I found this security bug in one of the prominent food startups of India. All their customer data including residential info , order info and contact details were vulnerable.
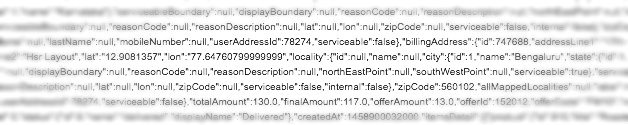
Look at the following code.
@app.route(“/customer/info”)
def customer_info():
customer_id = requests.args.get(‘customer_id’)
customer = customers.query.filter(Customer.id==customer_id).one()
customer_schema.jsonify(customer)
A customer of id 5453 will have the following request URL
http://server_ip/customer/info?customer_id=5453
Now look at the URL, the id is a number. A hacker will try changing the number from 5453 to 5454
http://server_ip/customer/info?customer_id=5454
This will allow him to fetch details of the customer with id 5454, which he is not supposed to see. Now he can write a script which loops through customer ids and fetch information; he has hacked into a company’s confidential data.
This can be prevented by adding authentication to check if the user has privileges to access the data. A unique string identifier is much better than an integer identifier.