The Mariana Trench, a crescent-shaped scar geologic feature, is the most profound feature in Earth's oceans and remains in the edges, yet to be explored to its full potential. The Challenger Deep is the deepest part of the trench, comprising of a maximum depth of 11,000 meters which lies towards the West Pacific ocean. The trench is one of extreme nature where crushing pressure, freezing temperatures along with perpetual darkness coalesce, aiding in forming an environment ranging between -525 to 270 Celsius, which is similar to another planets surface.

The Mariana Trench, is formed due to the complex geological phenomena that occur within our planet. The region comprises of tectonic plates, the pacific plate along with the smaller Mariana Plate, that are undergoing forced convergence along with volcanic constructions, which lead to the formation of the trench and the Mariana islands. The trench is in the same location of the horseshoe like Pacific Ring of Fire, that has immense seismic activities and many volcanoes.
With the recognition of its remoteness, the Mariana Trench has witnessed several scientific explorations. Jacques Piccard and Don Walsh made the first manned descent into the trench when they submerged aboard Trieste in 1960. Their voyage down to Challenger Deep was one of the greatest achievements known to man, it was summed up to be the Great Moon Landing. Thereafter, a few manned and unmanned explorations have been conducted into the deep waters in a bid to unveil its secrets.
Remarkably, the Mariana Trench has an ecosystem despite the sheer level of organisms that have evolved which is able to sustain itself. These organisms include massive amoebas, fish that live in the deepest parts of the ocean, and an array of invertebrates. Additionally, there are hydrothermal vents within the trench whose communities of creatures rely on chemosynthesis as opposed to photosynthesis along with photosynthetic organisms. All these findings have contributed to the discussion and the current level of understanding that humanity has in regards to the ability of life to adapt and survive as well the chances of life being present in other planets.
The trench is important to the global carbon cycle since it is a carbon sink. In other words, it stores carbon through the organic materials that are transported from the surface of the Earth and buried into the trench for a long time. This process aids in the maintenance of the Earth’s carbon dioxide concentration by balancing the climate system. The trench, however, has not avoided the effects of humanity. The most distant parts of the planet are still impacted by human behavior, as shown by the presence of pollution such as plastic trash in the trench.
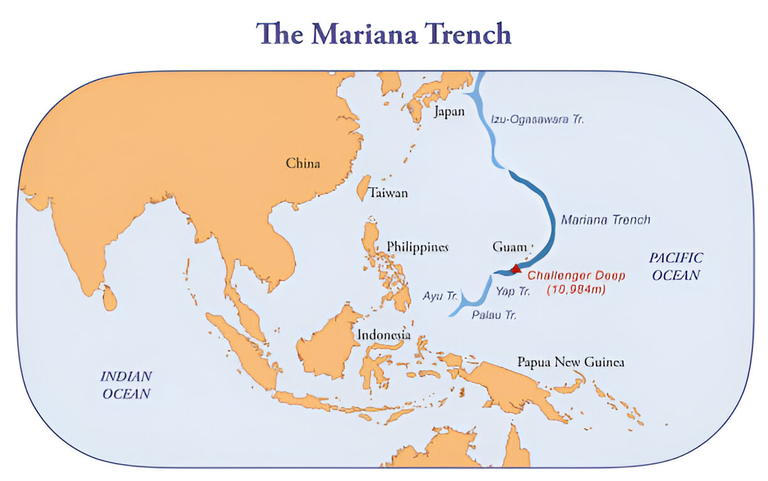
Research into the Mariana Trench is still placing extreme demands on technical resources and human resilience. The development of submersibles has made it possible to visit the trench more often and view finer details. These missions have enhanced our understanding of the geology and biology of the trench, as well as rekindled the desire to discover more about the so-called 'mystery.'
The Earth’s ever changing nature and the tenacity of life is encapsulated by the existence of the Mariana Trench. It poses the questions of what the limits of living beings are and how human activity is affecting this planet. Such mysterious borders show that our oceanic world is even more highly developed than we thought. The trench emphasizes the need to comprehend and conserve our oceans more effectively since they play an integral role in the existence of our planet.
The ocean is never explored fully yet and it holds dark secrets now one would ever think about
Congratulations @munawar1235! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
Your next target is to reach 26000 upvotes.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP