Stars in the sky will not always stay there. He will also grow old and die. Some end up as white dwarfs, black holes or supernovas. But there are also stars who are forced to die prematurely. How come? There is a star whose life runs ordinary to old age and then die, but there is also a star who in his life dare to take danger and was not saved from the danger. The stars are those who dare to be close to massive black holes.

Simulation of gravitational lensing by a black hole, which distorts the image of a galaxy in the background,wikipedia
The fate of the stars that were too close to the massive black hole was much more severe than previously thought. They are not only destroyed by the gigantic gravity of the black hole, but the process that took place could provoke a nuclear explosion that would tear it from the inside. In addition, the shock waves occurring in the star disk will carry a certain amount of temperature at the top of the heat, so that it may give rise to a new type of X-ray or gamma-ray burst.
It has long been known that massive black holes are roaming the galactic core with the weight of millions of Sun and will be ready to tear the stars that approach it. Due to the intense tidal force, the gravity of the black hole will attract the nearest star part of it. This attraction causes an imbalance for the Star for several hours until finally, the star will enter within the tidal radius. Not only that. Based on research conducted by Matthieu Brassart and Jean-Pierre Luminet from Observatoire de Paris-Meudon, France, the force of tidal force will also trigger a very powerful explosion that will tear the star from within. The last moments of the unfortunate star they managed to simulate when he sucked into the field of tidal.

When a star is close enough to a black hole, the presence of tidal forces from a black hole will flatten the star like a pancake. This flattened star, its density will be higher and the temperature inside is enough to trigger a nuclear reaction that will tear it apart. Other studies also say that the process will be more complex because of the shock waves generated during the process of splitting and no nuclear explosion will occur.
The latest simulations successfully investigated the effects of shock waves and showed their effects in detail. It turns out that the shock wave helps the nuclear explosion that will destroy the star. Even the explosion that occurred was strong enough to scatter the star material far out of the black hole's reach.
Star Fireworks
The tearing of the star's tidal forces by black holes may have been successfully observed by X-ray Telexopers such as GALEX, XMM, and Chandra, although it is already in the final stages of several months after the incident ripped the Star. At this point the star material will start spinning into the black hole, warming up and releasing ultraviolet light and X-rays. But if these pancake stars really explode, they will certainly give the observer an opportunity to observe them at an earlier stage. Well, advanced observations like the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST) that detects large numbers of supernovas will surely detect these explosions.
Interestingly, it seems the nuclear explosion is not the only danger facing this dead star. Brassart and Luminet calculations also show that the shock waves inside the flattened star will carry in a short time (0.1 seconds)) will have a very high temperature (> 10 billion) out of the center of the star. As a result, there will be a new type of X-ray or gamma-ray burst, which will soon witness the destruction of the star when it has sufficient heat.
The rate of these pancake stars is estimated to be about 1: 10,000 occurrences in each galaxy. Inside each galaxy, there is a massive black hole at its center including in the Milky Way. In addition, the universe is also quite transparent for large X-rays and for gamma radiation, so surely there will be several incidents of stars destroyed near black holes that can be observed each year.
Big Splash in Space
The black hole's reputation is bad: it's famous for sucking anything and what it sucks it will never be seen again. The lesser known fact about black holes is they sometimes create terrifying bursts that catapult matter. Astronomers have found two such powerful bursts, and both are breaking records!
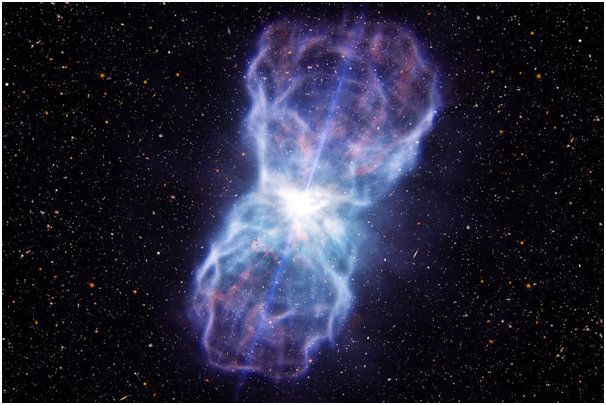

