The Big Bang theory tries to explain what happened at the very beginning of our universe. It is one of the most fundamental concepts of modern science but unfortunately, also one of the most widely misunderstood one. Just like with evolution, there’s a lot of really uneducated people who have no or very little idea about the Big Bang.
A short recap of Big Bang
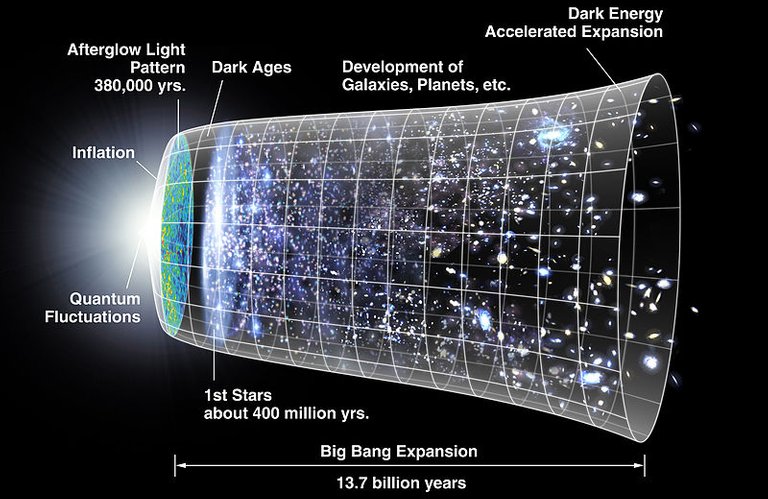
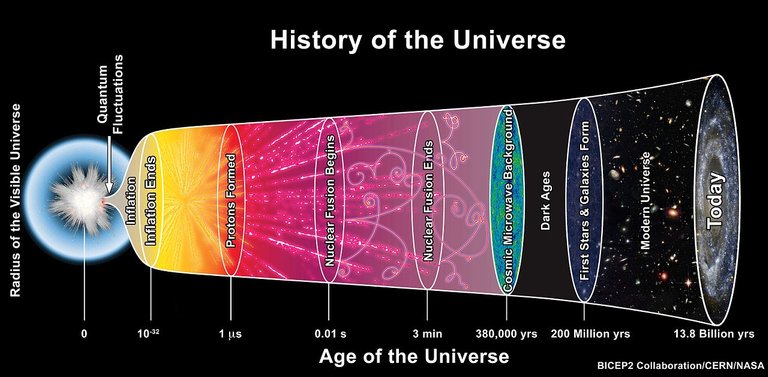
According to the standard theory, our universe sprang into existence as "singularity" around 13.7 billion years ago. Singularities are zones which defy our current understanding of physics. The limitation of the current model of Big Bang theory is that it can predict precisely what happens after the bang but has no idea before the bang. Our current physical theories do not explain what happened prior to the Planck age of the universe (~5*10-44 seconds). Strictly speaking, the big bang model has very little to say about the big bang itself, because It describes what happened afterward.
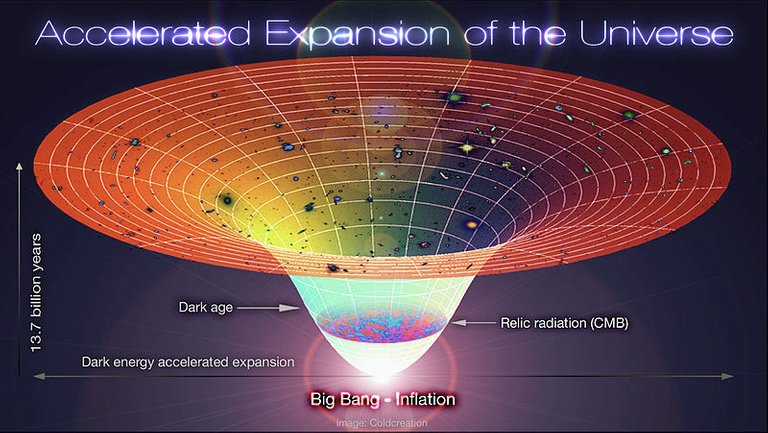
American astronomer Edwin Hubble observed that the distances to faraway galaxies were strongly correlated with their redshifts. This means that all distant galaxies and clusters are receding away from our vantage point with an apparent velocity proportional to their distance. The interesting thing is the farther they are, the faster they move away from us, regardless of direction. The continuous expansion of the universe implies that the universe was denser and hotter in the past. In 1965, Radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson discovered a 2.725 degree Kelvin (-454.765 degree Fahrenheit, -270.425 degree Celsius) Cosmic Microwave Background radiation (CMBr) which represents the early observable universe while it was too much denser and small.
List of some common Misconceptions
The main ones that we will discuss in this post are following
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 5 | |
| 6 | |
| 7 |
1. What types of the explosion were that (Fact 1, 2 & 3):
This is a big one. The term “Big Bang” was originally given to the theory (originally called “primeval atom”) by Fred Hoyle on a radio program in which he was mocking the theory. That misnomer stuck and has been causing confusion ever since. Now imagine the moment of BB(Big Bang), every time your mind will picture something like this- It was like a bomb going off at a certain location in previously empty space. In this view, the universe came into existence when matter exploded out from some particular location. The pressure was highest at the center and lowest in the surrounding void, this pressure difference pushed material outward. That's it, alright?
But unfortunately your imagination has a wrong framework, not that you lack it but you have fed your mind wrong information ever since. It was an explosion of three-dimensional space itself. The space we inhabit is itself expanding. There was no center to this explosion; it happened everywhere. Everywhere, from your bathroom to the place you're reading this now. The density and pressure were almost same everywhere (Proved by CMB), so there was no pressure difference to drive a conventional explosion.
Impressive, huh. Now, install this idea your brain's algorithm.
One might conclude that the expansion of our three-dimensional space requires the presence of a fourth dimension. But space is dynamic. It can expand, shrink and curve without being embedded in a higher-dimensional space.
Still, now, all the visible matter is all actually standing still while space itself expands dragging the matter with it. The distances to remote galaxies are increasing. But the galaxies are not traveling through space away from us. They are not fragments of BB explosions. Instead, the space between the galaxies and us is expanding. Galaxies may have some local velocity but the clusters of galaxies are essentially at rest.
So, what we learned so far is following. The universe is self-contained. When it expands, it doesn't claim previously unoccupied from its surroundings. Although string theory does postulate extra dimensions, as our three-dimensional universe expands, it doesn't need these extra dimensions to spread into. Thus, the big bang was not an explosion of space: it was more like an explosion of space. It occurred everywhere at once.
Bonus one: How can galaxies recede faster than light?

