
Company experts presented PhishLabs free tool to decrypt the files affected by the attack malware Alma. Hack malware researchers were able, having carried out man-in-the-middle attack , which helped to understand how the "official" decryptor intruders.
New extortionist Alma, appeared this month , found Proofpoint experts and studied BleepingComputer experts. Although the researchers came to the conclusion that the malware is still in its development stage, at the same time it became clear that even at this stage, Alma already poses a serious threat. At the time of studying the encryptor already massively distributed through an exploit RIG whale.
Infiltrating the system, of Alma generates a random five-digit extension for files and starts encryption using AES- 128. Also, each victim is given a unique eight-digit ID, which is created based on the serial number of the disk C:\ and the MAC-address of the first network interface in the list.
Malware attacks a wide range of files, but does not touch the directory name that is present : $ recycle.bin, system volume information, program files, programdata, program files (x86), windows, internet explorer, Microsoft, Mozilla, chrome, appdata, local settings, recycler, msocache and Unlock_files_.
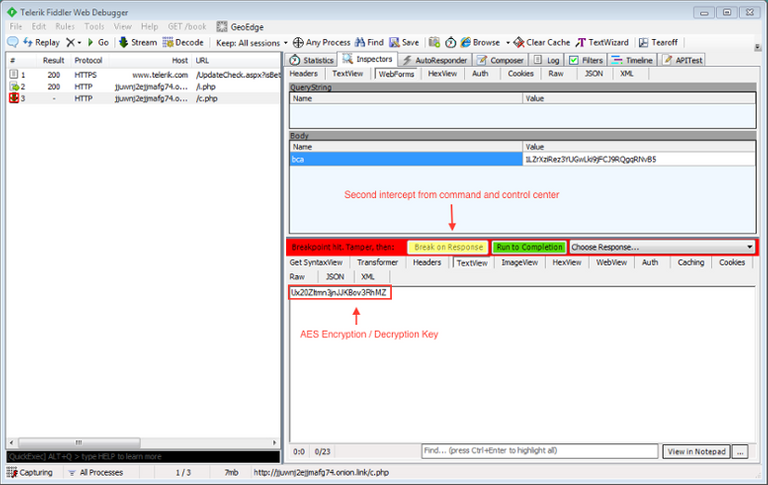
Since the malware developers protect their "product" , the experts had to break their heads over which side is better to approach the Alma. Fortunately, experts PhishLabs noticed a weak point in the malware. During file encryption Alma breaks down the process into two phases. First, start the encryption process and then extortionist associated with the management server and forwards via HTTP AES key in plaintext. Since AES is a symmetric cipher , the key can be used for file encryption and for decryption. However, after completion of the encryption process, the key the user is not available, unless he keeps logs network traffic.
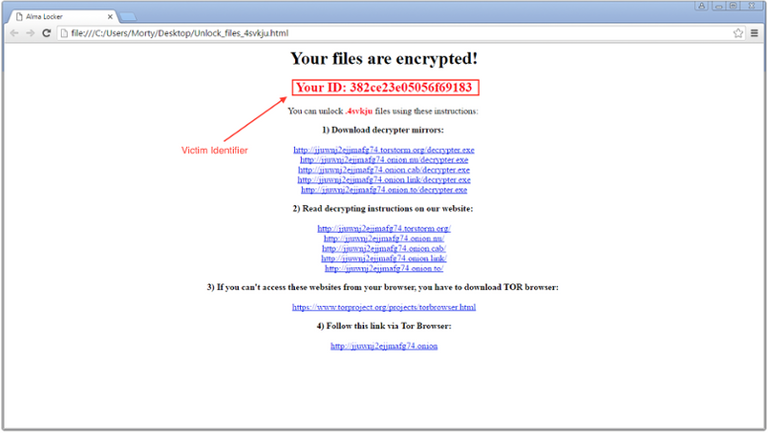
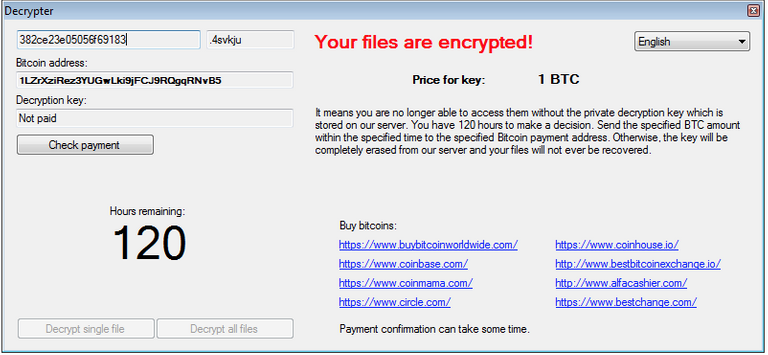
When encryption is finished files, of Alma displays a message demanding ransom by sending the victim to the site in .onion area, where you can download a tool to decrypt the data created by the intruders. Only after downloading decryptor, the user receives further instructions: bitcoin wallet-address and information on the amount of ransom , which is 1 Bitcoin (about 585 dollars), and learns that to pay for it has 120 hours.
!{}( )
)
Researchers PhishLabs managed to extract the source code of decryptor, which was not protected by obfuscation, using Red Gate .NET Reflector and understand that the tool vulnerable to attacks such as man-in-the-middle. To understand the mechanisms of the tool to decrypt, experts used Fiddler to forge answers to the management server. As a result, experts have created PhishLabs C-Sharp file, with which data can be restored for free.
With all the details of the work done by the experts can be found in the company's blog.