Hello everyone ,
Today i'm going to explain you another Interesting topic "The Eye" . Hope you will have a feel that you learned something today :) .
Let's get started ,
Introduction :-
The Eye is the organ of vision which is located in the orbit of the skull.Eye consist of Accessory structures & the Eye ball .In humans, vision is the most important sense, and much of the brain is given over to the processing of visual information.

To be short Eyes are wonderful sensory organs that helps to people learn about the world in which they live .
Accessory structures of Eye :-
- Eye lids , Eye lashes , Eye brows , Lacrimal appartus &Extrinsic eye muscles are the accessory structures of eye .
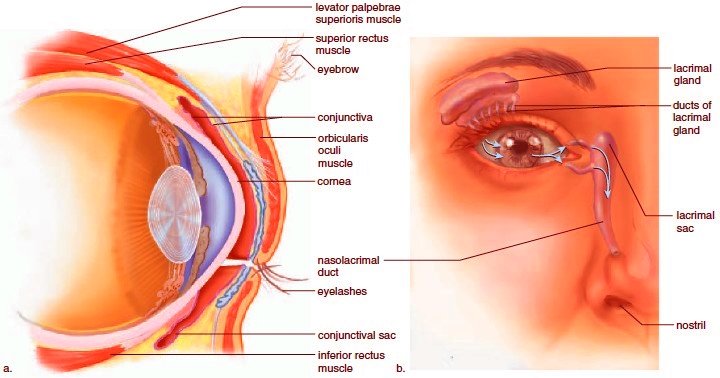
Source - The eye lids , eye lashes & eye brows are useful for the protection of the eye .
The Lacrimal appartus is a group of structures that produce & drain lacrimal fluid or tears which contains salts , mucus & Bactericidal enzyme called Lysozyme. There are Six Extrinsic[Extra ocular] eye muscles present attached to the human eye namely superior , interior, lateral, medial rectus muscles ,superior oblique & interior oblique muscles .These muscles aid in the movement of the eye & they receive their innervations from the 3,4& 6 Cranial nerves.
Eye ball :-
Automatically , the wall of the eye ball can be divided into 3 layers :Fibrous tunic , vascular tunic, Nervous Lunic (Retina). It has a lens which is held in a position by Suspensory ligaments .
Fibrous tunic :-
It is the outer coat of the eye ball consisting of the Anterior corner (acts as a sort of "Fixed lens") & the posterior sclera .The cornea is a Non-vascular transparent coat that covers the coloured iris .Cornea is covered by a thin layer called Conjuctiva .
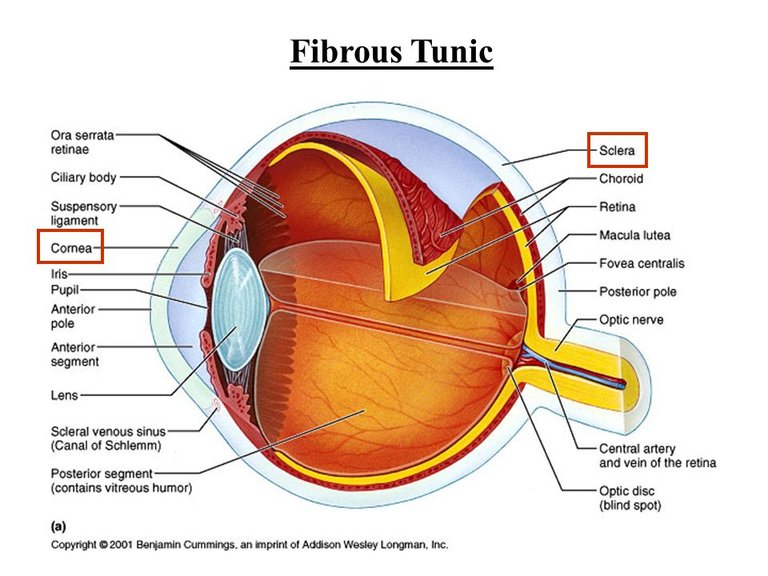
The sclera , white of the eye is a coat that covers the entire eye ball .It gives shape to the eye ball, makes it more rigid & protects its inner parts . At the junction of the sclera & Cornea is a channel known as the Canal of schlemm.
Vascular tunic :-
The vascular tunic is the middle layer of the eye ball . It has # portions : Choroid , Ciliary body & Iris .
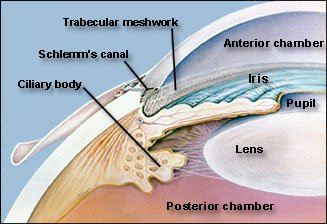
- The choroid is highly vascularized & looks bluish in colour .It is thick in anterior part to form the Ciliary body . It is a pigmented & vascularized part that consists of the ciliary processes.
The muscles associated with the ciliary body is a circular band of smooth muscle that holds & alters the shape of the lens for near or far vision ( Eye accommodation process : The process by which the eye changes optical power to focus on an object as its distance varies ).
- The Iris is the coloured portion of the eyeball. It is suspended between the cornea & the lens is attached at its outer margin to the ciliary processes .
- The aperture in the center of the iris is called pupil. The principal function of iris is to regulate the amount of light entering the vitreous chamber of the eye ball through the pupil . The diameter of the Pupil is regulated by the muscle of the Iris .
Retina (Nervous tunic):-
This is the third & inner coat of the eye. It consists of a pigmented epithelium (Non-Visual portion) & a neutral portion(Visual portion).
