The cellular wireless Generation (G) generally refers to a change in the nature of the system, speed, technology and frequency. Each generation have some standards, capacities, techniques and new features which differentiate it from the previous one.
First Generation (1G) :The 1st commercial automated cellular network was launched by NTT in Japan in 1979, followed by the launch of Nordic Mobile Telephone (NMT) system in Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden, in 1981.
Year – 1970 - 1980s
Standard - AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System).
Services – Only Voice
Technology – Analog
Speed - 1kbps to 2.4 kbps
Multiplexing – FDMA
Switching – circuit switching
Core Network – PSTN only
Frequency – 800- 900 MHz
RF Bandwidth - 30 kHz. The band can accommodate 832 duplex channels, among which 21 are reserved for call setup, and the rest for voice communication
Network Components of 1(G)
Poor voice links & no security at all since voice calls were played back in radio towers.
Second Generation (2G):-
GSM technology was the first one to facilitate digital voice & data and international roaming and allowing customer to roam from place to another. GSM maintains end-to-end security by retaining the confidentiality of calls using Signalling and Data Confidentiality and Mobile station Authentication.
Year – 1980 -1990
Technology – Digital
Speed – 14kbps to 64Kbps
Frequency Band – 850 - 1900 MHZ (GSM) and 825 – 849 MHz (CDMA)
Bandwidth/Channel - GSM divides each 200 kHz channel into eight 25 kHz time-slots. CDMA channel is nominally 1.23 MHzwide
Multiplexing /Access Technology – TDMA & CDMA.
Switching – Circuit switching
Standard – GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication), IS-95(CDMA) - used in the Americas and parts of Asia), JDC (Japanese Digital Cellular) (TDMA-based), used in Japan, iDEN (TDMA-based), proprietary network used by Nextel in the United States.
Network Components of 2(G)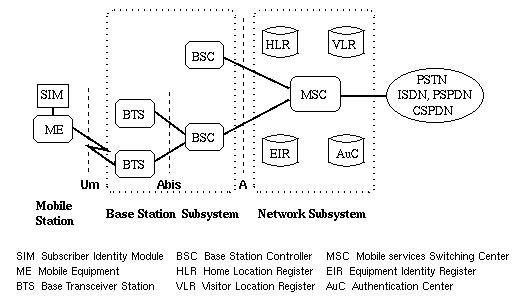 Services – Digital Voice, SMS, International Roaming , Conferencing, Call Waiting, Call Hold, Call Forwarding, Call Barring, Caller Number Identification, Closed User Groups (CUGs) , USSD Services, Authentication , billing based on the services provided to their customers e.g. charges based on local calls, long distance calls, discounted calls, real time billing.
Services – Digital Voice, SMS, International Roaming , Conferencing, Call Waiting, Call Hold, Call Forwarding, Call Barring, Caller Number Identification, Closed User Groups (CUGs) , USSD Services, Authentication , billing based on the services provided to their customers e.g. charges based on local calls, long distance calls, discounted calls, real time billing.
Temporary identification numbers are assigned to the subscriber’s number to maintain the privacy of the user. The privacy of the communication is maintained by applying encryption algorithms and frequency hopping that can be enabled using digital systems and signalling
2.5 Generation: Introduction of packet network to provide high speed data transfer & internet.
Year – 2000- 2003
Standards - General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) & EDGE (Enhanced Data rates in GSM)
Frequency: 850 -1900 MHz
Speed – 115kpbs (GPRS)/384kbps(EDGE)
Switching – packet switching for data transfer
Multiplexing – Gaussian minimum shift keying-GMSK(GPRS) & EDGE (8-PSK)
Services – push to talk, multimedia, web based info entertainment, support WAP, MMS, SMS mobile games, and search and directory, email access, video conferencing. Network Components of 2.5(G)
GPRS provides packet switching protocols, short setup time for ISP connections and the possibility to charge the subscriber according to the amount of data sent rather than connection time. GPRS supports flexible data transmission rates and provides continuous connection with the network.
GPRS is a packet-switched service that takes advantage of available GSM time slots for data communications , supports both X.25 and TCP/IP packet protocols, with quality of service (QoS) mechanisms and is considered most useful for bursty data applications such as mobile Internet browsing, e-mail, and various push technologies
EDGE provides nearly three times faster speeds than the outdated GPRS system. To support higher data rate EDGE adopts higher modulation schemes such as 8-PSK.
