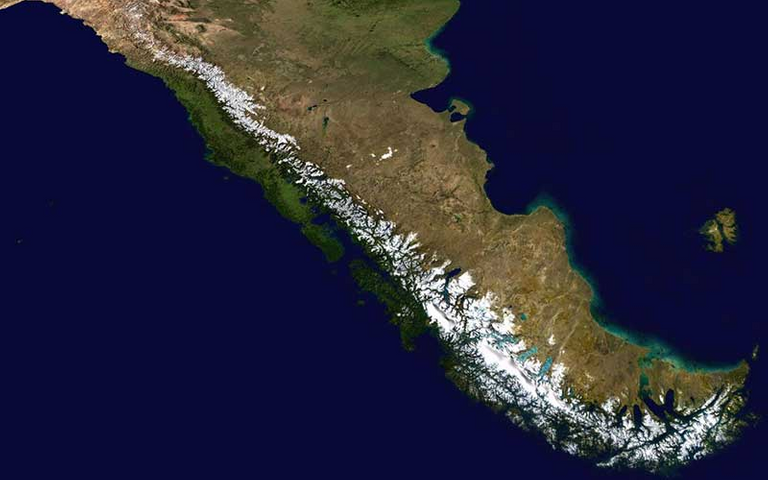
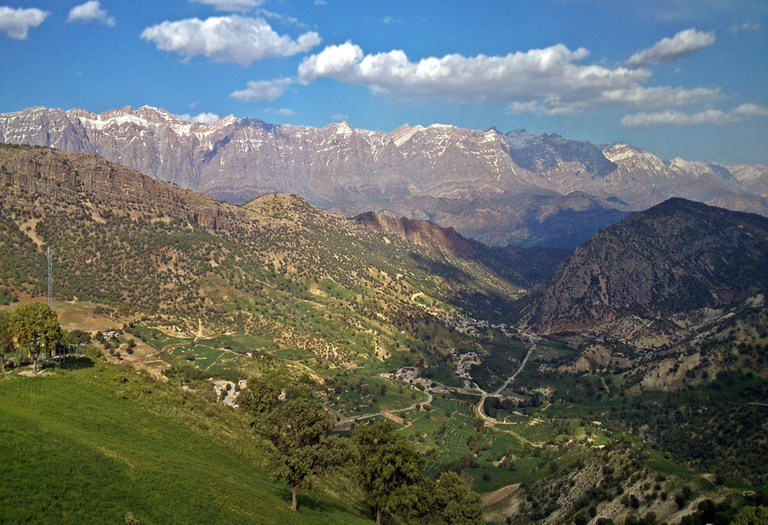
The Andes harbor the highest volcanoes on the planet. At the southern end, the Andes sink into the Atlantic Ocean east of the Island of the States.
In its southern part, it serves as a natural border between Argentina and Chile, an area in which the highest mountains of the continent are found. In the central zone, the Andes widen, giving rise to a high plateau known as the altiplano, shared by Argentina, Bolivia, Chile and Peru. The mountain range becomes narrow again in the north of Peru and in Ecuador, it widens again in Colombia where it is also divided into three branches, one of which continues in the northwest of Venezuela.
It was formed at the end of the Mesozoic era, at the end of the late Cretaceous, by the subduction movement of the Nazca plate beneath the South American Plate. Seismic movements and subsequent volcanic activity have been more important in the configuration of relief than external erosive agents. In the current morphology there are high mountain ranges, together with extensive highlands and deep longitudinal valleys parallel to the great mountainous axes. Transversal valleys are scarce, except in the Argentine-Chilean Andes.
Many of the world's major deposits of metallic minerals are associated with edges of converging plates, such as the Andes or the Rocky Mountains.
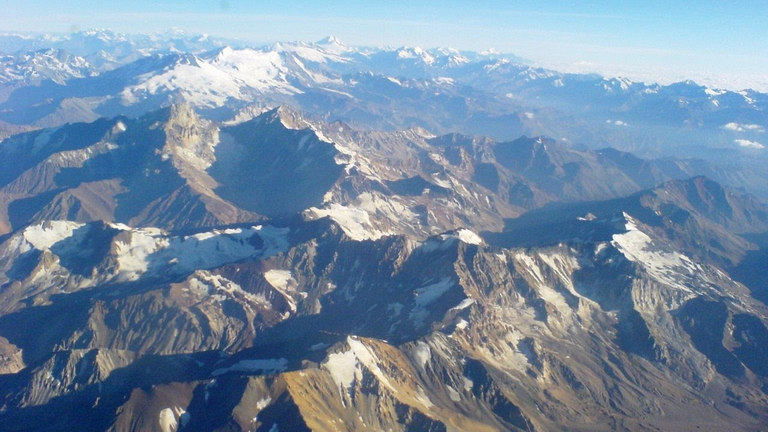

