Marketing 101 - Finding and Positioning within a Target Market

Market segmentation
Market segmentation is necessary, a single product is unlikely to meet the needs of all consumers in a mass market. For example Toothpaste, Shampoo, Chocolate and Cereal. Fundamental part of marketing strategy, helps organisations with their understanding of consumer needs and buying behavior, a popular approach to identifying target markets. Process of grouping customers into markets, heterogeneous markets into smaller, more similar segments by identifying customers into such groups. Enables marketers to develop product/service benefits appropriate to the segment. Products and brands designed to appeal to particular market segments.

These product/services are supported by appropriate promotional campaigns, customer service, pricing, place (distribution strategies)
Customer Analysis -> Competitor analysis -> efficient resource allocation -> Strategic Marketing Planning
Customer Analysis – How, why, what customers buy can be addressed and used to monitor trends which will keep organisations informed
Competitor Analysis – It is crucial for organisations to understand the competitive market place. They need to know who their main competitors are and which segment they are targeting. Answering these questions allow marketers to make decisions about what segments are appropriate and any competitive advantage there might be in the marketplace
Effective resource allocation - all organisations have limited resources, to target a whole market is usually unrealistic, organisations need to consider does they have enough resources and is the use of resources effective when focused on this particular segment
Strategic marketing planning – segmentation allows marketers to develop specific plans o meet the wants and needs of the different segments

Advantages:
Differentiation of the marketplace, helps target market selection, allows the tailoring of the marketing mix to suit the chosen segment, allows the organisation to assess opportunities and threats whilst building relationships throughout the market place
Disadvantages:
Market research is resource intensive, only allows limited market coverage, can weaken brands, misinterpretations of the target segment could have detrimental consequences, small segments rather than appealing to the mass market

3 stages of market segmentation:
1. Segmentation – consider segmentation variable, look at profile of emerging segments and validate segments emerging
Decide on targeting strategy, decided which and how many segments to target
Understand consumer perceptions, position products in the mind of the consumer by communicating the desired
positioning.Design an appropriate marketing mix

