Previously we have discussed the radioactive elements and examples, which is the introduction of this topic.
This article will discuss the example of radioactive waste and its classification.
Illustration of radioactive waste from Fukushima nuclear power plant
Image Credit : www.redlinepage.com
Classification of Radioactive Waste
A schematic nuclear fission chain reaction
Image credit : www.dreamstime.com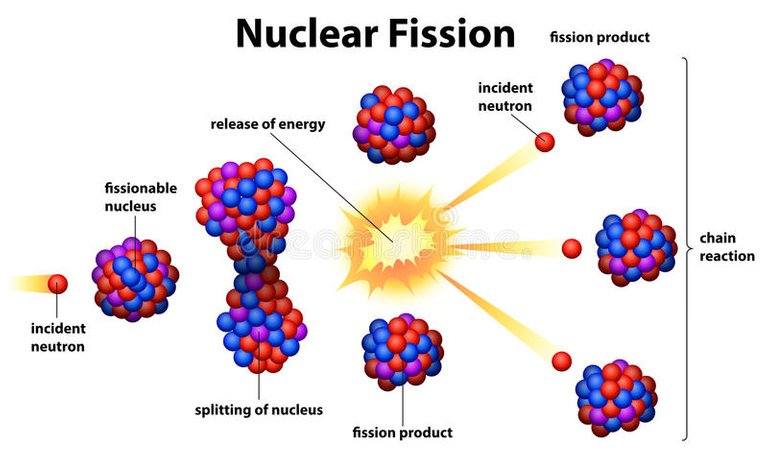
Radioactive waste is categorized into three types, based on its radioactivity. Here are the types:
1. High-Level Radioactive Waste (High-Level Waste / HLW)
Although the amount is very small (only 3% of the total waste), but the radiation energy is very large (reaching 90% of the total waste radiation). Higher radioactive waste is classified again based on the duration of its bill. This type of long half-life of waste is very important in the management of radioactive waste.
Yucca Mountain (Nevada), reactor fuel warehouse and other high-level radioactive waste
Image credit : worksthatwork.com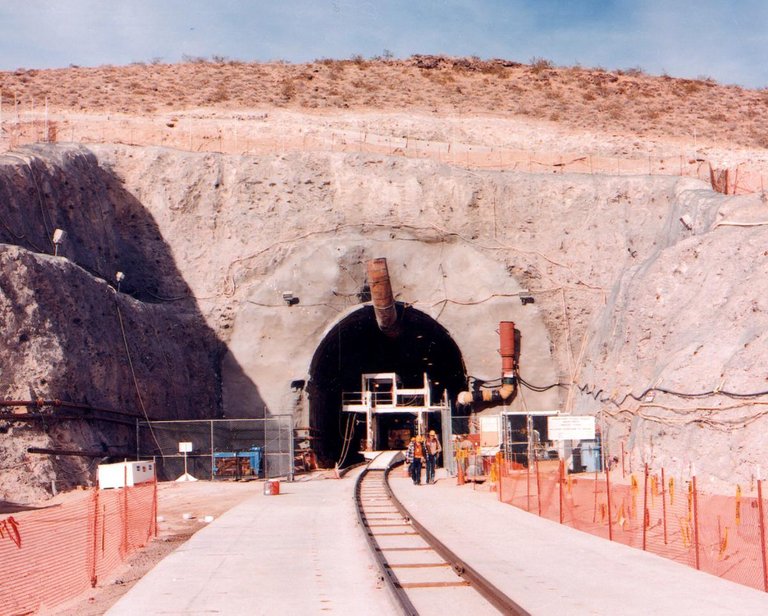
Because of its enormous energy, coating and cooling are required for the process of moving and storing heavy radioactive waste.
2. Medium Radioactive Waste (ILW)
The amount of waste is relatively small (only 7% of total radioactive waste), and the radiation energy is small (only about 4% of total radioactive waste).
