The solar system is very interesting to discuss, so because the solar system is so wide it comes to the question of whether the solar system has a limit? If indeed where is the limit? As on Earth, we know a country or a city must have a limit. Well in the solar system must have a limit of its final scope, before we will enter the next sphere of another star.
And what is the limit?
The environment in the solar system has limits, but what are the boundaries or lines? In the solar system where there are many planets and also including the Earth, boundaries have systems that must be owned by the Sun that has a very important role. As in the solar wind, sunlight, and solar magnetic field reactions greatly affect this limit.

If the received light fades, then that means the distance of the Sun is very far away. But if the sunlight disappears, where are we going to mark that disappearing spot of light? And what we know there is no limit to when the point of light disappears or dims.
What about the tensile force of the sun? At the attraction of the sun will also happen the same thing !. As the effect of the weakening force of the sun means its distance away from the sun when it tries to bind the object to remain in its system. Nevertheless, there is no definite limitation where the influence of the Sun's attraction forces ceases to affect the objects around it. For now, the Oort Cloud is known to be a cold reservoir of objects called comets located in the outermost areas of the Solar System. In the Oort Cloud's outer areas, the attraction of the Sun that affects the object is also weakened but not totally lost. So it is not really known where the deadline is.
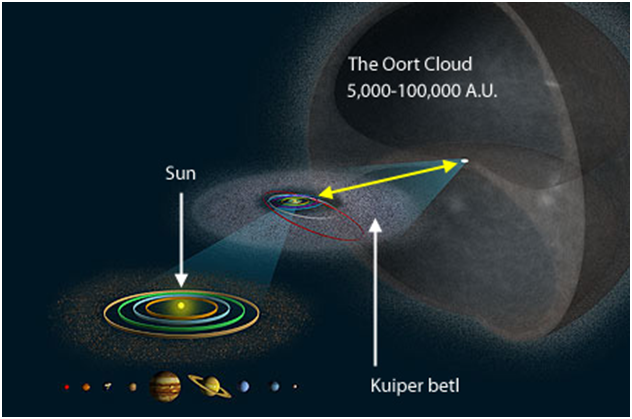
Therefore, then referred to as the limitations of the Solar System is the movement of the Sun Wind, or the material is thrown by the Sun in all directions at a speed of about 1.6 million km / h. The material is a charged particle such as electrons and protons that have a magnetic field of the Sun.
With a speed of 1.6 million km / h, of course, the solar wind will move very quickly across the objects in the Solar System. This wind will cross the planets and leave the Kuiper Belt area where Pluto is located and go to the interstellar space which is more than 16 billion kilometers. This interstellar space is not an empty space but is composed by clouds of different densities and temperatures. The magnitude and direction of the magnetic fields in the interstellar medium also vary.
The clouds in the interstellar medium are composed of frozen hydrogen gas, dust, ionized gases and other materials. The material in this area comes from the rest of the exploding star and/or material from other stellar winds.
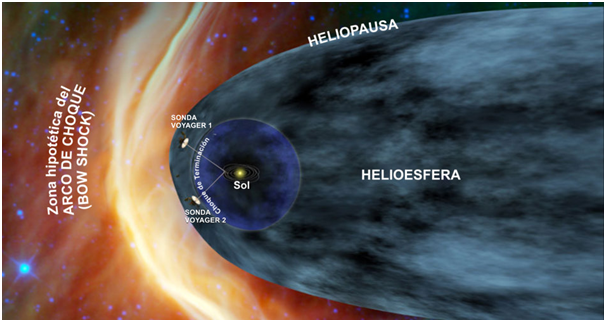
The solar wind that has arrived in the interstellar space will meet with interstellar clouds. When the magnetic field of the solar wind collides with the magnetic field of the interstellar medium, there is no unity or mixing. What happens, the solar wind will push the interstellar clouds and clean the cavities in the interstellar space. The longer the sun's wind drive will become weaker. And when the solar wind is too weak to push further, the solar wind will change and move downstream in the direction of interstellar clouds. As a result, bubbles form in the interstellar space called heliosphere. This bubble also serves as a cocoon that protects the Solar System from various dangers such as galactic cosmic rays that are harmful to life.
The outer boundary of the heliosphere where solar wind power is no longer able to push the stellar winds in the interstellar medium is what we know as heliopause which is also the outermost boundary of the Solar System.
You think the solar system is unique?
In the Solar System, Earth and planets move around the Sun with an almost circular orbit. But it seems the same thing is not common. The planets that surround other stars move in very eccentric orbits. The question is, is it exactly the Solar System that became our strange house?
When astronomers search for, observe and study planets in other stars, it is always this one question that arises: are we special?
Judging from the Copernican principle, the history of practical science is only a series of discoveries that show that we are not unique. Earth is not the center of the Solar System. And the Solar System is not the center of the universe. The Solar System is also one of the many galaxies that exist and may even be a universe that we know is not the only one. The planets found today are only one of the billions that have not yet been discovered.
