Astronomers are unique, ranging from the laboratory is very broad (universe), until the unit of distance used is fairly unique. this is nothing else because it is related to the heavenly bodies they study in the universe, from atomic to the extent of the universe itself. to illustrate it all, it is sometimes inconvenient to mention distance to the commonly used unit of society because it is not small enough or even too big to mention.
generally, we know the unit distance with centimeters (0.01 meters), meters, kilometers (1000 meters) or miles (1.63 km). but the units are not small enough to express the electromagnetic wavelength, and not large enough to express the distance and magnitude of the celestial bodies in space. Therefore, astronomers have their own units to declare such distances as Ångström (Å), Astronomical Units (AU), Light Years (ly) and Persec (pc). Let's discuss one by one the purpose of the units.
Ångström (Å)
The term angstrom itself is derived from the Swedish physicist Anders Jonas Ångström (1814-1874) who is the father of spectroscopy as a tribute to his services in the field of spectroscopy. Spectroscopy is a technique for identifying chemical compounds using the wavelength of light absorbed or produced depending on the characteristics of the compound. Light passing through or coming from a compound is passed through a prism that separates the various wavelengths to form the color spectrum. The resulting spectrum often has a bright band of light associated with the resulting wavelength, or dark band of light if the compound absorbs light. The light band pattern identifies a compound such as a fingerprint identifying a person.
the word Ångström comes from the Swedish language with the symbol Å is the unit of length. Although not an SI unit but often used with SI units. Due to orthographic difficulties, these units may be written as angstroms. This unit is commonly used as a measure of atomic particles and the length of chemical compounds using optical spectra. Angstrom units are also commonly used in measuring wavelengths of light. 1 ångström (Å) = 10-10 meters (m) = 0.1 nanometer (nm).
astronomers use these units to express electromagnetic wavelengths they observe such as ultraviolet light, gamma rays, infrared rays and so on. For example, infrared light has an electromagnetic wavelength of about 3000 to 4000 Angstroms.
Astronomical Units (AU)
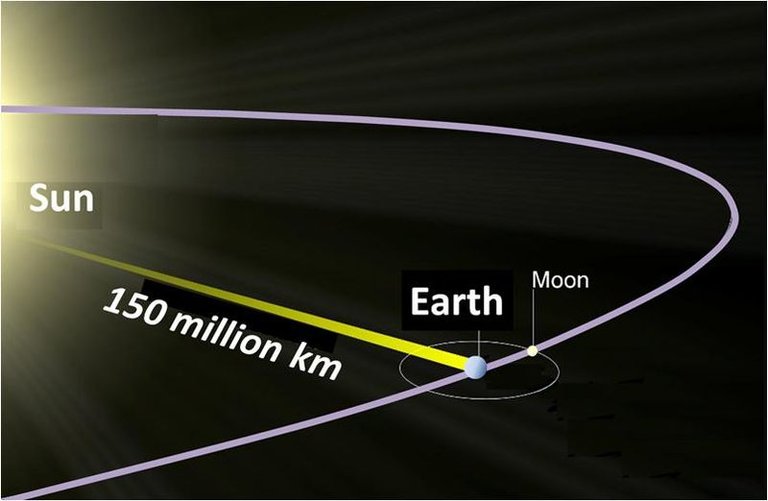
The astronomical unit (AU) is a unit of distance based on the distance between Earth and the Sun. The value of 1 AU is approximately 149,597,870.691 ± 30 meters (about 150 million kilometers or 93 million miles) that have been generally accepted.
Determining the distance of 1 Astronomical Unit (AU) is taken from the long half-axis length of the Earth's orbital path around the Sun. this distance is taken considering the distance of the Earth's orbit is not fixed because the Earth moves around the Sun in an elliptical trajectory.