Sure they can do that without breaking Special theory of Relativity. Special relativity does not apply to recession velocity. In expanding space, recession velocity keeps increasing with distance. Beyond Hubble distance (This distance is about 14 billion light-years), it exceeds the speed of light. This is not a violation of relativity, because recession velocity is caused not by motion through space but by the expansion of space. It is still true that nothing ever overtakes a light beam.
2. What fueled that bang (Fact 4 & 5):
Today, when we look at the night sky, we see billions of galaxies separated by huge expanses of empty space. At the earliest moments of the BB all of the matter, energy, and space we could observe were compressed to an area of zero volume and infinite density. But, wait. That is the most common explanation for what you find everywhere. How could something exist in an area of zero volume? It's super counter-intuitive.

Our intuitions are based on our lifelong experiences. Our brain is only familiar with the three-dimensional interactions and freedom. So, to get something out of the world out of the universe into your brain you have to think from a new angle.
By saying zero volume it suggests that the 3-Dimensional volume of it was zero. Because those 3-Dimensions didn't exist before that moment (Imagine). By saying moment, I meant Time. Spacetime is a model that fuses the three dimensions of space and the one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional continuum. For instance, without Time dimension the three-dimensions of space would be like a frozen photography. Time act as the freedom of three-dimensions which grants the interactions between them. Big Bang is the bang of spacetime itself.

We don't know for sure if it is from nowhere, from nothing. Maybe our universe created through the collision between two multidimensional membranes, cruising through a higher-dimensional space like dimension acts by a freedom dimension alike time. Maybe.
Additionally, the Big Bang doesn’t go all the way back because it really can’t. When you start going back to far, things become fuzzy. The physical laws of Physics that we’re all familiar with start to break down under such high energy densities. Really weird stuff starts to happen, like different fundamental forces ceasing to exist and merging with one another. We currently don't know and don't have a solution for it. And that's O.K.! Someday humanity will figure it out for sure.
3. Evidence of Big Bang (Fact 6):
I have actually seen several types of statement saying- Big Bang is a hoax, fairly often. I have no idea where people get the idea that scientists make things up without having good evidence behind it. Scientists may start things from 0, everything starts from 0. They aren't creating the universe beside they are revealing the secret of it. As Carl Sagan-"It matters to me because I am human and I do not like not knowing". That the spirit behind every single of the scientist.
Why the Big Bang definitely happened?

