Science fiction lovers will certainly not be unfamiliar with the book “The Nerve Wanderer.” This novel opens up the “digital punk” literary category, and the far-reaching film influenced by this science fiction novel is even better known. That is the "Matrix." This novel uses the background of the future Chiba City of Japan to describe an unprecedentedly developed world of computer networks. In this kind of world, bioengineering technology is advancing by leaps and bounds. Humans can connect their self-awareness with the computer network and give up the body into the control space for a wonderful adventure.
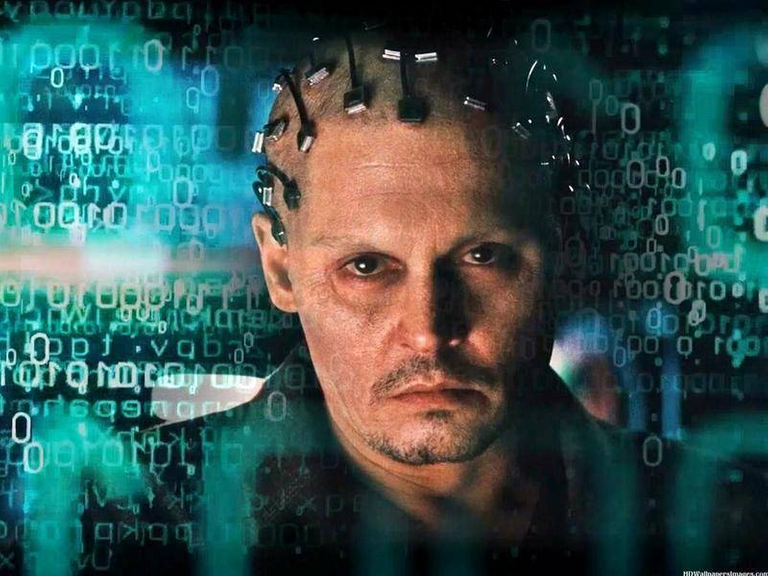
In Johnny Depp's 2014 film Transcendence, the brains of the dead AI expert (Johnny Depp) were copied by his wife to the computer network, which allowed him to be reborn in the virtual world. The episode of “awareness upload” has appeared in many science fiction works. In fact, it is also a common segment of “digital punk”.
But the most common bridge section in science fiction novels is that humans often have to work for decades or even hundreds of years before they can sleep. It is really difficult to replicate the human brain that sounds like a magical reality technology. However, we may wish to discuss this technology.
Is it not feasible to copy the brain?
In principle, it is feasible. The brain is an extremely complex collection. The human brain consists of 100 billion nerve cells, which is equivalent to the number of stars in the Milky Way. The number of synapses connecting nerve cells exceeds 100 trillion. Although the number is large, they are limited and can still be clarified.
There is a line in "Transcendence": "Thinking is an electronic signal mode." Although it sounds unbelievable, it will be true if I go back and see high school textbooks on biological sciences. All our senses, including hearing, sight, smell, touch, etc., are transmitted to the brain as electrical signals. And we all know that the electronic signal mode can be run on a computer.
In theory, it is also feasible. The physicist Stephen Hawking who had recently passed away said: “I think that thinking is a program stored in the brain, just like a computer, so theoretically we can copy the brain into a computer and provide a way to The way we live.” We can imitate the physical, chemical, and electronic structures of the human brain and enter all parameters into the computer to produce output that is similar to the real human brain, such as controlling virtual limbs, features, and other organs.
Smart relativity analyst Lei Yuxian talks to you about several techniques for replicating the brain.
- 3D printing brain
In 2015, at the US SXSW Science and Technology Conference, Theodore Berger, a professor at the University of Southern California, announced that through the artificial hippocampus, the “nearly perfect” conversion of short-term memory to long-term storage memory was completed. This technology can complete the backup of human brain memory. And copied to other people's brains, but given the complexity of the brain, such a bold attempt is accompanied by a very high risk. A slight carelessness can lead to epilepsy, delusions, illusions, or even complete loss of consciousness.
This year, MIT researchers used 3D printing technology to replicate the most accurate brain model. The breakthrough of this technology lies in the fact that researchers have combined 3D printers with brain imaging technology and performed 3D printing.
CT scans are very high resolution and produce fine-grained images that reflect all activities in the brain. However, because of the defects of 3D printing technology, grays are often turned into white or black during the printing process, and details cannot be seen. Therefore, the researchers decomposed each gray pixel into finer points, which are black or black. White, so that 3D printers can record images based on the very small ratio of black to white pixels, and finally get a more satisfactory result.