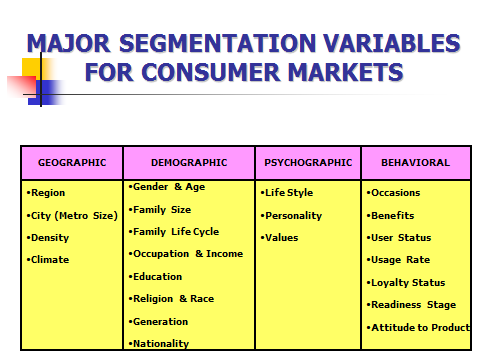
Segmentation Variables
Segmentation variables are the dimensions or characteristics of individuals, groups or businesses that are used for dividing a total market into segments. It can be broken down into single and multivariable segments.
The four main variables used for segmentation are; demographics, geographic, psychographic and behaviouristic variables.
Segmenting business markets often occurs, in the aim to satisfy the needs of businesses for products, this can be problematic as there are many variables to consider and some are hard to categorise. Some variables for segmenting business markets are; personal characteristic of buyers (life style of buyers, personality, demographics), Operating variables (technology and how the products ae used) situational factors (urgency of purchase and size of order) Organisational demographics (age of company, location and industry) Purchasing approach (Centralised/decentralised? buying policies, existing relationships, buying criteria).
Segmentation analysis:
Disorganised implementation = ineffective market segmentation, this can lead to missed opportunities and inappropriate investment. To avoid such difficulties there is some criteria for assessing effective segmentation;
Differential – there must be a real differences in the needs of consumers for the product/service
Substantial – large enough to be profitable to justify developing and maintaining a specific marketing mix
Dissimilar segments – in terms of wants, needs and purchasing behaviour should not be grouped together in the same segment
Accessible – easy to reach with the developed marketing mix
Measurable – easy to identify and measure
Stable – segments must be stable for organisations to make long-term strategic decisions
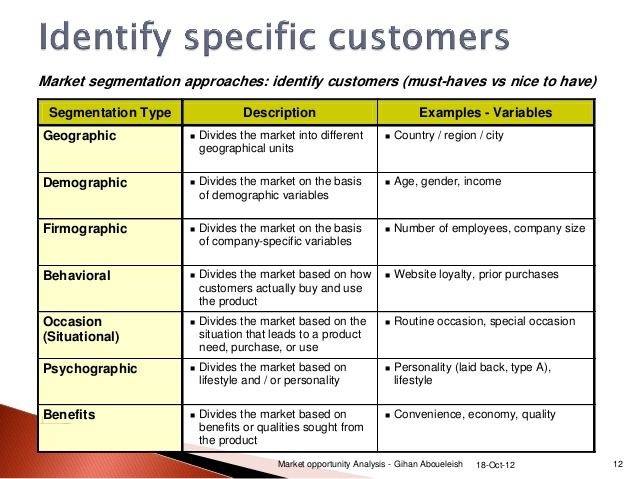
Targeting
‘’The decision about which market segments an organisation decides to priorities for its sales and marketing efforts’’
Undifferentiated strategy defines an entire market for a particular product as its target market. Organisation designs a single marketing mix, directs the marketing mix at the entire market and assumes all customers have similar wants and needs
Concentrated strategy occurs when an organisation directs its marketing efforts towards a single market segment, it creates and maintains one marketing mix and allow the organisation to specialise and to focus on the wants and needs of one distinct customer group.
Differentiated strategy is when an organisation directs it marketing efforts towards two or more market segments, it develops a marketing mix for each segment and can often be a natural progression from the ‘concentrated strategy’
Market segmentation is fundamental to the marketing strategy, segmentation variables are used to divide the total market into segments. These should relate to customers’ wants and needs, once the market segments have been clarified, an appropriate strategy must be employed.

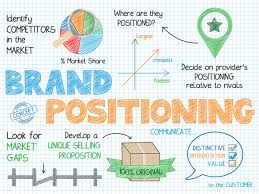
Positioning
Having decided which segments to target and how to target them, the marketer must focus on positioning. How is it currently positioned, is it different from desired positioning and what is the desired position. Successful positioning needs to be clear credible and consistent
‘’positioning is not what is done to the product, it is what is created in the minds of the target customer’’ it is ‘’the process of creating an image for a product in the minds of target customers’’
To successfully position your product/brand you need to be;
Clear – easy to understand,
Consistent – coherently communicate message overtime across platforms
Competitiveness – clearly differentiation and knowledge of competitors
Credible - organisation/products/brands must deliver up to expectation
Limited positioning discrepancies – Organisation’s desired positioning must match the positioning in the mind of the target segment

Market research
‘’Is the systematic design, collection, interpretation and reporting of information to help marketers solve particular problems or take advantage of marketing opportunities’’ (Dibb and Simkin 2009:203)
Can generate a greater understanding of consumers. Can highlights insight into market opportunities. Reveal strengths, weaknesses and threats related to an organisation or product. Ascertain the potential success of new products. Build an understanding of the current positioning. Determine the feasibility of a particular marketing strategy.
In-depth market research can generate deeper understanding of how consumers perceive brands/organisations used in conjunction with ‘perceptual mapping’. Perceptual mapping is a tool adopted by marketers, to visually depict consumers’ perceptions. Prioritise organisations/brands/products and their perceived attributes. Can highlight strengths and weaknesses perceived by consumers
 )
)
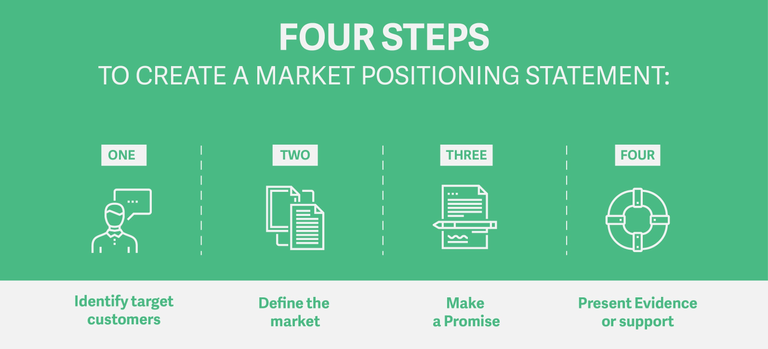
Steps in determining a Positioning Plan
Define the segments in a particular market
Decide which segments to target
Understand what the target consumers expect and believe to be the most important considerations when deciding on the purchase
Develop a product catering specifically for these needs and expectations
Evaluate the positioning and images, as perceived by the target customers, of competing products in the selected market segment
Select an image that sets the products apart from the competing products thus ensuring that the chosen image matches the aspirations of the target customers. The selected positioning and imagery must be credible
Inform target consumers about the product. This forms part of the overall marketing mix

