The term "cardiovascular disease" (CVD) is attributable to a variety of heart and blood vessel diseases, including:
Ischemic heart disease (CI) - a condition of blood vessels that irritate the heart
Cerebrovascular disease - diseases of the blood vessels that irrigate the brain.
Peripheral arterial disease - a condition of blood vessels that irritate arms and legs,
Myocardial infarction and cerebral accidents are predominantly caused by atherosclerosis, that is the progressive deposition of fatty material (cholesterol) on the arterial wall of the blood vessels that irritate the heart or brain.
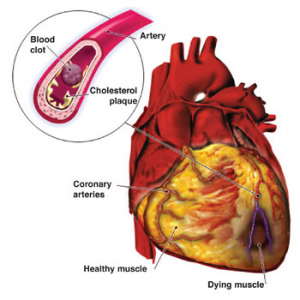
Residual accumulations cause lesions or atheromatosis. These lesions increase and dilate, narrowing the artery and limiting the amount of blood flowing through the vessels. The blood vessel can lose flexibility.
There are no symptoms characteristic of CVD. A myocardial infarction or a stroke demonstrates the importance of awareness of how many individuals are taking risks and taking measures to prevent CVD.
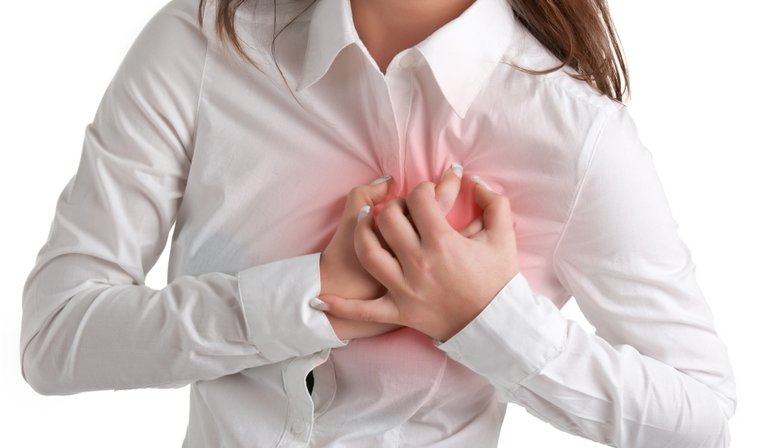

However, some people have certain symptoms.
There are a number of risk factors:
- Hypertension
- Dyslipidemia (abnormal cholesterol levels)
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Lack of physical activity
- Age (> 55 years for men,> 65 years for women)