EDGE can retransmit a packet with more robust coding scheme. In EDGE re-segmentation is possible while in GPRS re-segmentation is not possible. In EDGE packets are addressed up to 2048 and window size to 1024 while GPRS packets were numbered from 1 to 128 and addressing window size was 64.
Third Generation (3G)
The goal of 3G systems was to offer increased data rates. International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has defined the demand for 3G in the International Mobile Telecommunication (IMT)-2000 standards to facilitate growth, greater voice and data capacity, support diverse applications, and high data transmission at low-cost. The data are sent through the technology called Packet Switching .Voice calls are interpreted through Circuit Switching.
Year - 2000
Standards -
UMTS (WCDMA)– Based on GSM (Global Systems for Mobile) 2G system infrastructure,standardized by 3GPP.
CDMA 2000 – Based on CDMA (IS-95 ) 2G standard, standardized by 3GPP2.
TD-SCDMA radio interface was commercialized in 2009 and is only offered in China
Speed : 384KBPS to 2MBPS
Frequency : about 8 to 2.5GHz
Bandwidth – 5 to 20 MHz
Multiplexing/Access technologies
Radio interface is called WCDMA (Wideband Code Division Multiple Access)
HSPA is an upgrades to W-CDMA offers speeds of 14.4 Mbit/s down and 5.76 Mbit/s up.
HSPA+ can provide theoretical peak data rates up to 168 Mbit/s in the downlink and 22 Mbit/s in the uplink, using air interface improvements & multi-carrier HSPA and MIMO.
Cdma2000 1X: It can support both voice and data services. The max. Data rate can reach 153 kbps, belonging to 3G mobile communications.
Services –
Wireless voice telephony, high speed internet access, fixed wireless Internet access, video calls, chatting & conferencing, mobile TV, Video on demand, Location-based services, Telemedicine, Web browsing, e-mail, paging, fax and navigational maps, Mobile gaming, mobile music, multimedia services like digital photos and movies. Localized services for accessing traffic and weather updates, Mobile office services, like virtual banking. Greater security features than 2G like Network Access & Domain Security, User Domain and Application Security.
Network Components of 3(G)
logo
Editor Choice Blog
All Blog
Most Popular Blog
Evolution of Mobile Communication from 1(G) to 4G, 5G, 6G, 7G …
The cellular wireless Generation (G) generally refers to a change in the nature of the system, speed, technology and frequency. Each generation have some standards, capacities, techniques and new features which differentiate it from the previous one.
First Generation (1G) :The 1st commercial automated cellular network was launched by NTT in Japan in 1979, followed by the launch of Nordic Mobile Telephone (NMT) system in Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden, in 1981.
Year – 1970 - 1980s
Standard - AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System).
Services – Only Voice
Technology – Analog
Speed - 1kbps to 2.4 kbps
Multiplexing – FDMA
Switching – circuit switching
Core Network – PSTN only
Frequency – 800- 900 MHz
RF Bandwidth - 30 kHz. The band can accommodate 832 duplex channels, among which 21 are reserved for call setup, and the rest for voice communication
Network Components of 1(G)
Poor voice links & no security at all since voice calls were played back in radio towers.
Second Generation (2G):-
GSM technology was the first one to facilitate digital voice & data and international roaming and allowing customer to roam from place to another. GSM maintains end-to-end security by retaining the confidentiality of calls using Signalling and Data Confidentiality and Mobile station Authentication.
Year – 1980 -1990
Technology – Digital
Speed – 14kbps to 64Kbps
Frequency Band – 850 - 1900 MHZ (GSM) and 825 – 849 MHz (CDMA)
Bandwidth/Channel - GSM divides each 200 kHz channel into eight 25 kHz time-slots. CDMA channel is nominally 1.23 MHzwide
Multiplexing /Access Technology – TDMA & CDMA.
Switching – Circuit switching
Standard – GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication), IS-95(CDMA) - used in the Americas and parts of Asia), JDC (Japanese Digital Cellular) (TDMA-based), used in Japan, iDEN (TDMA-based), proprietary network used by Nextel in the United States.
