A 16-year-old male presents with lateral knee pain. Structural examination reveals an anterior fibular head somatic dysfunction. Which of the following physical exam findings are consistent with this diagnosis?
- Distal fibula is anterior and resists posterior springing
- Proximal fibular head resists anterior springing
- Talus externally rotated causing the foot to evert and dorsiflex
- Talus externally rotated causing the foot to invert and plantarflex
- Talus internally rotated causing the foot to invert and plantarflex
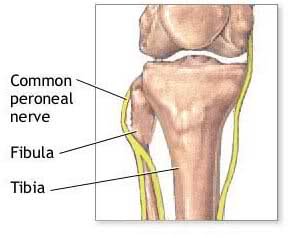
Talus externally rotated causing the foot to EVERT and DORSIFLEX
The physical examination findings of an anterior fibular head somatic dysfunction include:
When the proximal portion of the fibula (fibular head) is "stuck" either in anterior or posterior the distal fibula will be "stuck" in the opposite motion (e.g. an anterior fibular head will have a posterior distal fibula).
When the distal fibula is posterior the talus will prefer external rotation. This external rotation causes the foot to prefer eversion and dorsiflexion.
Conversely, when the distal fibula is anterior, the talus will prefer internal rotation causing the foot to prefer inversion and plantarflexion.
#OMM #ANATOMY #MEDICAL #COMLEX