Greetings to all and sundry on this platform once again. As a biochemistry student, today I did my research on the glycogenolysis pathway and decided to share it with you guys here. I hope that you will enjoy it and also learn from it.
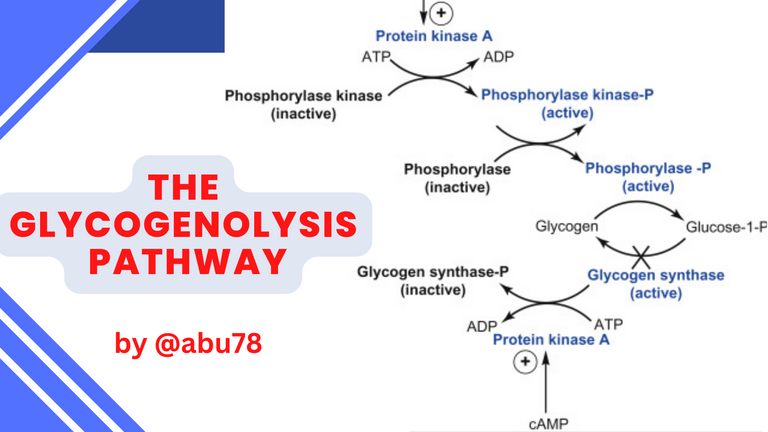
Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen, a polysaccharide and the main form of stored glucose in the body, into glucose, which is the primary source of energy for cells in the body. This process is stimulated during periods of exercise, fasting, and stress. It is important to understand the mechanisms of this process, as it is essential for maintaining energy balance within the body.
The first step in glycogenolysis is the activation of glycogen phosphorylase by phosphorylation. Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate group (PO4) to an enzyme or other macromolecule, and is catalyzed by a protein kinase.
In the specific case of glycogen phosphorylase, it is activated by the phosphorylation of a serine residue, which is catalyzed by the enzyme cAMP-dependent protein kinase. cAMP is a secondary messenger molecule involved in cell signaling and is important in regulating the activity of glycogen phosphorylase and other enzymes that are involved in glycogenolysis.
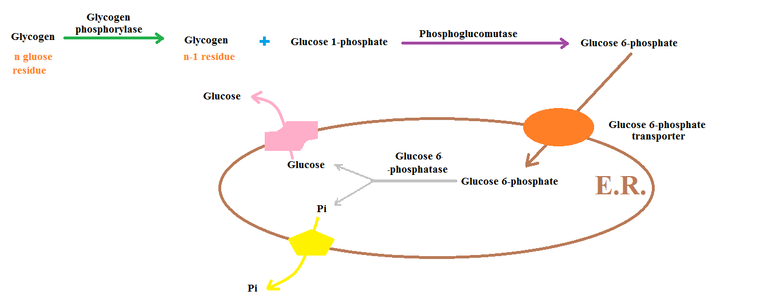
Once the glycogen phosphorylase has been activated, it is able to catalyze the transfer of a single glucose molecule from the terminal end of the glycogen molecule to a molecule of water, forming glucose-1-phosphate and releasing a glycogen molecule with one fewer glucose molecule. This process is repeated until all of the glucose molecules have been removed from the glycogen molecule.
The resulting glucose-1-phosphate is then converted into glucose-6-phosphate by the enzyme phosphoglucomutase. Glucose-6-phosphate is the molecule needed for the next step in the process, the conversion of glucose-6-phosphate into glucose. This conversion is catalyzed by the enzyme glucose-6-phosphatase, located in the liver and kidney cells. Once the glucose has been released into the extracellular space, it can be used as energy by the body.
The final step in glycogenolysis is the replenishment of glycogen stores. This is accomplished by the enzyme glycogen synthase, which catalyzes the formation of glycogen from glucose-6-phosphate. This enzyme is activated when glucose-6-phosphate levels are high and inhibited when glucose-6-phosphate levels are low. When glucose-6-phosphate levels are high, glycogen synthase will catalyze the formation of glycogen from glucose-6-phosphate, thereby replenishing glycogen stores.
A summary of How Gluconeogenesis Works
Gluconeogenesis is a pathway that helps you produce glucose when you need it. It works by turning amino acids into glucose. The first step in this pathway is called the citric acid cycle, which uses oxygen to turn carbon dioxide into carbon dioxide and water molecules. The second step is an enzyme called pyruvate carboxylase, which breaks down pyruvate into acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate. Acetyl-CoA is then converted into oxaloacetate, which goes on to be converted into fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (FBP), a compound that can join with glucose molecules to form glycogen or other sugars. FBP also reacts with another molecule of ATP to create fructose 6-phosphate (F6P), which goes on to become fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (F1P). F1P can then rejoin with F6P to form D-fructose 6-phosphate (DFP) or DFP 3-phosphate (DP3P).
Some health benefits of glycogenolysis pathway:
It helps to maintain blood sugar levels and reduce insulin resistance, which can lead to type 2 diabetes.
It helps to maintain your eyesight by providing a source of energy for cells in your retina called rod cells. These cells convert light into electrical signals that are passed along nerve fibers to your brain.
It helps to maintain your muscle mass by providing energy for muscle contraction and movement, which is why athletes often increase their intake of carbohydrates before they exercise so that they don't fatigue as quickly when working out.
Glycogenolysis is an important metabolic pathway, as it helps to maintain energy balance in the body during periods of exercise, fasting, and stress. It is regulated by several enzymes, including glycogen phosphorylase, phosphoglucomutase, glucose-6-phosphatase, and glycogen synthase.
These enzymes act together to break down glycogen into glucose, which is then used as an energy source, and to replenish glycogen stores by converting glucose-6-phosphate into glycogen. Understanding this pathway is important for the proper functioning of the body, as it is essential for maintaining energy balance.
The references given below are sites where you can learn more about gluconeogenesis pathway, especially about the cycle or process in detail.
Reference 1
Reference 2
Reference 3
Reference 4
Reference 5

Reading about it after 10 years since I last touched the biochemistry book. This was a good refresher. 😁
Wow, that’s interesting to hear after good 10 years, we learned that just last year and I decided to share that here. Metabolism of reactions in general is interesting to study. I am happy that you found my post interning and beneficial. Thanks for reading and stopping by.
Congratulations @abu78! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
Your next target is to reach 1500 upvotes.
Your next target is to reach 2500 upvotes.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPTo support your work, I also upvoted your post!
Check out our last posts:
Support the HiveBuzz project. Vote for our proposal!
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.