Rock salt that used as a subsurface container for storage of radioactive waste
Image credit : www.sott.net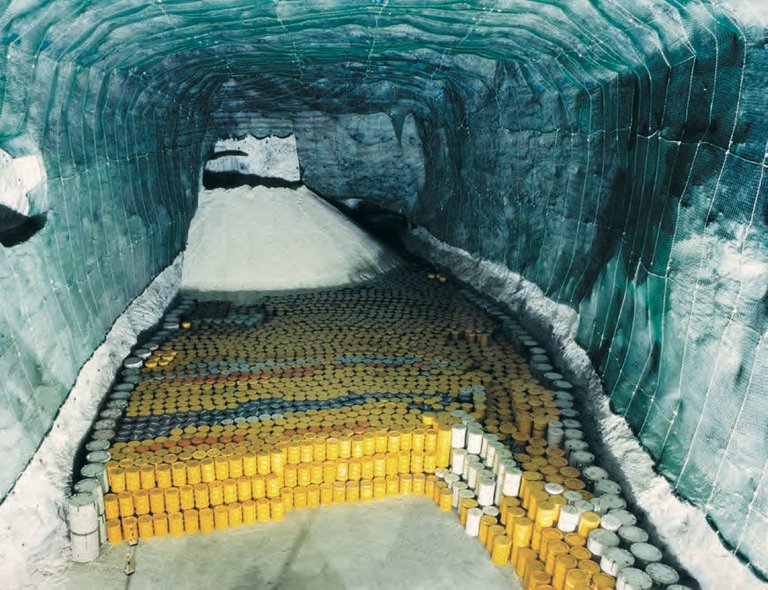
Because the energy is quite high then the storage of this waste is required coating on the process of disposal.
3. Light Radioactive Waste (Low-Level Waste / LLW)
The amount of radioactive waste is very much (up to 90% of total radioactive waste) but the radiation energy is very small (only 1% of the total waste radiation).
Radioactive waste disposal site in Andrews, Texas.
Image credit : www.texasvox.org
Because the radiation energy is very low, no coating is required during the removal and storage of this waste. Generally, radiation from this type of waste has a short decay time.
Examples of Radioactive Waste
Here are some examples of radioactive waste generated from their use in industry and in health and research:
Uranium 234: Waste from Nuclear Power Plant (NPP)
Neptunium 237: Waste from Nuclear Power Plant (NPP)
Plutonium 238: Waste from Nuclear Power Plant (NPP)
Iodine 131: Medical Waste Treatment of Thyroid Cancer
Strontium 29: Medical Waste Bone Cancer Perawatn
Cobalt 60: Medical Waste Radiotherapy
Ir 192: Medical Wastes Prostate Cancer Treatment
Cesium 137: Medical Waste Radiotherapy
Hopefully this paper on "radioactive waste and classification" can provide useful new knowledge.
Thanks!
Thanks a lot, for taking time to read this,
Stop the war, and make a Better World
 #### Reference:
1. World Nuclear Association, “Radioactive Waste Management”. http://www.world-nuclear.org/. June 2017. Feb 21, 2018.
2. Japan Atomic Energy Agency, “Generation and Classification of Radioactive Waste”. www.jaea.go.jp. Feb 21, 2018.
3. Wikipedia, “Radioactive Waste”. www.wikipedia.org. Feb 3, 2018. Feb 21, 2018.
4. Australian Government Department of Industry, Innovation and Science. “Categories of Radioactive Waste”. Feb 22, 2018.
#### Reference:
1. World Nuclear Association, “Radioactive Waste Management”. http://www.world-nuclear.org/. June 2017. Feb 21, 2018.
2. Japan Atomic Energy Agency, “Generation and Classification of Radioactive Waste”. www.jaea.go.jp. Feb 21, 2018.
3. Wikipedia, “Radioactive Waste”. www.wikipedia.org. Feb 3, 2018. Feb 21, 2018.
4. Australian Government Department of Industry, Innovation and Science. “Categories of Radioactive Waste”. Feb 22, 2018.
Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
http://www.world-nuclear.org/information-library/nuclear-fuel-cycle/nuclear-wastes/radioactive-waste-management.aspx