
In a data set, the difference between the upper and lower quartiles is called the interquartile range.
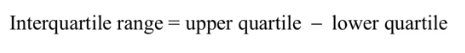
For example:
Find the interquartile range:
2, 4, 5, 4, 8, 7, 8, 7, 3, 1
You start by arranging the data set in order from least to greatest:

Now, in order to find the lower quartile and the upper quartile, we need to cut the data in half, like this:

The half is between the red 4 and the red 5.
We need to find the lower quartile which is the mean of the first half set of data:
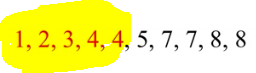
We have 5 numbers in the first half. The middle number is 3 so the lower quartile in this case is 3
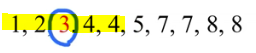
Now we need to find the upper quartile, and as you can see, we have 5 numbers in the second half:
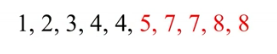
The middle number is 7 so the upper quartile in this case is 7.

Now we have:

Now try:
Find the interquartile range:
26, 36, 34, 25, 40, 41, 27, 32, 35, 38, 42.
Solution:

In Part 6, I will explain how to find the mean of a set of numbers from a table.

Team South Africa banner designed by @bearone
nice informative post
Good set of post my friend, short, precise and and concise, I have a suggestion if You think to publish another post like this, in the try for the readers, let the exercise open, I mean, let people to do the exercise and put their answer in the comments in order to do Your post interactive.