
Economic and social development has led to a constant increase in the world population with the need to improve food supply systems, the situation that requires the use of agrochemicals, since these chemicals in agriculture are necessary, since it deals with more agricultural production to avoid the spread of diseases transmitted by vectors, such as insects, mites and rodents. However, the benefits provided by these may be accompanied by a series of negative effects on the health of the population, on natural and hydrobiological ecosystems, and on flora and fauna.
Cases of pesticide poisoning are a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. However, in developed countries, incidents of acute exposure to these substances are rare in humans, due to both the severe restrictions on the use of these products and the use of new substances of lower toxicity for mammals and others. species, but fundamentally to strict compliance with the current legal framework, therefore, at present, the concern of researchers is focused on the chronic or long-term effects of these chemicals, since even so, new agrochemicals are introduced to the market with greater selectivity on the vector to be controlled and therefore less toxicity for non-target organisms, the critical of its danger at times is the manner and conditions of its application. In developing countries, on the other hand, epidemiological studies estimate that 25 million people per year would suffer from some form of agrochemical poisoning, due to poor product regulation, lack of surveillance systems, and lower compliance with standards.
The inappropriate use of agrochemicals is a problem of great importance because they are constantly applied in agricultural areas generate waste that can contaminate biota, soil, bodies of water and air, affecting trophic chains, resulting, in many cases, in damage to the human being These substances can be absorbed quickly through the respiratory, ocular, dermal, and digestive tract, as well as having disruptive effects on the endocrine system, considering themselves potentially mutagenic and carcinogenic, they also affect the nervous and immune system, as well as accumulating in the fatty tissue, being these most notorious findings in developing countries. Therefore, it is clear that the harmful effects of these substances are not limited to people who have direct contact with the substances, but involves people indirectly exposed, by living in the vicinity of the areas of application or deposit of agrochemical . being the prolonged exposures to low levels of agrochemicals that constitute major problem, since they are cause of effects such as teratogenesis, mutations, cancer, hepatic and renal alterations, just to name a few.
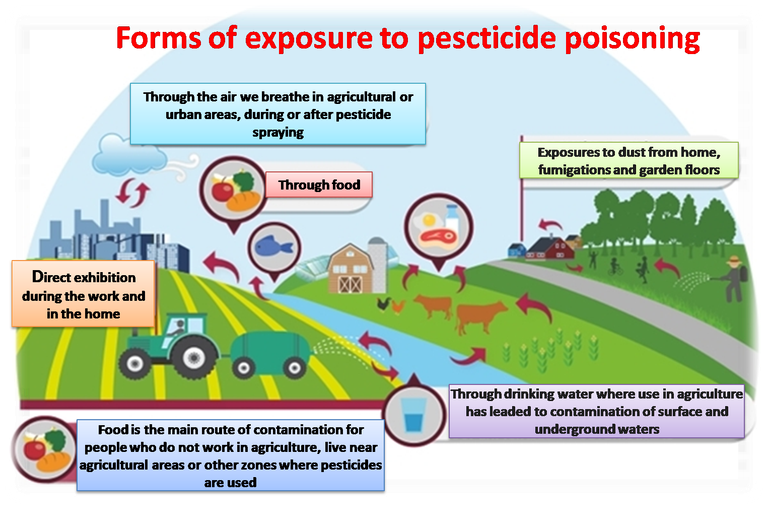
In this sense, families that inhabit the land near cultivated fields are exposed to the effects of xenobiotics, through environmental and occupational exposure. Since, in general, all family members collaborate in agricultural tasks, exposure can begin at a very early age or from conception, especially when basic protection measures such as inappropriate application techniques are not taken. Fumigation equipment in poor condition, lack of protective equipment, poor technical advice, illiteracy, incorrect hygienic measures, ignorance of the toxicity and the time of permanence of pesticides, which contributes to health risks extending to the population in general, generating, consequently, a public health problem.
The WHO for 2008 estimated an annual worldwide incidence of 3 million cases of poisoning, with some 50,000 deaths of children under 4 years. It is true that the use of chemical products can increase agricultural productivity, as well as control or eradicate some vectors of diseases; however, they are harmful agents that generate a public health problem of great importance, however the extent of the situation is still unknown, given that health systems do not detect all cases of acute poisoning, consequently, to a lesser extent performs surveillance on chronic poisoning from exposure to these products.
If you liked the publication and want to continue seeing more articles of this type, send us votes, follow me and reséteme.
References:
Cortés, P .; Villegas, A .; Aguilar, G .; Paz, M .; Maruris, M. and Juárez, C. 2008. Symptoms caused by pesticides in agricultural workers. Medical Journal of the Mexican Institute of Social Security, 46 (2): 145-152.
Ferrer, A. 2003. Pesticide poisoning. Annals of the Health System of Navarra, 26: 155-171.
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). 2003. Global Food security and the role of sustainable fertilization, Organización de Naciones Unidas. Roma, Italia.
Jáquez, S. 2014. Study of the socio-environmental impact caused by the use of pesticides in agricultural areas of the Guadiana Valley, Durango. Degree work to apply for the Master of Science degree in Environmental Management. Secretary of Research and postgraduate, National Polytechnic Institute, Durango.
Niño, Y. 2010. Determination of the level of exposure to pesticides due to well water consumption and the relation with the possible effects on the health of the population residing in the Chorrillos district of the Suba rural sector. Degree work to apply for the Master's Degree in Public Health. National University of Colombia, Bogotá.
Ward, M.; Lubin, J.; Giglierano, J.; Colt, J.; Wolter, C.; Bekiroglu, N.; Camann; D.; Hartge, P. y Nuckols, J. 2006. Proximity to crops and residential exposure to agricultural herbicides in iowa. Environmental health perspectives 114(6): 893-897.
Nice post. Factually correct I am sure. It would help the reader to cite your sources in the text as well (first author and year of publication). This would help the reader to read papers that deal with the specific statements that you are making. I would also make sure to use refs or sources for images you provide. If they are your own, state that.
excellent friend rating, I share your opinion since at the beginning I had made my post by placing at the end of each paragraph the bibliographical reference of where I had obtained it, however as I am new in this I thought about placing it at the end of a general form. Thank you for your guidance, please keep me in mind for the realization of other post, greetings
you are welcome. have a look at the @steemstem weekly digests. Posts mentioned there are considered conforming to style and general rules of thumb. Great posts to read as well as there are nice examples listed covering various scientific fields.
Congratulations @frank0990! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on any badge to view your own Board of Honor on SteemitBoard.
For more information about SteemitBoard, click here
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPThat need to meet demand for an ever increasing population results in some bad stuff sometimes ( ya know like pesticides as you were talking about) but it's choices of what tradeoffs are worth it and what aren't. I think these chemicals need to be a last resort and new methodologies found to improve agricultural practices but I also probably have a very biased opinion because I spent a summer spraying herbicides and the exposure even with ppe noticably reduced my immune system and I started getting sick all the time. I still have yet to fully recover and get sick much easier than I ever use to.
if the effects of these toxic in the salu is to deperder of the level of toxicity of the same one and also of the adequate use ppe, since as it is known these toxics can penetrate the human organism through diverse vias, as they are the respiratory, digestive and dermic. therefore if a basic ppe is used as for example mouth and glove cover, it does not mean that we are totally protected, in this sense the agrochemicals can penetrate other areas of the body that are unprotected. and we must also bear in mind that there are agrochemicals that have a greater range of toxicity compared to others.