Network Components of 2(G)Services – Digital Voice, SMS, International Roaming , Conferencing, Call Waiting, Call Hold, Call Forwarding, Call Barring, Caller Number Identification, Closed User Groups (CUGs) , USSD Services, Authentication , billing based on the services provided to their customers e.g. charges based on local calls, long distance calls, discounted calls, real time billing.
Temporary identification numbers are assigned to the subscriber’s number to maintain the privacy of the user. The privacy of the communication is maintained by applying encryption algorithms and frequency hopping that can be enabled using digital systems and signalling
2.5 Generation: Introduction of packet network to provide high speed data transfer & internet.
Year – 2000- 2003
Standards - General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) & EDGE (Enhanced Data rates in GSM)
Frequency: 850 -1900 MHz
Speed – 115kpbs (GPRS)/384kbps(EDGE)
Switching – packet switching for data transfer
Multiplexing – Gaussian minimum shift keying-GMSK(GPRS) & EDGE (8-PSK)
Services – push to talk, multimedia, web based info entertainment, support WAP, MMS, SMS mobile games, and search and directory, email access, video conferencing. Network Components of 2.5(G)
GPRS provides packet switching protocols, short setup time for ISP connections and the possibility to charge the subscriber according to the amount of data sent rather than connection time. GPRS supports flexible data transmission rates and provides continuous connection with the network.
GPRS is a packet-switched service that takes advantage of available GSM time slots for data communications , supports both X.25 and TCP/IP packet protocols, with quality of service (QoS) mechanisms and is considered most useful for bursty data applications such as mobile Internet browsing, e-mail, and various push technologies
EDGE provides nearly three times faster speeds than the outdated GPRS system. To support higher data rate EDGE adopts higher modulation schemes such as 8-PSK.
EDGE can retransmit a packet with more robust coding scheme. In EDGE re-segmentation is possible while in GPRS re-segmentation is not possible. In EDGE packets are addressed up to 2048 and window size to 1024 while GPRS packets were numbered from 1 to 128 and addressing window size was 64.
Third Generation (3G)
The goal of 3G systems was to offer increased data rates. International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has defined the demand for 3G in the International Mobile Telecommunication (IMT)-2000 standards to facilitate growth, greater voice and data capacity, support diverse applications, and high data transmission at low-cost. The data are sent through the technology called Packet Switching .Voice calls are interpreted through Circuit Switching.
Year - 2000
Standards -
UMTS (WCDMA)– Based on GSM (Global Systems for Mobile) 2G system infrastructure,standardized by 3GPP.
CDMA 2000 – Based on CDMA (IS-95 ) 2G standard, standardized by 3GPP2.
TD-SCDMA radio interface was commercialized in 2009 and is only offered in China
Speed : 384KBPS to 2MBPS
Frequency : about 8 to 2.5GHz
Bandwidth – 5 to 20 MHz
Multiplexing/Access technologies
Radio interface is called WCDMA (Wideband Code Division Multiple Access)
HSPA is an upgrades to W-CDMA offers speeds of 14.4 Mbit/s down and 5.76 Mbit/s up.
HSPA+ can provide theoretical peak data rates up to 168 Mbit/s in the downlink and 22 Mbit/s in the uplink, using air interface improvements & multi-carrier HSPA and MIMO.
Cdma2000 1X: It can support both voice and data services. The max. Data rate can reach 153 kbps, belonging to 3G mobile communications.
Services –
Wireless voice telephony, high speed internet access, fixed wireless Internet access, video calls, chatting & conferencing, mobile TV, Video on demand, Location-based services, Telemedicine, Web browsing, e-mail, paging, fax and navigational maps, Mobile gaming, mobile music, multimedia services like digital photos and movies. Localized services for accessing traffic and weather updates, Mobile office services, like virtual banking. Greater security features than 2G like Network Access & Domain Security, User Domain and Application Security.
Network Components of 3(G)
Fourth Generation (4G)
Initiation year-2010.4G - In 2008, ITU-R specified the IMT-Advanced (International Mobile Telecommunications Advanced) requirements for 4G systems.
The fourth Generation mobile system is all IP based network system. The main goal of 4G technology is to provide high speed, high quality, high capacity, security and low cost services for voice and data services, multimedia and internet over IP.
To use 4G mobile network, multimode user terminals should be able to select the target wireless system. To provide wireless services anytime and anywhere, terminal mobility is a key factor in 4G.
