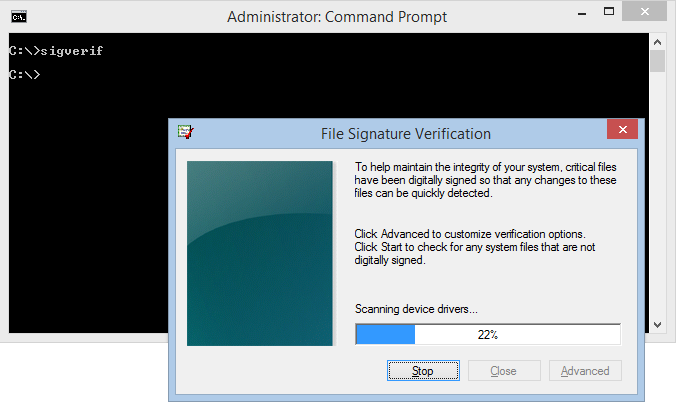
To check if the files on your computer system are in their original condition, you can use the sigverif command in Command Prompt. A GUI window will open, which will scan your system to check the shady files. The GUI window has an advanced option where you can change your choices and alter the name of the log file as per your needs.
Checking for Malicious Software
A screenshot of the Command Prompt showing the ongoing process of sfc /scannow command.https://fthmb.tqn.com/2nadkVcwNQQMmxfWppJK9B6ige0=/768x0/filters:no_upscale()/about/sfc-scannow-windows-10-5751aa6d5f9b5892e86da6a7.png
Many times when you download a pirated software or you click on a malicious advertisement, the malicious program tries to take over your machine by replacing the important files in your system.
The sfc /scannow command is used to verify the originality of the Windows files [if some of them are found missing], automatically replace them, and bring them back to their original form.