.jpeg)
Internal combustion engines that power majority of our cars today have not changed radically since their invention, but their design has been continuously refined gradually over the years. Technologies like variable valve timing, cylinder deactivation, direct fuel injection etc. make the combustion process efficient and hence the car too, they also simultaneously make them pollute less.
Electric cars and hybrids are available out there, they fail to register same level of sales, primarily because they are more expensive and somewhat impractical. Other reasons being, driving pleasure and noise (music rather) that’s more closely associated with larger IC engines.
.jpeg)
Due to the CAFE (Corporate Average Fuel Economy) norms, there is tremendous pressure on the industry to innovate and ensure that the mileage of cars on Indian roads improves by 10 percent by 2021 and the second phase would require them to be 30 percent more efficient by 2022.
The top five technologies that are used in mainstream in future cars.
Camless engines
DI Turbo Ethanol engine
KERS
HCCI
OPOC two stroke
- Camless engines
Variable valve timing and variable valve lift mechanisms that current engines employ, are even though quite flexible, they do not offer infinite flexibility. With the camless engine technology, the engine would get the flexibility to independently operate the individual valves inside any cylinder during the combustion cycle, therefore offering infinite variable valve timing. Engines would also be able to change the valve lift without the need for varying the mechanical architecture of the engine. Such engines would also be better suited for performance modification since you would be able to squeeze out better performance out of the same engines by simply remapping it without making any extensive mechanical changes.
- DI Turbo Ethanol engine
Even though higher compression ratios can increase the fuel efficiency significantly, it cannot be used in case of petrol engines simply because it would lead to knocking. The mixed fuel blends that current engines use has some amount of Ethanol (having higher octane rating than petrol) and this helps. However, a normal engine that runs on a blend cannot utilize higher compression ratios without the aid of Ethanol boost. A DI Turbo engine would be able to use higher compression ratios and it would make them as efficient as the diesel engines. These engines would require a separate tank for E85 or would be able to use ethanol based windshield washer fluid that is already present in the car.
- KERS
KERS (Kinetic Energy Recovery System) was used first time in the 2009 F1 season. The technology was put in place to recover the kinetic energy under braking that would have otherwise being lost as heat. The same recovered energy could then be utilised in the form of boost by the transmission system to power the car. In one of the most highly developed form, the flywheel that is used for storing energy can spin upto 60,000rpm and can take upto 30 minutes to stop. The same flywheel is then used to power electric motors that worked as generators while braking. The very complex but equally clever design is now being exploited by many manufacturers like Volvo and Jaguar to improve the fuel efficiency of their cars.
- HCCI
The HCCI engine operates on the combination of CI (Compression Ignition) and SI (Spark Ignition) engine principles. HCCI utilises heat generated from high compression to ignite the fuel, the fuel-air mixture is pre-injected before the power stroke like in case of SI. The engine neither has injector nor a spark plug and the homogeneous mixture is ignited from pressure alone. The engine is more efficient and utilises principle of a diesel engine at modest loads. At the time when high power is required, it operates as a petrol engine and the combustion is initiated by a spark plug.
- OPOC two stroke
OPOC stands for “opposed piston opposed cylinder” and is one of the most radical and the most promising engine design on this list. The engine has geometry like that of the flat engine utilised by Porsche or Subaru. However, in this case there are additional set of pistons that oppose the conventional pistons within the comparatively longer cylinders. A single combustion chamber is used for pushing two pistons. The engines do not have a conventional valvetrain and uses ports for breathing and thereby reducing pumping losses and cost of production. Another great advantage of this engine is that it’s fully balanced and offers about 15% more fuel efficiency than conventional engines.
Good post.
Do you know what manufactures are looking into KERS?
The technology is extremely expensive at this time and may not make it to every car. But it surely helps the car manufacturers increase the fuel efficiency goals significantly required as per FAME, we believe that more expensive cars in future would be equipped with this technology.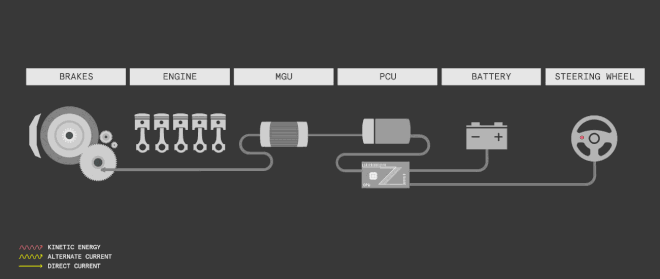
Congratulations @sahilbunts98! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!