4G introduced new physical radio interface known as Evolved UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) and new packet –switching based core network called as Evolved Packet Core (EPC). IP-based network architecture, allows for seamless handovers for voice and data to GSM, UMTS or CDMA2000 technology.
Standards - Long-Term Evolution Time-Division Duplex (LTE-TDD and LTE-FDD) Mobile WiMAX standard (802.16m standardized by the IEEE
Speed - 100Mbps while moving and 1Gbps while stationary ,with the help of following features
IP telephony
OFDMA multi-carrier transmission and frequency-domain equalization (FDE) schemes
Smart antenna arrays for multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) communications.
New frequency bands, wider channel frequency bandwidth
Multiplexing/Access Technologies - OFDM, MC-CDMA, LAS-CDMA and Network-LMDS
Bandwidth - 5–20 MHz, optionally up to 40 MHz
Frequency Bands :- LTE standard covers a range of many different bands.
In North America, 700, 750, 800, 850, 1900, 1700/2100 (AWS), 2300 (WCS) 2500 and 2600 MHz are used (bands 2, 4, 5, 7, 12, 13, 17, 25, 26, 30, 41); 2500 MHz in South America;
700, 800, 900, 1800, 2600 MHz in Europe (bands 3, 7, 20); 800, 1800 and 2600 MHz in Asia (bands 1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 11, 13, 40)
1800 MHz and 2300 MHz in Australia & New Zealand (bands 3, 40).
Services - Mobile web access, IP telephony, gaming services, high-definition mobile TV, video conferencing, 3D television, and cloud computing, manage multi broadcast streams and handle quick-moving mobile phones , Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB), Dynamic information access, wearable devices. smooth handovers across heterogeneous networks and automatic roaming between different wireless networks
4G implementation variants :
The LTE standard supports only Packet Switching & is all IP Network. Voice calls in GSM, UMTS and CDMA2000 are circuit swiyched, so with the adoption of LTE, carriers will have to re-engineer their voice call network. However since it requires lot of infrastructure changes, three different approaches are
Voice over LTE (VoLTE) : VoLTE is based on the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) network i.e. voice service (control and media planes) being delivered as data flows within the LTE data bearer. VoLTE has up to three times more voice and data capacity than 3G UMTS. Furthermore, it frees up bandwidth because VoLTE’s packets headers are smaller than those of unoptimized VoIP/LTE.
Circuit-switched fallback (CSFB : In this approach, LTE just provides data services, and when a voice call is to be initiated or received, it will fall back to the circuit-switched domain. When using this solution, operators just need to upgrade the MSC instead of deploying the IMS, and therefore, can provide services quickly. However, the disadvantage is longer call setup delay.
Simultaneous voice and LTE (SVLTE) : In this approach, the handset works simultaneously in the LTE and circuit switched modes, with the LTE mode providing data services and the circuit switched mode providing the voice service. This is a solution solely based on the handset, which does not have special requirements on the network and does not require the deployment of IMS either. The disadvantage of this solution is that the phone can become expensive with high power consumption.
One additional approach which is not initiated by operators is the usage of over-the-top content (OTT) services, using applications like Skype and Google Talk to provide LTE voice services
Network Component
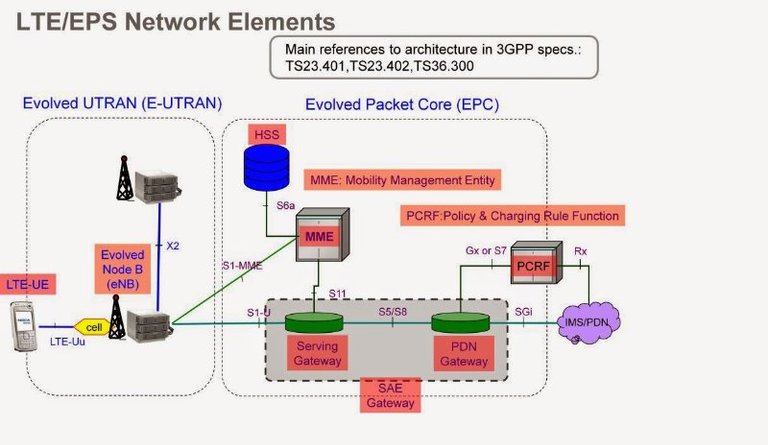
Fifth Generation (5G)
Initiation year-2015
It will make Unified global standard. The Physical and Data Link layer defines the 5G wireless technology indicating it as an Open Wireless Architecture(OWA).The 5G technology also maintain virtual multi-wireless network.
