
MONET is an open network architecture for mobile blockchains on demand. A blockchain on demand means that participants of a certain activity can form a temporary network for the duration of their interaction without a need of any centralized third party.
About
The MONET.network — an open network architecture for mobile ad hoc blockchains — enables groups of individuals involved in common tasks to form temporary connections, or networks, by using their mobile devices to coordinate themselves. This all takes place devoid of the need to rely upon third parties to handle their data. By creating an infrastructure for distributed mobile p2p applications, Monet is attempting to bolster the sharing economy by deploying blockchains to mobile.
Use Cases
There are many different ways that mobile ad hoc blockchains can be applied to real life user interactions: delivery, housing, office space, payments and loans, professional and personal services, pre-owned goods and custom products, networking, and learning, etc.
- Transportation: Monet could enable a fully decentralized Uber that would cut out the expensive service provider intermediary via ad-hoc blockchains.
- Finance: Monet could allow for the creation of sharded cryptocurrencies, where the shards are mobile. Groups of individuals could withdraw funds from the main ledger, deposit into a temporary ad hoc blockchain, transact exclusively among themselves and then return to the main ledger.
- Gaming: Monet could provide a free framework for game developers to connect with a network of users already equipped for p2p coordination, eliminating the need for a centralized server to coordinate multiplayer game participants.
Technological Strength of Monet
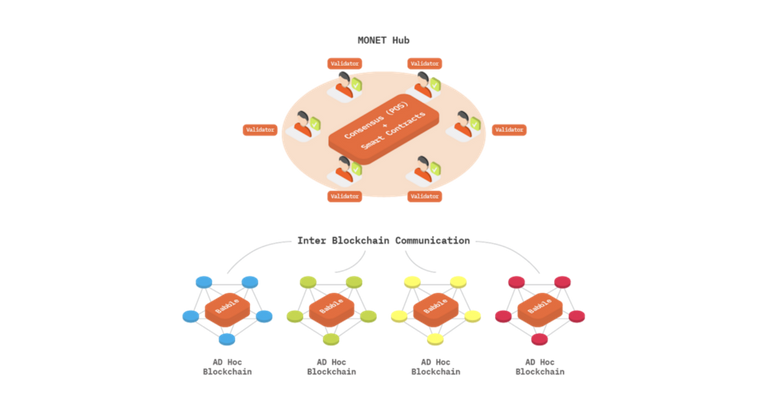
- Babble This powerful consensus mechanism takes advantage of an asynchronous DAG protocol, combined with the benefits of a blockchain’s linear data structure in order to achieve: low latency, high throughput, fault-tolerance, and pluggability. Babble-powered blockchains can seamlessly interface with any application and communicate with other blockchains via Inter-Blockchain Communication protocols.
- Babble SDKs This is what makes it easy for Babble to broadcast messages directly to other network participants, and come to a consensus on an order of events. This function allows the MONET.network to replace centralized servers.
- Monet Hub The first of its kind and a unique type of blockchain in the Monet ecosystem. It is an always-on network that enables inter-blockchain communication.
- Babble Core The core of Babble is based on an asynchronous, Full Information Protocol, which like all FIPs involves three operations: 1) Gossiping and constructing the Communication Graph, 2) Determining which events will eventually be common knowledge, 3) Sorting events with a deterministic function.
- EVM-Babble A wrapper around the Ethereum Virtual Machine that is specifically designed to plug into Babble.
The key components of MONET architecture are:
- Multiple ephemeral blockchains dynamically formed by users with their mobile devices;
- Inter-Blockchain Communication, enabling these blockchains to speak to one another; and
- MONET Hub — an always-on network that provides optional infrastructure services to the first applications and ad hoc blockchains.
Weaknesses and Threats
Since Monet Network is using an equivalent of the Ethereum Virtual Machine the question remains how much proprietary software Monet will contribute to its project. It is unclear which milestones Monet has achieved so far apart from the release of the modular Babble blockchain. The roadmap is vague and no private investors have been released so far.
Monet Network is not the only attempt to serve marketplaces with blockchain technology. Other solutions, such as Origin, which is built on Ethereum, are focussed on the same market niche and count with more developers and external funding.
The advantages of peer to peer network are as follows:
- The main advantage of peer to peer network is that it is easier to set up
- In peer-to-peer networks, all nodes act as a server as well as a client, therefore, no need for a dedicated server.
- The peer to peer network is less expensive.
- Peer to peer network is easier to set up and use this means that you can spend less time in the configuration and implementation of peer to peer network.
- It is not required for the peer to peer network to use the dedicated server computer. Any computer on the network can function as both a network server and a user workstation.
The disadvantages of peer to peer network
- A computer can be accessed anytime.
- Network security has to be applied to each computer separately.
- Backup has to be performed on each computer separately.
- No centralized server is available to manage and control the access of data.
- Users have to use separate passwords on each computer in the network.
- As with most network systems, unsecure and unsigned codes may allow remote access to files on a victim’s computer or even compromise the entire network
Team & Advisors
The Monet core team consists of three members. On top, Monet counts with four advisors.
#Martin Arrives is the CEO and co-founder of Mosaic Networks. He counts with five years of experience in software development and holds a Master Degree in Mathematics from the University of Chicago.
#Giacomo Puri Purini is the CFO and co-founder of Mosaic Networks. He holds a Master Degree in Mathematics from Columbia University.
#Kevin Jones is a software developer at Mosaic Networks with eight years of previous experience in software development.
Among the advisors of Monet is Mark Stuart Day, a researcher and blockchain author with several patents, Mauro Martini, a professor in Boston, Ronan Lynch, an early blockchain pioneer, and Abdi Hersi, who has a background in asset management and private equity.


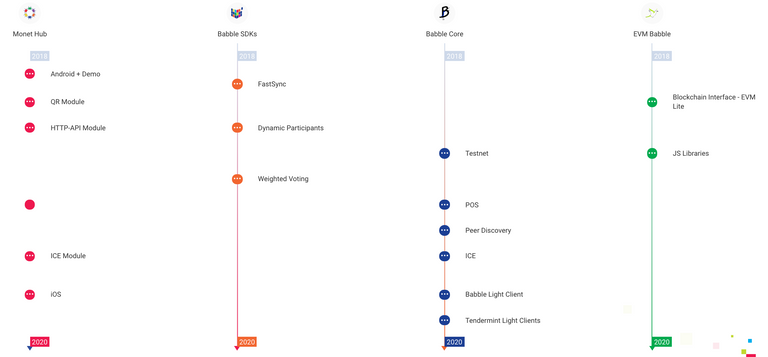
Roadmap of Monet
Useful Links
- Monet Network Website: https://monet.network/
- Monet Network Whitepaper: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1PcI69i_oJpWdsIsOciLliYEsFv9hHCVr/view
- Monet Network Github: https://github.com/mosaicnetworks
- Monet Network Telegram: https://t.me/MonetNetwork
- Monet Network Twitter: https://twitter.com/MonetNetwork
- Monet Network Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/Monet_Network/
- Monet Network Medium: https://medium.com/@monet.network
- Monet Network Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/MonetNetwork
- Monet Network Bounty: https://medium.com/monet-network/announcing-monet-bounty-campaign-2de1663080ee