¿What is Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory?
The psychologist Abraham Maslow developed a theory that suggests we, humans, are motivated to satisfy five basic needs. These needs are arranged in a hierarchy. Maslow suggests that we seek first to satisfy the lowest level of needs. Once this is done, we seek to satisfy each higher level of need until we have satisfied all five needs.
Maslow (1943, 1954) stated that people are motivated to achieve certain needs and that some needs take precedence over others. Our most basic need is for physical survival, and this will be the first thing that motivates our behavior. Once that level is fulfilled the next level up is what motivates us, and so on.
The original hierarchy of needs five-stage model includes:
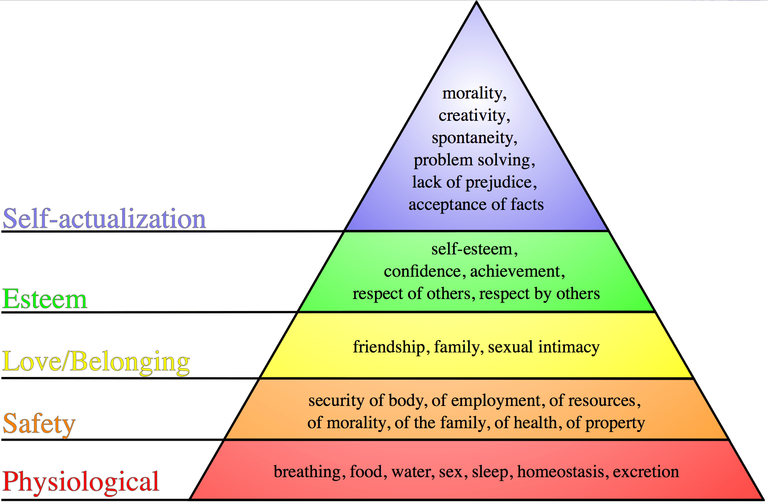
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is often portrayed in the shape of a pyramid with the largest, most fundamental needs at the bottom and the need for self-actualization and self-transcendence at the top.
The most fundamental and basic four layers of the pyramid contain what Maslow called "deficiency needs" or "d-needs": esteem, friendship and love, security, and physical needs. If these "deficiency needs" are not met – with the exception of the most fundamental (physiological) need – there may not be a physical indication, but the individual will feel anxious and tense. Maslow's theory suggests that the most basic level of needs must be met before the individual will strongly desire (or focus motivation upon) the secondary or higher level needs. Maslow also coined the term "metamotivation" to describe the motivation of people who go beyond the scope of the basic needs and strive for constant betterment
THE PYRAMID OF MASLOW
Deficiency needs arise due to deprivation and are said to motivate people when they are unmet. Also, the motivation to fulfill such needs will become stronger the longer the duration they are denied. For example, the longer a person goes without food, the more hungry they will become.
The Hierarchy of Needs is as follows:
Physiological Needs (basic issues of survival such as salary and stable employment)
Security Needs (stable physical and emotional environment issues such as benefits, pension, safe work environment, and fair work practices)
“Belongingness” Needs (social acceptance issues such as friendship or cooperation on the job)
Esteem Needs (positive self-image and respect and recognition issues such as job titles, nice work spaces, and prestigious job assignments.)
Self-Actualization Needs (achievement issues such as workplace autonomy, challenging work, and subject matter expert status on the job)
"It is quite true that man lives by bread alone — when there is no bread. But what happens to man’s desires when there is plenty of bread and when his belly is chronically filled?
once other (and “higher”) needs emerge and these, rather than physiological hungers, dominate the organism. And when these in turn are satisfied, again new (and still “higher”) needs emerge and so on. This is what we mean by saying that the basic human needs are organized into a hierarchy of relative prepotency" (Maslow, 1943, p. 375).
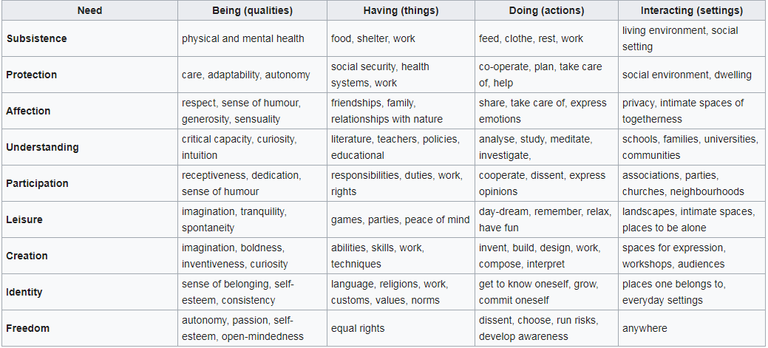
Fundamental human needs
Needs are also defined according to the existential categories of being, having, doing and interacting, and from these dimensions, a 36 cell matrix is developed
Human scale development
Human scale development was created in response to neoliberalist and structuralist traditional hierarchical development systems in which decisions start at the top and flow down instead of in a democratic manner. It focuses on development by the people and for the people and is founded upon three pillars: fundamental human needs, increasing self-reliance, and balanced interdependence of people with their surroundings. This system of development gives people a platform for community organizing and democratic decision making to empower people to take part in the planning process to ensure it meets their needs. Max-Neef's fundamental human needs forms the basis for the creation of his alternative development and, as opposed to Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, which focuses on a ranking of psychological needs, Max-Neef includes needs that are complementary, each one necessary for achieved satisfaction. This proposal for an improved development system is useful on a small scale and gives insight into achieving fundamental needs through societal institutions.
The results of the study support the view that universal human needs appear to exist regardless of cultural differences. However, the ordering of the needs within the hierarchy was not correct.
The specific form that these needs will take, of course, will vary greatly from person to person. In one individual it can take the form of the desire to be an ideal mother, in another it can be expressed athletically, and in another it can be expressed in pictures of painting or in inventions "(Maslow, 1943, pp. 382-383).)

hey so nice I really like your post! Thanks for it! I actually wrote my 2nd part of my introduceyouself and I write about that I went to jail because of cryptos... lets make steemit together to a better place with our content! I would like to read a bit more about you and maybe do you have some more pictures? Maybe you upvote me and follow me swell as I do? https://steemit.com/counterfeit/@mykarma/2-jail-review-counterfeit-euro-speeeeending-time