Characteristics
The Andes mountain range has a length of approximately 7,000 kilometers, an approximate width of 200 to 700 kilometers and a maximum elevation of 6,961-6,962 meters, or the maximum elevation of the Aconcagua. It is located in the western region of South America, from the Caribbean coast to the southern tip of the continent, through 7 countries: Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Bolivia, Peru, Chile and Argentina. The mountain range is constituted by several mountains and volcanoes, among which are the Aconcagua, the Nevado Ojos del Salado, the Huascarán, the Chimborazo, the Nevado del Ruiz, the Galeras and the Bonete.
Its highest peak is Aconcagua, and the highest peaks are found in Peru, Argentina and Ecuador, while the lowest are at the extreme north and south. Some of the highest volcanoes in the world are found in the mountain range, and it is estimated that it contains around 183 active volcanoes. There are also some thermal springs and mineral deposits.
The entire mountain range is divided into 3 sections: the northern Andes, in Venezuela and Colombia; the central Andes, in Peru, Bolivia and Ecuador; and the southern Andes, in Chile and Argentina; they serve as a natural border between these two last ones, as well as between some regions between countries. The mountains are, for the most part, within the tropics, but the high peaks tend to be covered with snow and near the equator some harbor glaciers. However, a large part of the Andean territory has arid conditions, especially in the east. In the west, rainfall is more abundant.
Despite the rugged terrain of a large part of its extension, in the Andean region several plateaus are found at considerable altitude; There are some of the most important South American cities, such as Quito, La Paz and Bogotá. The Andean Altiplano is the second largest plateau in the world, and emerges between Bolivia and Peru, at an elevation of more than 3,600 meters above sea level.
Training
The Andes are located on a still tectonically active region, where earthquakes and volcanic eruptions are not rare events. These mountains are considered to be geologically young; it is presumed that its formation had its genesis after the fragmentation of Pangea, and that during the time of the dinosaurs the region was occupied by a large lake or an inland sea.
The tectonic plates continued to move during the course of the years of the Jurassic Period until, in the Cenozoic era, the Nazca plate and the Antarctic plate moved under the South American plate. A subduction zone was created, and plates began to collide, which exerted a force that compressed the crust. As a result, intense earthquakes took place, but also the crust began to push upwards, to fold and to form ridges that eventually became mountains. The mountains rose during the last 100 million years, mainly between the Cretaceous and the Tertiary.
As the Andes area is still very active, there are still transcendental movements under the ground. It is estimated that the central Andes have doubled in height over 10 million years.

Flora and fauna
Because of its extension, in the Andes there is a variety of climates and environments, from the aridity of the Atacama desert to the iciness of the peaks covered with ice and snow, as well as many salt pans and bodies of water, including the Titicaca, the most navigable lake. high of the world.
The climate, flora and fauna of the Andes are determined by altitude. Many of the snow-covered peaks rise to more than 6,000 meters, where few species of living things can live, but thousands coexist at lower elevations. In the north of Chile is the Atacama desert, where the diversity of species is lower due to the dry conditions of the environment and the scarcity of rainfall.
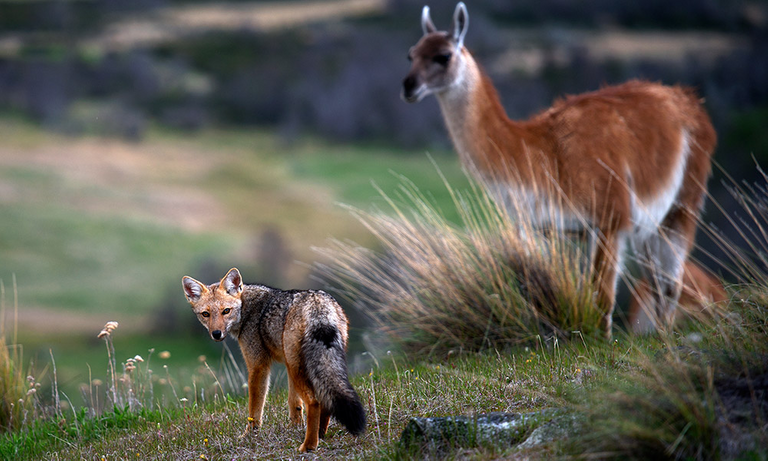
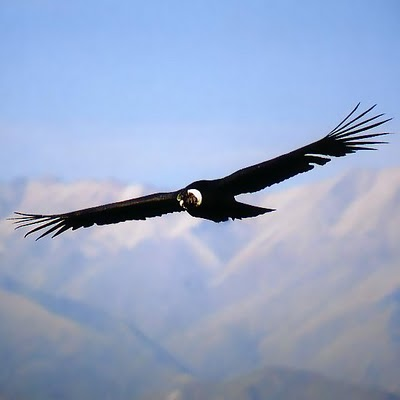
The flora and fauna depend on the region given the great extent of the mountain range, but we can not fail to mention the cauquén (Chloephaga melanoptera), giant frogs from Lake Titicaca (Telmatobius culeus), cockroaches from the Andean rocks (Rupicola peruviana), llamas , alpacas, vicuñas, guanacos, pumas (Puma concolor), culpeo foxes (Lycalopex culpaeus), Andean condors (Vultur gryphus), flamingos, spectacled bears (Tremarctos ornatus), hummingbirds and opossums.
They emphasize dry forests and tropical jungles. In part of the Altiplano the vegetation is rather scarce, with grasses and cushion plants, where the yareta (Azorella compacta) and the ichu (Stipa ichu) stand out.




Congratulations @josebompart! You received a personal award!
Click here to view your Board
Congratulations @josebompart! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!