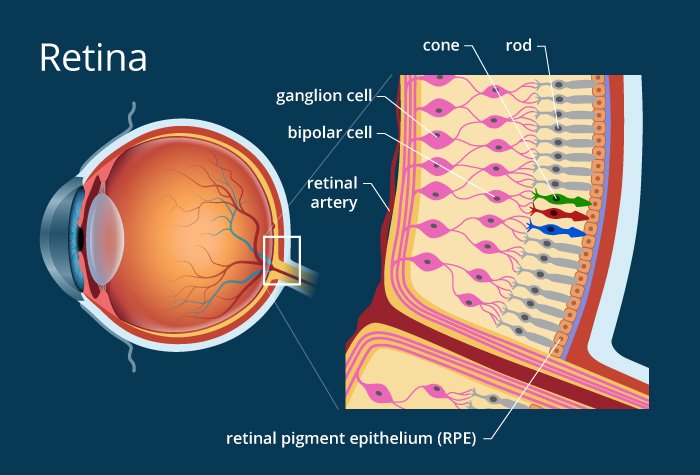
The Pigmented epithelium is a sheet of melanin containing Epithelial cells that lie between the choroid & the neutral portion of the retina . The neutral portion of the retina has three layers of retinal Nervous namely :-
- Photo-receptor layer : The layer closest to the Choroid coat .
- Bipolar cell layer
- Ganglion Cell layer
Note :-
Light must pass through Ganglion layer ,Bipolar cells to reach the photo-receptor cones & rods. Ganglion cells are the only cells of the retina capable of sending " Action Potentials" to the brain .
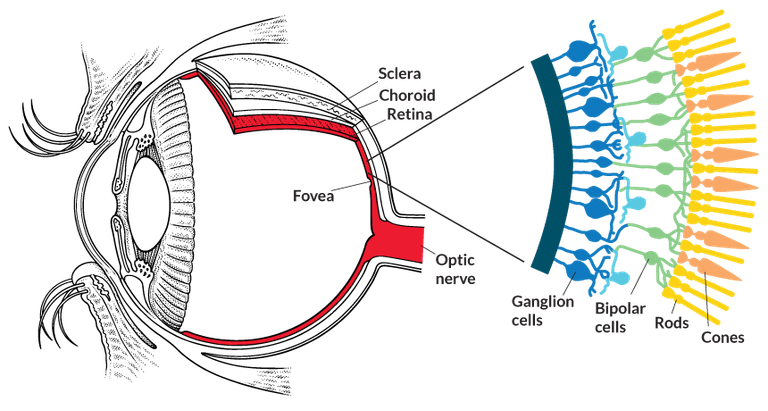
- Rods contain a purplish red protein called the Rhodopsin/visual purple which is formed by the reversible combination of the protein opsin & a light absorbing molecule called "Retinal" Derivation form Vitamin-A.
- Cones contain a visual pigment called Iodopsin & they are important in daylight(Photopic) vision & colour vision .
There are three layers of cones each having different sensitive (difference in light absorption pattern) & they provide 'Optimal response' to Red,Green& blue colours .Equal stimulation of all the cones produces a sensation of white colour Trichromacy Theory . The center of the posterior portion of the retina is called the macula lutea or yellow spot .
A small depression present in the center of the yellow spot is called Fovea centralis & contains only cones .Fovea is responsible for sharp central vision , which is useful while walking , Reading & Driving etc.,
The site of retina where the optic nerve exists the eye ball is called optic disc or blind spot which is devoid of Photo-receptor cells ( No image is formed at that spot).
lens:-
A Non-vascular & transparent lens is present within the cavity of the eye ball just posterior to the pupil & iris . The lens is held in position by encircling suspensory ligaments . Ciliary muscles controls the shape of the lens helping focusing light of the retina .
Chambers of Eye's Interior :-
The interior space of the eye ball is divided by the lens into Anterior & posterior chambers .
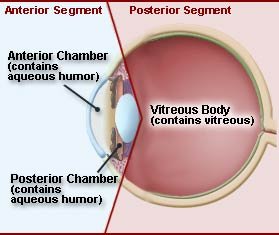
The Anterior chamber is filled with Aqueous humor ( secreted by Ciliary processes) which helps in neurishing the lens & corner.
The posterior cavity lies between the lens & the retina & contains a jelly like substances called vitreous body or vitreous tumor .
The vitreous body contributes to the aqueous humor & helps to protect the shape of the eye ball .
Mechanism of vision :-
The light rays of visible wave length focused on retina through the cornea & lens generate potentials (Impulses ) in rods & cones .
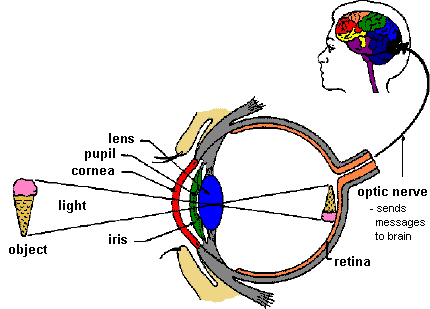
As mentioned as earlier , the photosensitive compounds(Photo pigments) in the human eye are composed of opsin( a protein) & retinal .Light includes dissociation of the retinal from opsin resulting in changes in the structure of the opsin .This causes changes in membrane permeability as a result action potentials develop . These action potentials(Impulses) are transmitted by the optic nerve to the visual cortex area of the brain where the Neural impulses is analyzed.
References :-
- Fibrous tunic
- Nervous tunic
- Mechanism of vision
- Anterior & posterior chambers
- Ganglion layer
- Bipolar cells
- Pigmented epithelium
- Lacrimal appartus
- wikipedia

Awesome .... @meghana123 detail explanation :)
The eye is really one complex organ. One cannot overlook the mechanics around it, it is more than meets the 'eye'.
Nice post, upvoted and resteemed
nice eye
wow this is amazing and enlighten