Indeed if we look further not unique. But on a larger scale, it seems we are unique because we live.
Questions related to the uniqueness of the Earth will not be separated from the questions related to other life in the universe. Does another planet have water? Are the planets found to be in the habitable zone? Do they have a good atmosphere? Is there a tectonic plate there? And the list of questions adapted to Earth conditions will continue to grow longer and at one point the Copernican Principle may be violated. Earth is unique!
One of the things that debate is the structure of the Solar System. Along with the increasing understanding of other planetary systems, the Solar System has not become mediocre but looks unique! It is not yet known with certainty whether the conditions that exist on Earth is the ideal conditions for life. But with only one instance, it seems that other planetary systems are very different from Earth. Until now there is no planet that can be called Earth, is not it?
Having only the Earth and the Solar System, the theory of planet formation was built by examining the information provided by the Solar System. And the discovery of exoplanet actually spawned new questions. In the Solar System we know, giant hot gas planets like Jupiter are far from their parent stars. But in the planetary system in other stars, astronomers actually find it different. Jupiter's hot planet orbits very close to the host star, the planets are found to move around the double star, and the planet moves in a very tall orbit.
In the Solar System, the planets that move around the Sun actually consistently show the small eccentricity of the orbit. This means that the orbits of planets in the Solar System are not oblong but almost circular. Different conditions are shown by exoplanets. Its orbit has a high eccentricity which also shows the shape of a very oval orbit. What is the importance of this orbit?
In the theory of planetary evolution involving multi-planet, the interaction between planets in the system will cause the planet's orbit inside the system is not oval.
Therefore, astronomers then perform tests with exoplanet data, especially systems that have multiple planets, in order to know whether interactions between planets in the system will be able to dampen the eccentricity of the planet's orbit.
Analyzes were conducted on 403 planets found with radial velocity techniques since the observational technique allows for better measurements of the eccentricity of planetary orbits. Most of the systems studied have only one or two planets, but there are also systems with four, five, and six planets. In the analysis, the Solar System with eight planets is also included.
Analysis and modeling results show a negative correlation between diversity and eccentricity. The more planets the system has, the lower the eccentricity of its orbit. In other words, modeling gives results that match the trends that exist in the Solar System. So maybe the Earth is not unique. Deviations occur in one or two of the eccentric planetary systems as predicted. Believed, the system still has other planets that have not been detected causing the eccentricity of its orbit to be low. Thus, it can be concluded that the interactions of the planets in a system contribute to causing the planet to have an almost circular orbit. thanks

BEST REGARDS @irza
Refence :
https://www.space.com/56-our-solar-system-facts-formation-and-discovery.html
http://solarviews.com/eng/solarsys.htm
https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/ibex/IBEXDidYouKnow.html
https://www.smh.com.au/technology/nasas-voyager-1-approaches-outer-limit-of-solar-system-20130628-2p16e.html
https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/solar-system/oort-cloud/overview/
https://space-facts.com/oort-cloud/
https://www.space.com/5595-earth-special-compared-planets.html
https://phys.org/news/2004-08-solar-unique-universe.html
https://courses.lumenlearning.com/astronomy/chapter/orbits-in-the-solar-system/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5068330/
http://sciencenordic.com/new-discovery-small-planets-have-circular-orbits
http://www.planetary.org/blogs/guest-blogs/2014/0505-how-weird-is-our-solar-system.html

Very brilliant read! An unlimitless solar system is what i have grown up with.... The possibilities of it having limit is quite astonishing!
I look forward to more researches on it, earnestly.