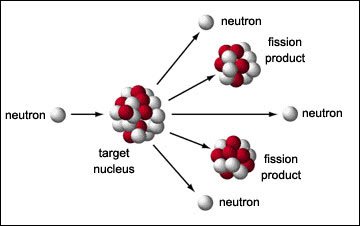
Nuclear fission is the process in which a large nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei with the release of energy. In other words, fission the process in which a nucleus is divided into two or more fragments, and neutrons and energy are released.
The mass changes and associated energy changes in nuclear reactions are significant. For example, the energy released from the nuclear reaction of 1 kg of uranium is equivalent to the energy released during the combustion of about four billion kilograms of coal.
The Process
This is Albert Einstein's famous equation relating mass and energy:
einstein
This means that any reaction produces or consumes energy due to a loss or gain in mass. Energy and mass are equivalent. Note that because c to the second power is large, a small change in mass results in a large change in energy. When nucleons, or particles that comprise atomic nucleus, combine together to form an atom, the energy is released. Corresponding to the mass defect, the mass of the nucleus is always less than the sum of the masses of the individual protons and neutrons that comprise it.
Conversely, energy is needed to break apart a nucleus into its nucleons. Nuclear binding energy can be defined as the amount of energy needed to break one mole of nuclei into individual nucleons. The larger the binding energy per nucleon, the stronger the nucleons are held together, and the more stable the nucleus is. Less stable atoms have lower binding energies per nucleon. In other words, it is harder to break apart a nucleus with a high binding energy than a nucleus with a low binding energy. The binding energy per nucleon is a function of the mass number. Light nuclei gain stability by undergoing nuclear fusion. Heavy nuclei gain stability by undergoing nuclear fission.
The following figure shows the binding energy as a function of the mass number.
bonding energy
Binding energies in this figure indicate that heavy nuclei tend to be unstable. To gain stability, they can fragment into several smaller nuclei. Because atoms with mass numbers around 60 are the most stable, heavy atoms (those with mass number greater than 60) tend to fragment into smaller atoms in order to increase their stability. The splitting of a nucleus into fragments is accompanied by a very large release of energy.
https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-is-nuclear-fission-definition-process-quiz.html (Source)
Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-is-nuclear-fission-definition-process-quiz.html