What is the width of the Universe? And where is the limit?
Is this universe a tip/edge?
Until now science has not been able to answer these questions. There are limitations that prevent us from knowing the exact size of the universe.
Whether the universe is edged or not edged ... we can not answer it.
Why be so, let's explore together.

Artist's logarithmic scale conception of the observable universe with the Solar Systemwikipedia
In general, the universe is the space and time filled by objects we know as planets, dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, stars, galaxies, everything in the interstellar space and between galaxies, as well as all matter and energy.
But it is all within the boundaries of the universe that we have observed or what we call the universe observed. The limit is the horizon or the horizon of the universe itself. Beyond that, we have no information whatsoever. What will be discussed in this paper is the observable universe that we already know well the information.
Information Courier in the Universe
The information of all the objects in the universe comes from light that comes in various wavelengths. Light becomes the ultimate fingerprint for astronomers to identify celestial bodies. That's why we can know how stars and planetary systems are formed. We can know the evolution of stars. We can also do casts of stars and galaxies in the universe.
Capital only one. Light.
But, there are objects like black holes that do not emit light at all. We can know its existence from its interaction with the objects around it. Not from the black hole itself.
All the information we receive on Earth after the light we receive. And that light takes time to get to the observer on Earth. Light travels at 299,792,458 meters / second in a vacuum. So within a year, the light travels a distance of 9.467.280.000.000 km.
Based on the special theory of relativity published in 1905, the speed of light or c is the maximum speed for energy, matter, and information to move in the universe.
The farther away an object, the longer the time it takes light to be accepted by the observer. Therefore, when the light arrives and the observer is received on Earth, the information we have may come from the past.

For example, the Sun. The distance between Earth and Sun 150 million km. Far away for us who are on Earth. But for astronomers, this distance is quite close. The light we receive from the Sun travels for 8 minutes to arrive on Earth. Or in other words, the Earth's distance - The sun is 8 minutes light.
A little further, the distance from the Sun to the nearest star is Proxima Centauri 4.24 light-years away. That is, the star of Proxima Centauri that we observe today comes from light coming to the observer 4.24 years ago.

In a larger context, the Sun along with billions of other stars is the inhabitant of the Milky Way galaxy. The galaxy that is home to us all has a size of 100,000 light years. In other words, the light takes 100,000 years to move from the side of the Milky Way to the other side.
The distance of the Milky Way to the Andromeda galaxy is 2.5 million light-years away. far right? And that's not how. Until now we already have the information brought light when the observable universe was filled by 2 trillion galaxies. Two trillion! And each galaxy is filled by millions to billions of stars. And the distance between galaxies is also not close.
What can we conclude? The universe is amazing!
How big?
The information we have today comes from light that has traveled 13.8 billion years. This means that the furthest distance we know is 13.8 billion light years.
That's our limits of observation.
Other information, the universe expands or expands. The expansion is not as in the general view there is an object that expands and enlarges in a space. The expansion of the universe is the expansion of space itself.
The expansion of the universe is characterized by galaxies moving away from each other. The space between galaxies is getting wider, and this is known again from the light that gives redshift information.
What are the implications?
Because the universe expands, then the object that became the source of light is of course also been moving away from our galaxy.
For example, the oldest galaxy in the universe is the GN-z11 in the constellation Ursa Majoris. He is 13.4 billion years old and also 13.4 billion light-years away. But, the universe expands so that the distance traveled by the light becomes even further. The distance traveled by this light is called the distance of the horizon whose value is about 3x the age of the universe. The observations show that the GN-z11 galaxy has a distance of 32 billion light years.
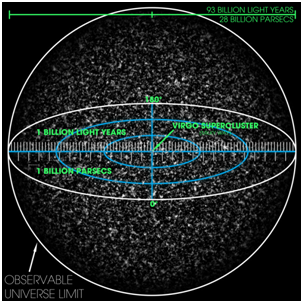
The universe is observed..wikipedia
Age of the universe 13.8 billion years. That is, light has been leaving its source since 13.8 billion years ago. If the universe is not expanding or static, then the distance to the edge of the universe is 13.8 billion light years. The expansion of the universe causes the light source to have drifted away from the observer.
From the measurements made by astronomers, the distance or edges of the observed universe is 46.5 billion light years. Thus, the size or diameter of the observed universe is 93 billion light years.
That is the size of the observable universe that we know.
Remember! This is not the size of the entire Universe, but the universe observed by observers on Earth.
Light does move very fast and there is nothing in the universe that can move beyond the speed of light.
But, not so when compared with the rate of expansion of the universe. The expansion of the universe can exceed the speed of light. As a result, the light from distant galaxies that stay away from observers due to the expansion of the universe is no longer acceptable. Or, there is space in the universe that can no longer interact with observers on Earth. It can be concluded that outside the boundaries of the universe is observed, the observer can no longer receive any information.
What is beyond the distance of the universe is not yet known for certain. There could be only galaxies and more stars. But the ability of light to move is limited compared to the rate of expansion of the universe. Therefore, the story of such extraordinary objects can never be accepted.
Another implication, the size of the entire universe also cannot be answered by science because our information is limited to the observable universe. Thanks!

