Many of us have heard what Proof-of-Work & Proof-of-Stake is, what are their main advantages and disadvantages, but let's try to calculate on real numbers what is the difference between PoW & PoS. In this article, we will “simulate” mining two assets: Ethereum (PoW) & Tezos (PoS), and then summarize
What is Proof-of-Work
Proof-of-Work (proof of work) - an algorithm of consensus, which is based on the proof of the work performed. This process includes an attempt to find the hash of the block header, which contains a link to the previous block, and the total value of the transactions included in it.
Proof-of-Work involves the compulsory execution of labor-intensive calculations and at the same time quick and easy verification of results. This feature of the PoW algorithm is called time-wary asymmetry.
In the PoW technology, the decisive factor in finding a unit is the use of large computing power of its participants, and, therefore, there are problems associated with high energy costs.
The idea of the PoW mechanism appeared in 1993 to protect email from spam. The term Proof-of-Work itself appeared only in 1999. For the first time, PoW was implemented in 1997 in the HashCash project.
In a nutshell about Proof-of-Stake
Proof-of-Stake (proof of ownership) is a method of protection in cryptocurrencies, in which the probability of the formation of the next block in the blockchain is proportional to the share of cryptocurrency, which belongs to the miner. Consequently, the miner with the highest balance is more likely to generate a new block.
In some networks using the PoS system, there is no reward for the unit, and the miners' income is only commissions per transaction. For mining in the PoS system there is a separate term - staking.
PoS is an alternative mechanism for PoW, first implemented in 2012 in the PPCoin cryptocurrency (renamed PeerCoin). The idea of Proof-of-Stake is to solve the problem of Proof-of-Work associated with large amounts of electricity.
The theory we learned, now move on to practice
Ethereum (ETH is a platform for creating decentralized online services based on the blockchain operating on the basis of smart contracts.
Tezos (XTZ) is a software blockchain platform that can change and adapt through community consensus with minimal network disruption.
- Scaling
Vitalik and Arthur decided to argue which consensus algorithm is better: PoW or PoS. Acne loves Ethereum, so he decided to mine it, and Arthur is an adherent of Tezos.
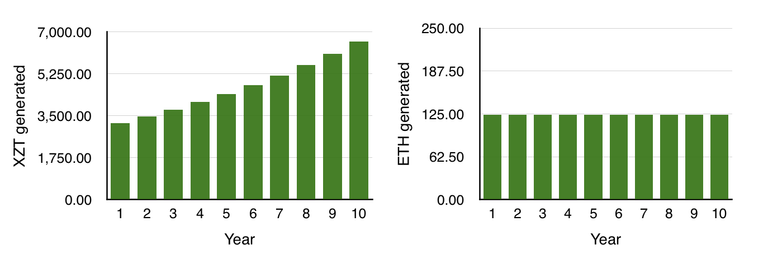
Acne bought several GPUs and within a year he successfully confirmed the blocks and received awards, the lion’s share of Ethereum's inked funds went to cover the costs (electricity / maintenance of the GPU, etc.), also it is necessary to take into account possible technical problems that occur during the operation of the GPU (for example, overheating cards or failure of a separate component).
At the same time, Arthur bought Tezos, in which only the presence of coins (XTZ) is required to participate in the validation of the blocks. Arthur finds a suitable Tezos pool for him, where he can delegate his XTZ. After a month, he checks his balance and sees a gain on n-XTZ from his initial deposit. Arthur leaves his tokens in the pool and does not withdraw profits, because he knows about compound interest . After some time, Acne and Arthur meet to compare who earned more. Here is what they did: