Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid(DNA)
DNA is a molecule in the form of a double helix as a part of the chromosome-forming components present in every living cell. Each piece of DNA thread is a source of specific genetic information, which determines the nature or characteristic of an organism (living thing) called a gena. In prokaryotic cells, DNA threads can always be seen in a cell using an electron microscope whose enlargement is a million times. But in eukaryotic cells, DNA threads can only be seen at the time of the cell in the resting phase, because during the cleavage (Mitosis and Meiosis) the DNA is packed in chromosome form.
Chemically
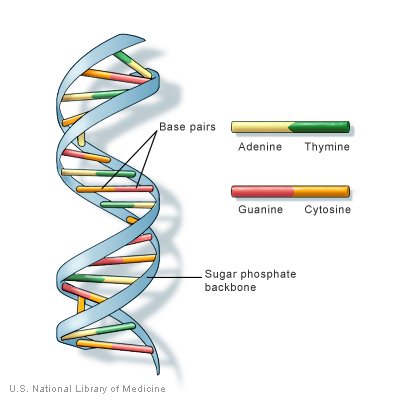
Chemically, DNA consists of four types of chemicals (four basic nitrogen), the pyrimidine group (cytosine and thymine) in pairs with purines (Adenin and Guanin). The intercostal couples are Adenine with Timin (AT) and Guanine with Cytosine (GS) connected by hydrogen bonding, and each base is attached to a sugar molecule linked to phosphate (ribulose-phosphate) groups as a ladder in a spiral thread DNA.For each splitting of two spiral DNA threads can occur the composition of the spouse pair, for example:
- If a spiral strand of DNA on the next chain contains a base G and T only, then the base on the next chain is S and A, so that one fragment of the GSTA, GSTA ..., and so on.
- If the chain next to it is a base of TAS, then next to it is ATG, so one piece has the arrangement of TAATSG, TAATSG ...
- If the next chain there is a base GTAS, then the next base is SATG, then the next base is SATG, so one has a GSTAATATSG base, GSTAATATSG ... and so on.
Thus, only with these four kinds of bases as "genetic codes" can be formed of an infinite number of possibilities to manifest as a kind of gena for the properties possessed by every type of organism. The combination arrangement as well as the amount of alkaline substances in DNA produce "genetic information code". The higher the level of the organism, the more complex the arrangement of combinations of the nitrogen-base pairs.
The duplication of DNA begins with the opening of a double thread of DNA spiral done by an enzyme that destroys the bond between the base pairs, then each part of the DNA thread is formed by a new base pair according to the first code, thus forming two spiral double DNA threads; both new double-spiral threads have an arrangement of base pairs according to the parent. A spiral double thread of DNA produces two new spiral DNA double threads. DNA doubling occurs at the fixed intervention stage of the synthesis. The benefits of DNA duplication so that every child cell inherits the same DNA.
Conclusion
In the case of Mitosis, the child cell inherits an amount of DNA equal to the amount of parent DNA, but in Mayosis only inherits half the amount of parent DNA so that at the time of marriage the male and female gametes continue to produce as much DNA as the parent.
Woow