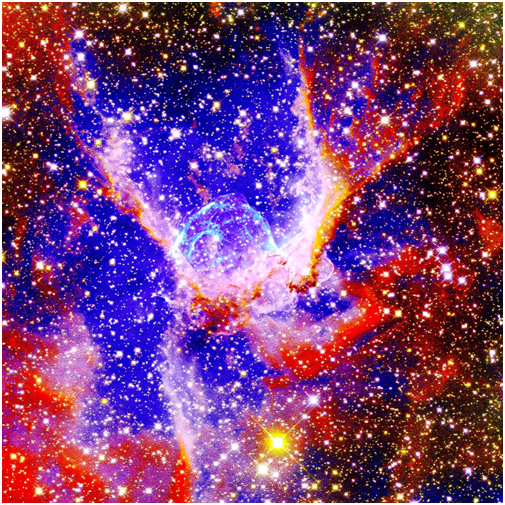
The day we feel love and affection for couples all over the world ... or usually called Valentine's Day and everywhere in the universe! In this illustration will show a pair of stars who spend their days with dancing whirling around their partner. Slowly they became closer. Eventually, they will unite into one star.
However, this story is not as romantic as imagined. About 700 million more years, when the two stars kiss, they will become very strong and cause a supernova explosion! Supernova is the end of life of a star (or two stars in this case) in a terrible explosion.
The star pair is a pair of white dwarfs, the 'remnant' stars left by stars like the Sun when they die. The white dwarf is very small and very compressed. Other remains form a cosmic gas ring called a planetary nebula.
When combined, the stars will contain as much as about twice as much gas in the Sun. Therefore, this pair of stars became the longest white dwarf pair ever found.
A group of scientists who discovered this massive pair originally wanted to solve another problem. They want to find the cause why the remains of stars sometimes do not form a ring but instead shaped strangely. One of the objects they investigate is the cloud. Astronomers unintentionally saw the dying couple were hidden in the heart of the nebula.

However, the star pair is actually contributing to a scientific inquiry, namely by supporting the theory that double stars can cause strange shapes on some nebulae.
A white dwarf is one of the oldest objects in the universe as it is the final stage of the life cycle of most stars, including the Sun.
Cosmos Also Cleaned By Supernova
Supernova is the end of life of many spectacular giant stars. This is an explosion that creates enormous amounts of energy and can shine as bright as a galaxy of billions of stars!
This event is very important because the remnants of an exploding star flew into the air. The material continues to form new stars, planets, and moons-in fact, neither you nor I are made of supernova material!

As it expands, the remaining cloud of star material (called "supernova rubble") sweeps away all the material they encounter and binds to the material.
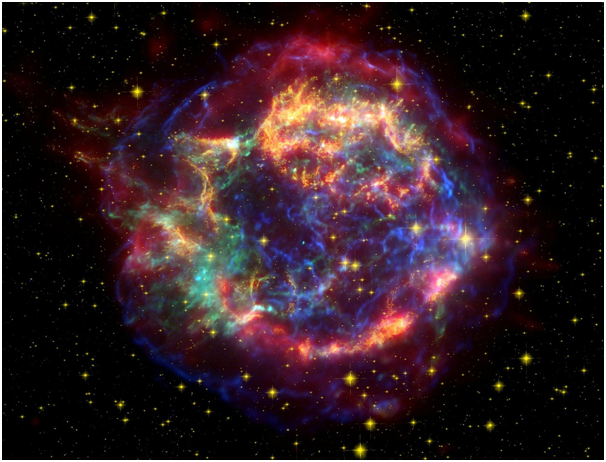
This space photo shows a 2200-year-old supernova rubble that sweeps a lot of matter-enough to form 45 Sun! The picture shows the supernova debris in blue, while cosmic dust is shown in pink.
A large amount of material swept away by these remains may be the first clue that something special happened to this star before it exploded.
Another clue is the temperature of the remains, which are unusually hot and still emit high-energy light, called X-rays. Within 2200 years after the supernova explosion, the swept gas and dust would have cooled.
The last supernova observed in the Milky Way Galaxy was the Kepler Star in 1604 (known as SN 1604).
Unfortunately, we must continue to observe the sky to find the cause of these peculiarities, like scientists still searching for them!

BEST REGARDS @irza
Refence :
https://www.space.com/6638-supernova.html
https://abcnews.go.com/Technology/supernova-making-twin-stars-meet-explosive-death-700/story?id=28856513
https://www.space.com/28507-doomed-stars-crash-supernova-birth.html
https://www.space.com/17715-planetary-nebula.html
http://www.unawe.org/kids/unawe1416/