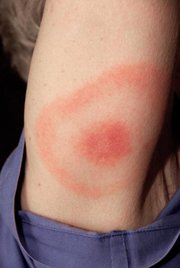
A 29-year-old male presents to the office with the complaint of bilateral knee pain. History reveals the patient is a park ranger at Niagara Falls and noticed a small target-like rash in his armpit a few weeks ago. He states the knee pain has been worsening over the last few weeks and he has also been experiencing more fatigue than usual. Vital signs reveal show a temperature of 37.1ºC (98.8ºF), a blood pressure of 116/74 mmHg, a heart rate of 68/min, and a respiratory rate of 14/min. Physical examination reveals a mild effusion and erythema in both knees. Range of motion is within normal limits and McMurray and Apley tests are negative. There is no ligamentous laxity.
The best initial test is?
- blood culture
- drug screen
- enzyme linked immunosorbent assay
- urinary antigen testing
- western blot
The initial test is found to be positive. The test to confirm the diagnosis is?
- blood culture
- drug screen
- enzyme linked immunosorbent assay
- no further testing is necessary
- western blot
The best initial test is?
enzyme linked immunosorbent assay
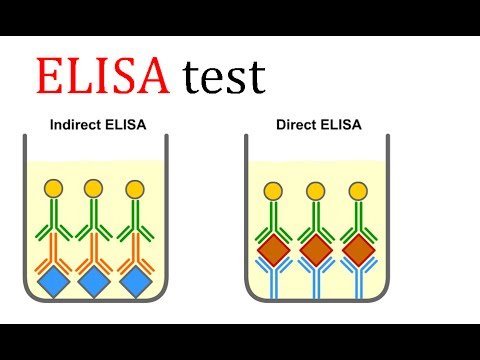
Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is the initial screening test for any patient with a recent history of travel or residency in an area endemic for Lyme disease, has a risk of exposure to ticks, and has symptoms consistent with early disseminated or late Lyme disease.
This patient meets all of these criteria for initiating this screening serologic testing.
Lyme disease, caused by Borrelia burgdorferi, is transmitted by the black-legged ixodes tick and is typically found in northeastern United States.
Early localized disease typically includes a bullseye-like rash called erythema migrans and other nonspecific viral-like syndrome symptoms such as fatigue, joint pain and swelling, and fevers.
The knees are common sites of joint pain in Lyme disease.
EARLY disseminated disease manifests with possible neurologic, cardiac, ocular, or other cutaneous findings.
LATE disease includes arthritis, worsening neurologic findings resembling encephalopathy, and further cutaneous features.
The initial test is found to be positive. The test to confirm the diagnosis is?
Western Blot
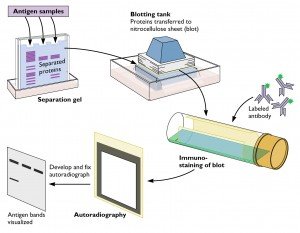
Western blot is the confirmatory test for determining whether a person has Lyme disease.
It provides more information than enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) regarding the type of antigens that are reacting, and has a high specificity.
This test is utilized when the ELISA test is either positive (due to chance of false positive results) or if the test is equivocal.
*If the ELISA test is negative, then a person is considered negative and would not require further testing.