Another Day another lection in neuronal Networks.
today we are going on with the third part.
You can find all previous posts in this list:
| Part | Headline | Steemit Link: |
|---|---|---|
| I | Introduction | https://steemit.com/neuronalnetwork/@haggy2k3/neuronal-networks-part-1-introduction |
| II | Units | https://steemit.com/science/@haggy2k3/neuronal-networks-part-ii-units |
| III | Connections | Current Document |
| IV | Inputs | https://steemit.com/science/@haggy2k3/neuronal-networks-part-iv-inputs |
| V | Activities and Outputs | |
| VI | Training and Test | |
| VII | Metrics | |
| VIII | Learning Rules | |
| IX | Types of NN | |
| X | Features of NN | |
| XI | Use Cases | |
| XII | Bonus: Getting started with Membrain |
Connections between units
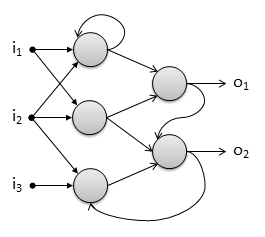
Units are connected to each other by edges. The strength of the connection
between two neurons is expressed by a weight. The greater the absolute value of
the weight, the greater the influence of one unit on another unit.
A positive weight indicates that one neuron exerts an excitatory influence on
another neuron.
A negative weight means that the influence is inhibitory.
A weight of zero indicates that one neuron currently has no influence on another
neuron.
The knowledge of a neural network is stored in its weights.
Learning in neural networks is usually defined as weight changes between the
units. How exactly the weight change is made depends on the learning rule used.
If you like this post and you want to read more please upvote, resteem and/or
follow my blog.
Best regards
Haggy2k3