By printing the brain in 3D, it will help people reconstruct the brain structure, understand the brain network form during the development, and help to understand the mechanism of action of some difficult-to-cure diseases, such as how Alzheimer's disease affects the brain network.
- Holographic brain modulation
Also this year, researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, have developed a new device that projects holographic images onto brain cells. This new device is called a "holographic brain modulator," which uses holographic projection to activate or suppress certain neurons. Its ultimate goal is to control a large number of neurons at the same time, so that they present patterns of real brain activity, thus achieving sensory replication. In the future, we can use this technology to edit memories, remove pain, and implant non-existent images.
At present, the "holographic brain modulator" technology is still in its early stages, but the prospects can not be ignored. The researchers used mice to do an experiment. The experimental target was a small three-dimensional brain area of the mouse, containing 2,000 to 3,000 neurons. Among them, each neuron is supplemented by a virus that contains a certain protein. When it is struck by a flash, the protein activates neurons.
Subsequently, the researchers used computer-generated holographic images to create 3D patterns and projected the images on the surface tissue of the somatosensory cortex of the mouse - a tactile, visual, and motorized brain center. Researchers monitored the rats' brain activity in real time and found that their brain activity was the same as that caused by real sensory stimuli.
The equipment required for this technology is very large and can only act on a small area. But once this technology is developed, we can use this technology to edit memories, remove pain, implant non-existent images, and even debug the brain by monitoring brain activity. For example, blind people can see the world and make limbs less healthy. The elderly people traveled all over the country, and so on.
- Living brain preservation
A U.S. startup called Nectome plans to save the living brain of humans and upload it in the future. The company first cryopreserves the brain. Next, they need to wait for the further development of science and technology, and then change all the information stored in the brain, such as feelings and knowledge, into a digital existence, realize consciousness uploading, and ultimately realize human eternal life. .
Lei Yu, an analyst with the theory of intelligence relativity (aixdlun), once wrote an article about freezing human bodies, which mentioned that the golden time for freezing human bodies is 2 minutes to 15 minutes after death. However, this technology for the replication of living brains does not differ significantly from that of frozen humans. The only difference is that this brain-preserving technology needs to be performed when the person is still dead.
The three technologies mentioned above, no matter from what point of view, are not really copying the brain. There are still many technical barriers that have yet to be overcome. For example, in the 3D printing brain, even if humans really print out every subtle structure perfectly, they may not be able to start because of lack of understanding of the brain, and holographic brain modulation is still in the early stages of development, and its technology is far from being applied. To people. As for the preservation of living brains, it is obviously akin to the affluence of the rich people of Utopia.
At the same time, there have been different voices in the academic world for copying the brain. Some scientists believe that the consciousness of the human brain cannot simply be copied because most of its important features are the result of unpredictable, nonlinear interactions between billions of cells.
If a technology is controversial for a long time, but it has been developed methodically (at least, the official saying goes), there is no doubt that there is certainly a steady flow of support from various stakeholders behind it. After all, for some well-to-do rich people, what they care more about may not be money, but how to achieve longevity. Do not believe you go to Google, "rich", "eternal life", you will find too many rich people in the tangle.
We do not discuss whether the replication of the brain can really achieve eternal life. Only if consciousness exists, can we be called eternal life but also be open to question. If the copy of the brain can better overcome the disease, can be used to save lives, everyone can enjoy the dividends of technology, then it is undoubtedly worth encouraging.
in conclusion
Finally, it ends with the “brain in the brain.” It comes from “rationality, truth, and history” and was proposed by Hilary Putnam. Specifically described like this:
One person (presumably yourself) was underwent surgery by a mad scientist. His brain was removed and placed in a tank containing a brain-sustaining nutrient solution. The nerve endings of the brain are connected to a computer. The computer sends information to the brain according to the program so that he can maintain all normal illusions.
For him, it seems that people, objects, and the sky still exist, and their own movements and feelings can be input. The brain can also be input or intercepted (cutting out the memory of the brain and then typing in the various environments and daily lives that he may experience). He can even be coded and "feel" that he is reading an interesting and absurd word here.
Are you really convinced that your brain has not been copied, modified, or deleted?
Please leave your opinion?


wow, how did you get so smart? I took a philosophy class called "philosophy of mind" or something like that, hilary putnam was mentioned... the thought of copying or replicating the brain is beyond boggling to me
peace