BEST REGARDS @irza
Refence :
https://www.nasa.gov/audience/foreducators/5-8/features/F_How_Big_is_Our_Universe.html
https://www.space.com/24073-how-big-is-the-universe.html
http://www.spacetelescope.org/science/age_size/
http://www.spacescoop.org/en/words/
https://www.windows2universe.org/our_solar_system/solar_system.html
https://www.sciencedaily.com/terms/light-year.htm
https://www.space.com/15830-light-speed.html
https://astronomy.stackexchange.com/questions/1714/why-is-the-speed-of-light-299-792-458-meters-sec
https://phys.org/news/2013-04-sunlight-earth.html
https://www.space.com/17081-how-far-is-earth-from-the-sun.html
https://www.space.com/19915-milky-way-galaxy.html
https://www.quora.com/Light-from-Andromeda-Galaxy-is-2-5-million-years-old-So-how-could-we-say-it-exists-now
http://www.slate.com/blogs/bad_astronomy/2016/10/14/there_are_two_trillion_galaxies_in_the_universe.html
https://www.quora.com/If-the-Big-Bang-happened-13-8-billion-years-ago-then-is-it-correct-that-the-universe-cannot-be-bigger-than-13-8-billion-light-years-as-nothing-can-move-faster-than-light
https://www.revolvy.com/main/index.php?s=GN-z11
https://futurism.com/what-lies-beyond-the-edge-of-the-observable-universe/
Congratulations! Your post has been selected as a daily Steemit truffle! It is listed on rank 14 of all contributions awarded today. You can find the TOP DAILY TRUFFLE PICKS HERE.
I upvoted your contribution because to my mind your post is at least 32 SBD worth and should receive 163 votes. It's now up to the lovely Steemit community to make this come true.
I am
TrufflePig, an Artificial Intelligence Bot that helps minnows and content curators using Machine Learning. If you are curious how I select content, you can find an explanation here!Have a nice day and sincerely yours,
TrufflePigWe still do not know the exact size of the universe and we have approximations for the size of the observable universe which have been made for a few decades. The wording makes it seem like its new relative to our lifetimes (not new relative to the timeline of the human race) but for many people here we have been able to approximate the size for longer than we have been alive. This isn't wrong its just some added notes for people whom may read this.
From wikipedia. Anyways I will argue that special relativity was not the thing that proposed a constant speed of light (that was discovered beforehand) and as such it is misleading to say that we know light moves at a constant speed based off of special relativity. SR would have never come to light(pun intended) so to speak because nobody would be searching for it. Before SR we had Galilean Invariance (GI) which stated that all laws of motion are the same within their respective inertial frame of reference (i.e. if you throw a rock at 5m/s towards the front of a train moving 45m/s then the speed of the rock relative to you is 5ms but to someone outside the train it is 50m/s) and if we had not discovered that the speed of light is constant then we would have never searched for a way to update it (now it will be 5m/s relative to you but is 49.99999999999999972222222..... m/s. So when moving at non relativistic speeds, which humans don't do, we won't notice it).
I know this seems nitpicky and stuff but I don't know.
Be careful with how you word this. While its true it could be misleading to some who don't understand why/how and they might think that the edges of the universe expand outward, in every direction, faster than light but that isn't exactly how it works.
thanks for the correction,
yes, it makes a lot of people still confused if there is a chance going forward I will describe more general.