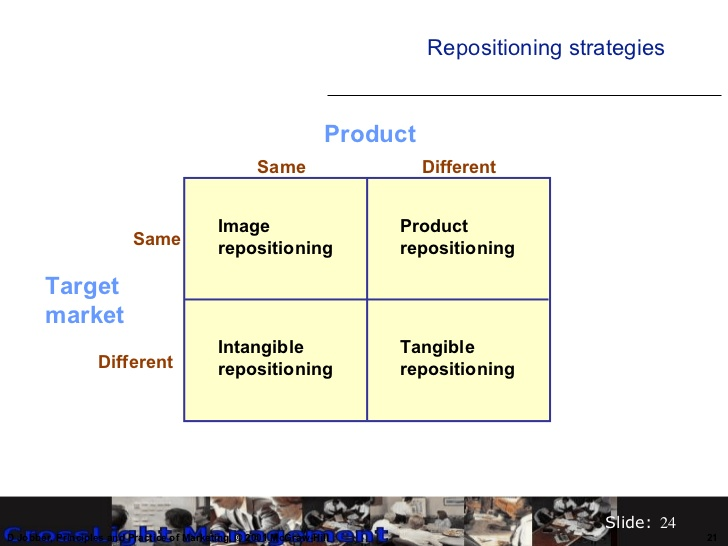
Repositioning
Occasionally, a product will need to be repositioned, this due to changing customer tastes, poor sales performances and negative position in the mind of the consumer. Lucozade was originally targeted at sick children, research found mothers were drinking it so they found an new segment so they were intangibly reposition.
Positioning statement:
‘’ a plausible, memorable image-enhancing written summation of a product’s or brand’s desired stature’’
Clear, short, relevant to the target markets perceptions, intention to develop a distinctive image, platform for its effective communication
The three stages of market segmentation
segmentation, targeting and positioning are fundamental to the marketing strategy.
You have to think how it is currently positioned, is it different from the desired positioning. What is desired position of the product/brand? Successful positioning needs to be clear, credible and consistent. Remember positioning can be conceptualised as; core message, imagery, perceptions, and associations, mapped.
@originalworks
The @OriginalWorks bot has determined this post by @co0pz97 to be original material and upvoted it!
To call @OriginalWorks, simply reply to any post with @originalworks or !originalworks in your message!
To nominate this post for the daily RESTEEM contest, upvote this comment! The user with the most upvotes on their @OriginalWorks comment will win!
For more information, Click Here!
Really good info! What would you say is the hardest part about entrepreneurship?
First. Good post
Loved the post. Looking forward to more content! Hope you have a good time here.
Nice post, I am a photographer, it passes for my blog and sees my content, I hope that it should be of your taste, you have my vote :D greetings
This post recieved an upvote from minnowpond. If you would like to recieve upvotes from minnowpond on all your posts, simply FOLLOW @minnowpond