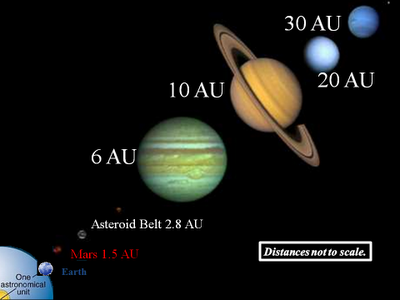
A distance of 1 AU = 150 million kilometers is sometimes considered sufficient because the calculated distance does not require high accuracy. and also a distance of 1 AU = 150 million kilometers will be easier to remember. This unit is usually used to express the distance of celestial bodies around our solar system. for example, the distance between the dwarf planets Eris with the sun about 67 AU. using this unit makes fewer numbers used, instead of using kilometer. And it also illustrates how far away the object is when compared to the distance between the earth and the sun (67 AU means 67 times the distance of the earth-sun.
Light Years (ly)
A light-year (ly) is a unit of length defined as the distance traveled by light in a year through a vacuum. The term year used for calculation is the Julian year which has 365.25 days or 31,557,600 seconds. Sometimes a tropical year of 31,556,925,9747 seconds is used. Since light travels at 299,792,458 meters per second (ms-1) in a vacuum, using a Julian year, a light year equals 9,460,730,472,580,800 kilometers or is often rounded to 1015 kilometers.
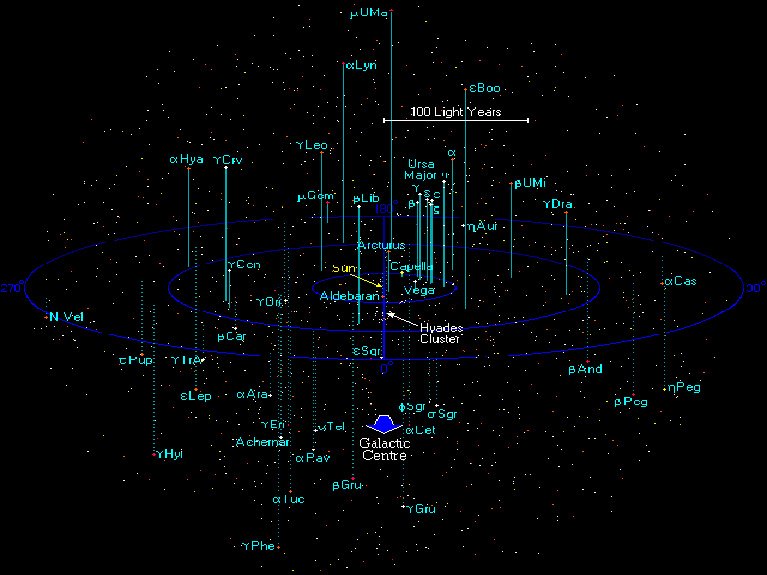
Light years is not a unit of time! but "light year" is the unit of distance. this distance may be a bit too big, but astronomers need this distance to declare the distance of the celestial body that is closest to the earth outside the solar system. for example, the distance of the nearest star Proxima Centauri with the earth is 40 trillion kilometers. This enormous distance is of course too long expressed or written in kilometers, but it is easier to write it in light years, which is 4.22 light years. The picture beside shows the stars around the sun that are 100 light-years away.