Terrible bursts that astronomers found.wikipedia
Most galaxies have black holes at their center. So is our Galaxy, the Milky Way. These black holes can reach millions or even billions of times heavier than the Sun, but their size is only the size of a small ball, very small. The material is forced as tightly as possible so that the force of gravity is strong - strong enough to swallow the light and prevent it from escaping!
The black hole is known for its ability to attract matter, and just as the inhaled water enters the drain, it forms a disk around the black hole as it feeds the black hole. Because the disk is spinning faster and accelerating, the disk gets hot and then spits out a lot of light and matter. These dazzling bursts are often found bursting from the brightest centers of galaxies and are called quasars.
One of these newly discovered bursts is at the edge of the universe that we know. The other bursts throw enough material to make 400 suns a year and about 100 times the energy of all the stars in the Milky Way galaxy combined - truly a monster!
Greedy Monster Behind the Dusty Blanket
Almost all galaxies have gigantic monsters at their center. Some of the monsters are secretly hiding in the dark, waiting for their prey to be separated from their entourage and being too close to the monster. Some of the other monsters were eating greedily, growing bigger and bigger as they gobbled up the torn material from their surroundings. These wild monsters are of course still black holes. When one of them eats, the brightest and most energetic objects in the universe will be produced: the active galaxies!

Artist’s impression of supermassive black hole seed..wikipedia
When a black hole sucks cosmic gas and dust, a donut-shaped ring is formed, like water being sucked into the drain. The ring spins faster as it falls in, and gets very hot. When that happens, the ring throws out a powerful and bright burst that our telescope can detect.
So, when we see one of these bursts of light, we're most likely to find a giant black hole in the middle of a hot dust ring, which is preoccupied with eating dinner. We would not expect to find him hiding under a cold blanket of dust. But, that's what has just been observed around the active black hole. The dust temperature is around room temperature, much cooler than other dust temperatures that are about 700 degrees Celsius! The dust creates a sooty wind blowing away from the black hole.
This new discovery is very strange. Usually, black holes need to suck the material to give him energy. In this case, however, the powerful energy created while it occurs seems to throw the material away. Currently, it is still an unsolved mystery.
Interesting facts:
A black hole is not a real hole and is the opposite of empty. Compared to other objects in the universe, black holes have the most material in the smallest space.
As with other objects in the universe (including planets, galaxies, and stars), there are various types of active galactic nuclei. However, the difference between the types is generally only determined based on the direction of the active galactic core when we observe it. For example, there are "blazar" and "Quasar", which direction of the outburst in the direction of our perspective, while "Seyfert" seen from the side bursts. That is all and thank you!

BEST REGARDS @ aneuktulot
references and related reading :
https://www.space.com/15421-black-holes-facts-formation-discovery-sdcmp.html
https://www.space.com/18668-biggest-black-hole-discovery.html
https://worldbuilding.stackexchange.com/questions/36103/is-there-a-way-to-create-a-bomb-to-destroy-a-star
http://astronomy.swin.edu.au/cosmos/S/Supermassive+Black+Hole
https://science.nasa.gov/astrophysics/focus-areas/black-holes
http://www.skyandtelescope.com/astronomy-resources/how-big-is-a-black-hole/
https://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2017/collapsing-star-gives-birth-to-a-black-hole
https://www.space.com/16861-giant-black-holes-growth-mystery.html
https://www.obspm.fr/spip.php?page=imprimer&id_article=2039&lang=fr
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2017/08/170830114800.htm
http://www.spaceref.com/news/viewpr.html?pid=25395
http://www.sciencemag.org/news/2017/02/dark-matter-made-black-holes
http://www.eso.org/public/news/eso1247/
https://phys.org/news/2012-05-black-hole-universe-physicist-solution.html
https://www.eso.org/public/news/eso1327/kids/
Thank you for your contribution.
=======================================================================================
This post was upvoted by Steemgridcoin with the aim of promoting discussions surrounding Gridcoin and science.
This service is free. You can learn more on how to help here.
Have a nice day. :)
Congratulations! Your post has been selected as a daily Steemit truffle! It is listed on rank 21 of all contributions awarded today. You can find the TOP DAILY TRUFFLE PICKS HERE.
I upvoted your contribution because to my mind your post is at least 33 SBD worth and should receive 154 votes. It's now up to the lovely Steemit community to make this come true.
I am
TrufflePig, an Artificial Intelligence Bot that helps minnows and content curators using Machine Learning. If you are curious how I select content, you can find an explanation here!Have a nice day and sincerely yours,
TrufflePig