On March 27, 1987, Chinese scientists in the United States found that there was a change in the temperature of superconductivity in the oxide superconducting material at 240. Soon our company found by Lanthanum Kagoshima university, Japan, strontium, copper, ceramic materials composed of oxygen at 14 ℃ temperature superconducting signs. So can levitating mountains exist in reality?

Science fiction movie "Avatar" mysterious Pandora one of the most unique scenery, is the place of the suspended the Hallelujah Mountains, hanging on the wall between the clouds flying waterfall is how spectacular! A mysterious room-temperature superconductor called Unobtanium suspended the Hallelujah Mountains. In order to plunder these rare treasures, crazy people even at all costs will destroy the home of the Na'vi people. But what about room temperature superconductors? How does superconducting magnetic levitation come about?

Superconducting material
With the help of external forces such as gas, sound, magnetism and electricity, the object can be suspended as long as it can offset the influence of gravity. In the real world, there are a lot of floating phenomena around us. Birds and fish and shrimp use the buoyancy of air or water, and the rocket relies on the thrust of the gas to be suspended, while the superconducting magnetic levitation seems to be the most mysterious.
So what is superconductivity? Superconductivity refers to the phenomenon that some materials suddenly become zero when the temperature drops below a certain temperature. This type of material is called superconducting material, and the temperature point corresponding to the superconducting phenomenon is called superconducting critical temperature. If you pass an electric current on a ring of superconductors and disconnect the loop, the current will continue to flow through the superconducting loop and will not decay. This is because the electrons in the material are already paired at low temperatures, and the electronic pairs are all in step, canceling the possible resistance effects of the motion. If put superconductors in magnetic field conditions, the existence of the superconducting induced current will make superconducting automatic body to form a "compression" "iron cloth shan" block field, effective offset by external magnetic field, caused in superconducting magnetic field is zero. This is another characteristic of superconductors - complete diamagnetism. To the existence of diamagnetic completely, the lines of magnetic force cannot enter inside the superconductor, superconductors to close to the rejection of the magnetic materials have a strong, if the counter gravity repelling force, magnetic levitation is achieved.
In fact, superconducting materials are not rare in real life. Most metals in the periodic table are superconductors, and some non-metallic materials are superconductors under high pressure. Unfortunately, these critical temperature of superconductors are very strict, such as the first discovered in 1911 superconducting critical temperature of mercury in 4 (269 ℃), are close to absolute zero, until 1986, the highest critical temperature of superconductors is niobium alloy (Nb3Ge), germanium is only 23. To achieve such a low temperature depends on the use of expensive liquid helium to cool it, which has brought many limitations to the superconducting experiment, which is far beyond the reach of practical life.
In 1957, physicists Bardin, Cooper and Schriff established the BCS theory of traditional superconductors and successfully explained the superconductivity of metal and alloy. Theoretical physicists predict will not be able to go beyond 40 open superconducting critical temperature (233 ℃). Experimental physicists, however, have not given up on the quest for higher temperature superconductors. Everything comes to him who waits, in 1986, German scientists binel and Swiss scientists mill in normally considered to be an insulator lanthanum barium copper oxygen (La - Ba - Cu - O) ceramic materials were found in 35 (238 ℃) of superconductivity, followed by Chinese scientists by Zhu jingwu, Wu Maokun and Chinese scientists Zhongxian Zhao and others found with 93 open (180 ℃) of YBCO superconducting (Y - Ba - Cu - O) system. Finally, the maximum critical temperature of the copper oxide superconductor is raised to 165 (-108), which is called a high temperature superconductor. The critical temperature of high temperature superconductor enters the liquid nitrogen temperature zone, which greatly reduces the cost of research and application. But people soon discovered that this kind of high temperature superconducting material with ceramic properties and plasticity and low critical current density of birth defects, and the microscopic mechanism of superconducting superconductor is much more complicated than conventional metal, people also no consistent understanding so far. So scientists to speed up the pace of exploration of superconducting materials, superconducting new family have found many, the representative of which is: the critical temperature up to 39 2001 open two mgb2 superconductor by Japanese scientists found; 2008 Japanese scientists found 26 fine wild male show, open superconducting iron arsenic oxide lanthanum (La - Fe - As - O) system, then, the United States, Germany, Japan and other nations in the efforts of scientists in just three months will be critical temperature to 56, and in this family of superconducting found more new members. Such superconductors are known as "iron-base superconductors", and are the largest superconducting family. The continuous emergence of many new superconductors has led to the climax of the field of superconducting research, and the continuous understanding of superconductivity has greatly promoted the research of modern condensed matter physics.
Superconducting magnetic space shuttle (design)
In history, at least 10 scientists have won the Nobel Prize in physics for their research on superconductivity. In the research team of new superconducting materials exploration and superconducting mechanism, Chinese people are more and more numerous, and they have made many important contributions to the research of superconductivity. These days, superconductivity is not identical in microscopic mechanisms, from alloys to oxides, to iron-based superconductors, and even to organic superconducting materials. It seems to imply that "all roads lead to superconductivity". People have every reason to believe that in the near future, scientists could find the critical temperature at room 300 (about 25 ℃) open near room temperature superconductors.
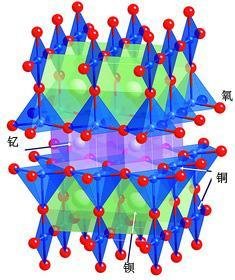
High temperature superconducting material barium copper oxide.
Reprinted from:
A very interesting article! I just shared one on holographic cosmology that may interest you.