Parsec (pc)
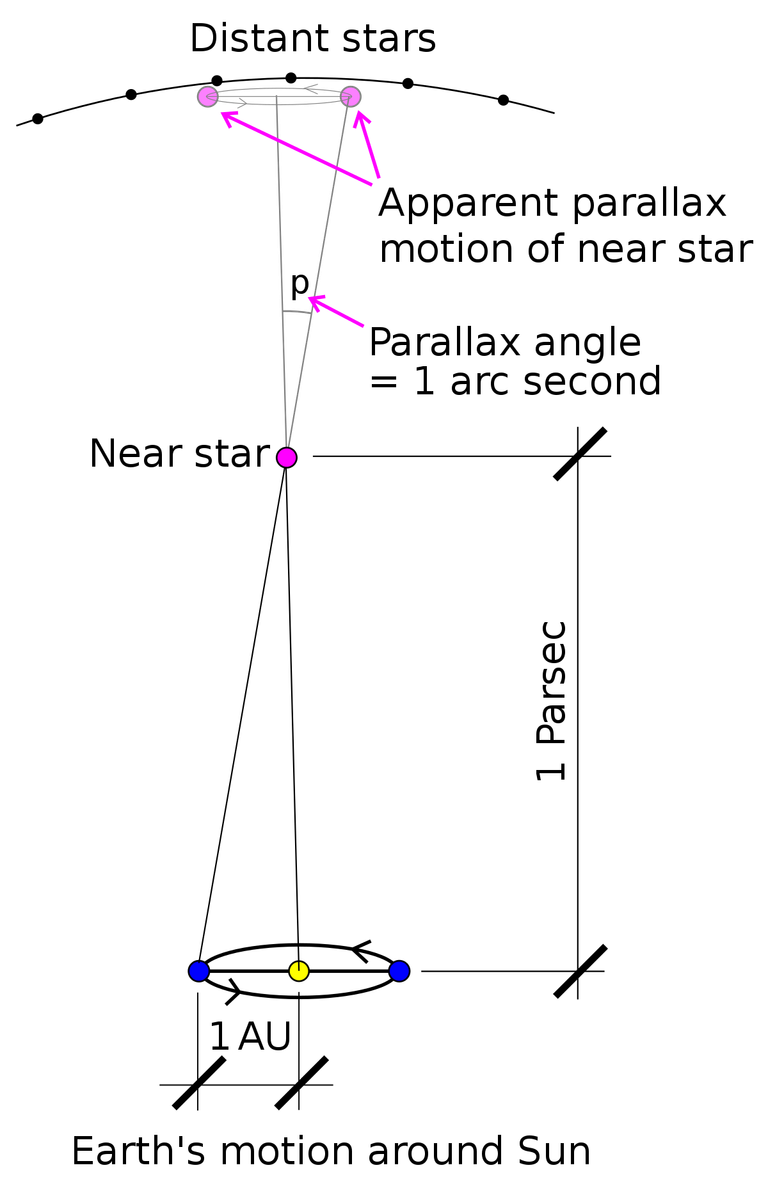
Parsec (abbreviated pc) is the long unit used in astronomy for objects far beyond the Solar System. Parsec stands for "paralax of one arc second".
This unit is based on the trigonometric parallax method, the most ancient standard method used to determine the distance of stars. The angle made by the star against the radius of the earth's orbit around the sun is called parallax. Parsec is defined as the distance of a star that has a parallax of 1 arc of the earth. On the other hand, the parsec is the distance at which two separate objects at a distance of 1 astronomical unit, appear to be separated by an angle of 1 degree arc. Therefore, 1 pc = {(360x60x60) / (2x22 / 7)} AU = 206,265 AU = 3.08568 × 1016 m = 30.8568 Pm (petameter) = 3.2616 ly (light years).
astronomers are more interested in using this unit although this unit is only slightly larger than the light year or 3 times the light year. but this unit can be attributed directly to the observed quantity ie the parallax angle. this unit can also be paired with kilos to denote 1000 pc and mega units for 1 million pc. so by using this unit, we can reveal a very long distance with just a few numbers. for example, the approximate radius of our universe is 24 Gigaparsec or Gpc. 1 Gpc = 1000 Mpc. You can imagine for yourself if these fingers are expressed in kilometers.
Reference :
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/%C3%85ngstr%C3%B6m
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Astronomical_unit
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Light-year
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parsec



One or more of your photos is breaking some form of copyright or it is not sourced, whether it be that the photos require proper attribution or are licensed in such a way that they are not free to use. For more information, check out this post here on steemstem copyright standards.
Sincerely,
@kryzsec
This post has received a 1.94 % upvote from @booster thanks to: @alf4t1h.