Physical therapy and stroke
Physical therapy plays an important role in the treatment of stroke patients. What is the disease that we hear every day of people who died or were hampered by it?
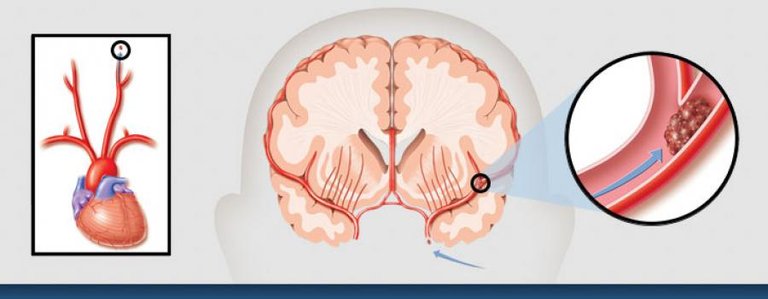
The brain cells feed through the arteries that supply it with blood. The blood carries oxygen and glucose to those neurons so that they continue to function properly.
If the blood is cut off from a region of the brain led to death and thus lose the body function that was carried out by that region.
The stroke is a defect in the blood vessels that feed the brain, and this imbalance either be a lock in the artery or explosion, and thus lack of blood and blood vessels of that region, which reflects the symptoms of neurological injury.
Stroke is a leading cause of death globally and affects nearly 20% of people over the age of 65. It is the second leading cause of death in the world and, more importantly, a major cause of disability.
The impact of these injuries is not confined to the patient but extends to his or her family, to the community and to the health care system in general. In the United States, stroke in 2004 cost $ 53.6 billion.
The most common contributing factor to this stroke is age. The most common infections occur for people over the age of 65 years, in addition to high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, high cholesterol, body fat level, excess nervousness, smoking and excess weight.
The most important factors that determine the symptoms: the injured artery and the location of the affected area, the size, the wider, the worse the symptoms.
When the right hemisphere is infected, the symptoms appear on the left side of the body because the right half of the brain controls the left side of the body, and vice versa. The left half of the brain controls the right side of the body.
Initial symptoms of dizziness include dizziness, sudden headache, impaired vision, nausea, vomiting, loss of consciousness, low hearing ability, difficulty in speech, swallowing and imbalance.
The delayed symptoms are weakness or paralysis of affected limbs, impaired sensation, impaired muscle tone, impaired vision, hearing, difficulty in speech, swallowing, memory impairment, difficulty in perception, understanding, imbalance and walking.
Stroke is diagnosed through clinical examination, ie, examination of brain function, the ability of the patient to move the hand or foot or sensation, laboratory tests and scans (class images and MRI images).
Temporary clot
Before a stroke occurs, a temporary clot is a warning to the patient about the possibility of a stroke, sometimes called a small clot because it gives the same symptoms of a permanent clot, but these symptoms do not last more than 24 hours.
How to reduce the incidence of stroke:
Control of cardiovascular diseases.
Follow the blood pressure regularly and use the required medication.
Improved diet.
Stop smoking, alcohol and drugs.
Relieve excess weight.
Exercise regularly.
Stress relief.
Knowledge of early symptoms of stroke.
What are the chances of recovery?
95% of stroke patients improve and the degree of improvement depends on many factors, including: stroke severity, patient age, stroke quality and previous patient conditions.
Glaucoma prevention methods should be better targeted than post-stroke care.
What is the latest medication for stroke treatment?
The anticoagulants prevent platelets from sticking to the walls of the arteries. Aspirin is the oldest known drug in general and is described at this stage. It has been shown to reduce the risk of heart attack and cerebral thrombosis caused by blockage of the arteries.
The role of natural therapy:
Physical therapy is a very important factor in treating the patient after stroke. It helps the patient to rely on himself to spend a lot of daily work such as walking, eating, cleaning, dressing, etc.
Medications given to the patient after the infection help to prevent another clot but does not help restore movement.
Exceptions are milded depressants, as many stroke sufferers suffer from depression after the injury. Medications for depression treat their condition very efficiently and make them more cooperative in initiating physical therapy and are therefore more self-reliant.
The role of physical therapy lies from the first moment of the stroke, not as some believe after the patient is discharged from the hospital.
The natural therapist evaluates many things, including the following:
Mental state, tone, tone of muscle, strength of the injured limb muscles, rate of joint movement, functional assessment of the patient and walking.
And then devises a proper treatment plan for the patient. The plan includes exercises to prevent the deterioration of the condition and remedial exercises for existing problems such as: Exercises to strengthen the weak muscles