The Big Bang theory does have a good amount of evidence behind it. Here we would discuss main three of them. Which are-
+ The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB)
+ Cosmological Redshift &
+ Distribution of Elements
3.1 The Cosmic Microwave Background radiation (CMBr):
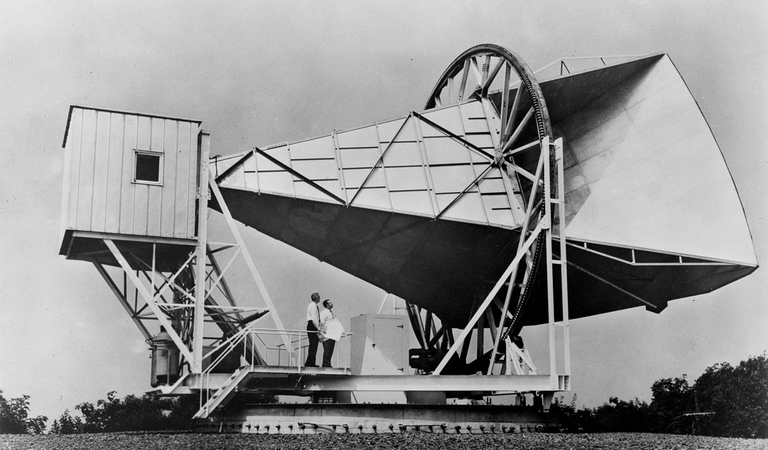
The most strong piece of evidence for the Big Bang is the existence of microwave background radiation approaching earth from every direction in space. George Gamow first predicted the existence of this radiation long before it was actually observed. It is the afterglow of Big Bang. For the first 350,000 years or so, after Big Bang, the universe was essentially too hot for light to shine. The heat of creation smashed atoms together with enough force to break them up into a dense plasma, an opaque soup of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Approximately 350,000 years after the Big Bang, as the temperature of the universe falls to around 3,000 degrees, matter cooled enough for atoms to form during the era of recombination, resulting in a transparent, electrically neutral gas. The universe finally becomes transparent to light, making this the earliest epoch observable today. This set loses the initial flash of light created during the Big Bang, which is what today we know as cosmic microwave background radiation or CMBr.

