As a part of my Bachelor’s project last year, I went through detailed research on efficiency and cost analysis of Rural Distribution System (RDS). I would like to share my experience and research result analysis with steemit community. 🤗
Energy plays a crucial role as a global commodity and as a cornerstone of socio economic development of a country.
For pursuing a nation’s goal geared towards greater economic and social development the demand for energy is increasing over decades. The primary objective of the power distribution system is to provide the remotest consumer with reliable, maximum efficient and minimum cost power supply.
But in general, a large amount of electricity is wasted in distribution phase. This system losses,
- Increase the operating cost of electric utilities.
- Result in high cost of electricity.
The system loss can be classified by the following,
Technical loss
The physical properties of the components of the power system is responsible for the technical loss. Power dissipation in electrical system components such as transmission lines, power transformers, measurement system cause the technical failure resulting in wastage of power supply.
Non-Technical loss
This losses, are caused by actions external to the power system. This occur as a result of theft, metering inaccuracies and unmetered energy.
Our research was focused on the effect of technical losses and how to reduce the Technical losses in tap lines.
The design standards and the construction of High Tension (HT) and Low Tension (LT) transmission line is one of the vital reasons for technical loss.
In general, Rural distribution system (RDS) maintains standard of constructing three phase backbone distribution High Tension lines of 11 kV. This backbone line is consists of both single phase High Tension taps of 6.35 kV and three phase High Tension taps of 11 kV of voltage along with single phase Low Tension lines of 0.23 kV and 0.415 kV Low Tension three phase lines.
Single Phase & Three Phase System
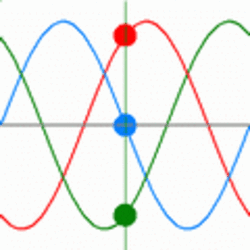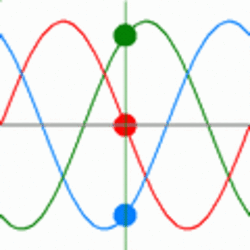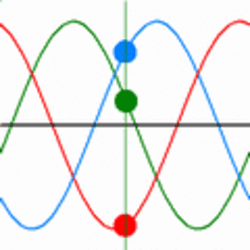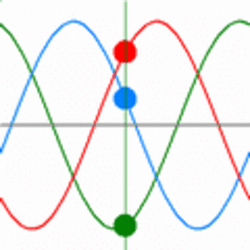
In a three-phase system, three conductors carry the same single-phase sine wave power reaching their peak values at different times. The power in three phase system never goes down to zero while in a single phase system power goes down to zero three times in every cycle. This arrangement can provide more constant power transfer over a cycle compared to single phase system. Three phase lines can avoid the additional system loss due to the neutral current in the grounded Y-connected line [2]. So in terms of power transmission, three phase system is more efficient than single phase. An oscilloscope trace of three-phase power would appear as shown in Fig. 2 & 3.
References
[1] Muhammad Usman, Fabio Bignucolo, Roberto Turri, Alberto Cerretti, “Power Losses Management in Low Voltage Active Distribution Networks”, iEEE Xplore, accessed on 22nd February, 2018.
[2] “Single-Phase vs Three-Phase Power Explained”, WEB, accessed on 22nd February, 2018.
[3] "Alternating current", Wikimedia Commons, accessed on 22nd February, 2018.
[4] "Three-phase electric power", Wikimedia Commons, accessed on 22nd February, 2018.
Part #2 of this series will include the detailed modeling on Single & Three phase system followed by optimization and result analysis of this research work.
Stay blessed..! Keep the good work going..!😇
~Tennis Girl 🎾🎾
.gif)
Being A SteemStem Member
This is fantastic. . . I studied Electrical Engineering in university, this brings back fond (aka: painful) memories of my classes on power distribution systems. Very happy to see this content here, please keep it coming!
Great to know tht u were in EE too..!!! 🙏
I'm planning to continue this series and write about my research and experiments here in steemit..!
@steemstem inspiring me to write more about science and engineering..! 🤗
~Tennis Girl 🎾🎾
his is very amazing for me, I really like your post, I am really impressed, this is a lesson for me, because I am newbie, and just new in steemit, I wait for your next posting
@irham
thank you for the post, I liked found you in the chat