To perform this the Network layer is sub-divided into two layers; upper network layer for mobile terminal and lower network layer for interface. Here all the routing will be based on IP addresses which would be different in each IP network worldwide.
In 5G technology the higher bit rate loss is overcome by using Open Transport Protocol (OTP).The OTP is supported by Transport and Session layer. The application layer is for quality of service management over various types of networks. 5G brings forward a real wireless world-Wireless World Wide Web (WWWW)
Speed - 1 to 10 Gbps.
Bandwidth - 1,000x bandwidth per unit area.
Frequency - 3 to 300 GHz
Multiplexing/Access Technologies - CDMA and BDMA
Standard – IP broadband LAN/W AN/PAN & WWWW
Features :Real time performance – Fast response, Low Jitter, latency & delay
Very High Speed Broadband – Gigabit data rates, high quality coverage, Multi spectrum
Virtualized Infrastructure – Software defined network, scalable and low cost system.
Support IoT & M2M - 100 times more connected devices, Deep Indoor Coverage & Signalling efficiency
About 90% reduction in network energy usage.
Its radio technology will facilitate different version of radio technologies to share the same spectrum efficiently.
Services : - Some of the significant applications are –
Connected people & devices anywhere anytime. Its application will make world real Wi Fi zone.
Mobile IP address will be assigned as per the connected network and geographical position.
Radio signal at higher altitude as well.
Parallel multiple services, such as you can know weather and location while talking
You can control your PCs by handsets.Education will become easier. A student sitting in any part of world can attend the class.
Remote diagnostics is a great feature of 5G. -A doctor can treat the patient located in remote part of the world.
Monitoring will be easier − A governmental organization and investigating offers can monitor any part of the world. Possible to reduce the crime rate.
Visualizing universe, galaxies, and planets will be possible.
Possible, natural disaster including tsunami, earthquake etc. can be detected faster.Architecture
Sixth Generation (6G)
6G is proposed to integrate 5G with satellite networks for global coverage.
It is considered to be a cheap and Fast Internet Technology to provide unbelievably high data rates or very fast Internet speed access on air through wireless and mobile devices possibly up to 11 Gbps, while travelling or in a remote location.
The satellite communication network may consist of telecommunication satellite networks, earth imaging satellite networks and navigation satellite networks. The goal of 6G is to integrate these kinds of satellite networks to provide network position identifier, multimedia and internet connectivity, and weather information services to the mobile users.
Specially designed Nano Antennas will be implemented at different geographical locations or positions along roadsides, villages, malls, airports, hospitals etc to broadcast such high speed electromagnetic signals.
The globe will be decorated by fly sensors with the help of 6G technology. These fly sensors will provide information to their remote observer stations; further these stations will check any activity upon a special area such as the activity of terrorists, intruders etc.
The point to point wireless communication networks that transmit super- fast broadband signals through the air will be assisted by high speed optical fibers lines to broadcast much secured information from transmitters to destinations.
Features/Advantages of 6G Technology:
Ultra fast access of Internet.
Data rates will be up to 10-11 Gbps.
Home automation and other related applications.
Smart Homes, Cities and Villages.
May be used in the production of Energy from galactic world.
Space technology, Defense applications will be modified with 6G networks.
Home based ATM systems.
Satellite to Satellite Communication for the development of mankind.
Natural Calamities will be controlled with 6G networks.
Sea to Space Communication.
Mind to Mind Communication may be possible
Standards :- The Global Position System(GPS) by USA, the Galileo by Europe, the COMPASS by China and the GLONASS by Russia. If 6G integrates with 5G with these satellite networks, it would have four different standards. So handoff and roaming will be can be a big issue in 6G
7G deals with space roaming.
The 7G of mobile wireless networks which aims to acquire space roaming. The world is trying to become completely wireless, demanding uninterrupted access to information anytime and anywhere with better quality, high speed, increased bandwidth and reduction in cost.
Good best knowlwdgable
Thank