Satellite
Today it has a temperature less than three degrees above zero. The CMB radiation predicted and observed is incredibly uniform, varying from one direction in the sky to another by only a few parts per million. When the radiation began its journey 350,000 years after the Big Bang it was not microwaves but visible light. Its wavelength has increased by a thousand times, just as the universe itself expanded a thousand times.
3.2 Cosmological Redshift:
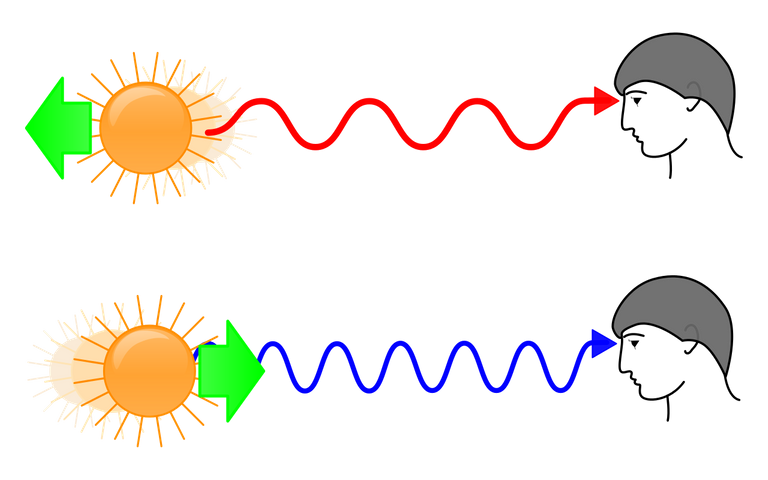
This is the easiest point to grab. When scientist study the universe, what they find, is that all galaxies in the universe are moving away from us. The further they are, the faster they’re moving away.- Now take a break and imagine it. Imagination is better than knowledge.- So if we play the whole thing in reverse, all the galaxies will come back together at a single point in time. This point in time is what we call the Big Bang.
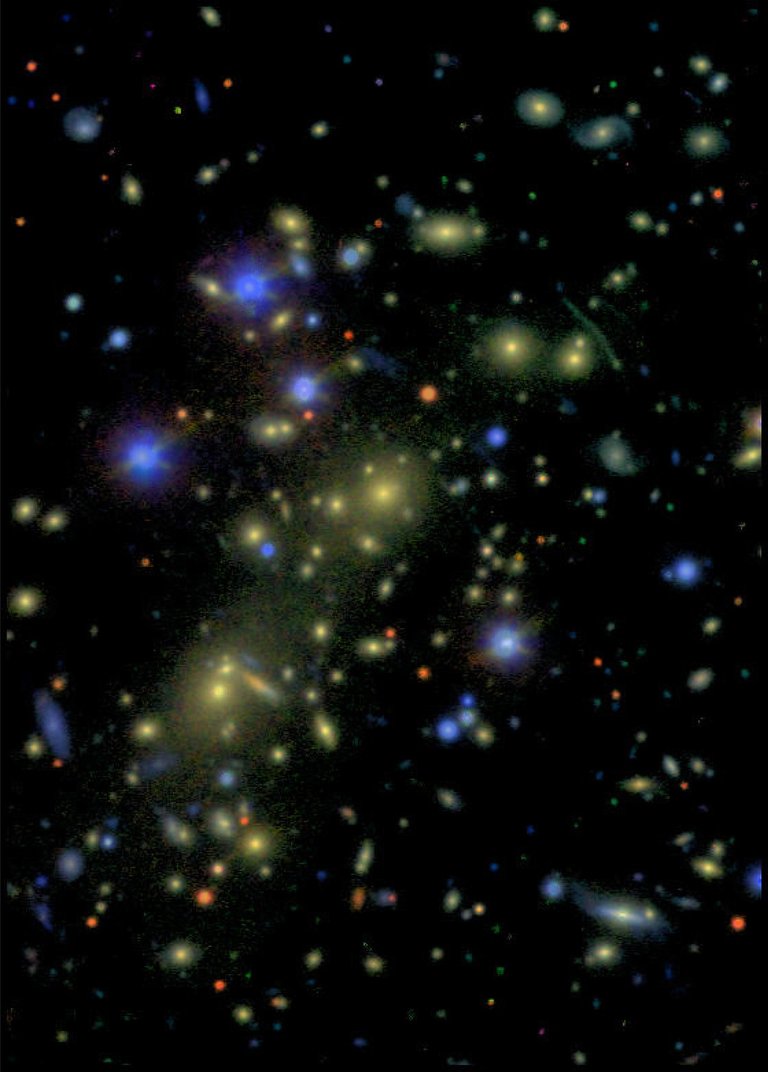

Since all galaxies are composed of the same elements, the light emitted from distant galaxies should have the same characteristic wavelengths as that from the nearer galaxies. So the first clue that the universe is expanding is that light from distant galaxies has a longer wavelength than it should. Because the wavelength gets longer during the journey through ever-expanding space. Thus, the light gradually reddens.
3.3 Distribution of Elements:
The third, and just as important, like of evidence comes from nuclear physics. The relative proportion of Hydrogen, Helium, and Lithium fit very closely with the predictions of theoretical models of Big Bang.

The big bang model predicts 80% hydrogen, 20% helium would be there and neglected the rest since it would be statistically insignificant. In the universe today, we observe 70% hydrogen, 28% helium, and 2% everything else. This discrepancy is easily accounted for by nearly 14 billion years of stars cooking hydrogen into helium and other heavier elements. In addition, a vital 2% of heavier elements has appeared.
4 The Big Bang doesn’t leave room for God:

Well, this point deserves a whole post. So, next time.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
& Wikipedia or Google for hundreds of time.
Thanks, I hope you liked it.

Hi, it would be nice to add sources you have used (:
sources for text and sources of images. This is excellent post. Try using tag steemstem and check their profile as well. https://steemit.com/@steemstem
I am relatively new on this platform. Thanks a lot for your guideline. I edited the post and sources are now mentioned.
Thanks.@milosm2302
You are welcome, I have a few more things to mention,please contact me on discord Milosm#9774 (:
I couldn't find you.
This post has received a 6.33% upvote from @lovejuice thanks to @dolon. They love you, so does Aggroed. Please be sure to vote for Witnesses at https://steemit.com/~witnesses.