
Chemical Composition of Coffee
Structure of Caffeine

The reason why coffee tastes bitter is mainly due to three compounds namely chlorogenic acid lactones, phenylindanes, and melanoidins which are formed via the reaction between proteins and sugars upon roasting known as Maillard reaction. But as mentioned, its key stimulant is caffeine whose structure is shown at the right. If you have taken organic chemistry, you'd notice it contains three methyl groups (-CH3) and 2 carbonyl groups (=CO) which are attached to a purine group hence it's systematic name is 1,3,7-Trimethylpurine-2,6-dione. The numbers indicate the position of the carbon atom in the double-ringed purine.
Why We Feel Sleepy?
Structure of Adenosine
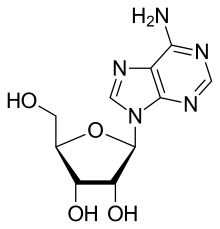
To understand how coffee keeps us awake, we need to understand why we feel sleepy in the first place. When we are awake, a chemical called adenosine is gradually released by the brain which will then bind to receptors. The more adenosine bounded to the receptors, the more tired your brain would feel. As time goes by, more and more adenosine is there which creates a sensation of wanting to go to sleep. Without adenosine, you would not feel sleepy even after reading several chapters of the book you have an exam on. That may sound a good thing but actually, adenosine is important signal for you to get some rest. Conversely, after a good sleep, the concentration of adenosine declines which translates to sensations of wakefulness.
How Caffeine Fights Sleepiness?
Once you drink coffee, the caffeine goes to the bloodstream and find its way to your brain. Now, notice that both adenosine and caffeine contain two conjoined rings with four nitrogen atoms called purine group. Due to this striking similarity, caffeine can block adenosine from binding to the receptors which prevents the latter from inducing the sleepy sensation as intended. If we consider it like an enzyme, this process is called competitive inhibition.
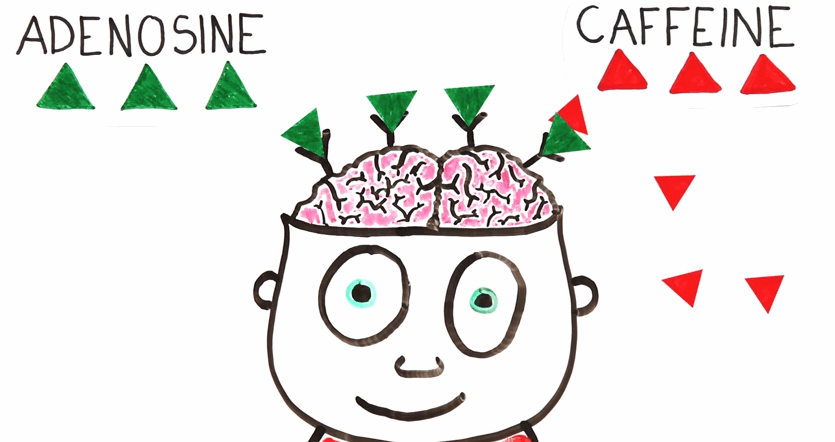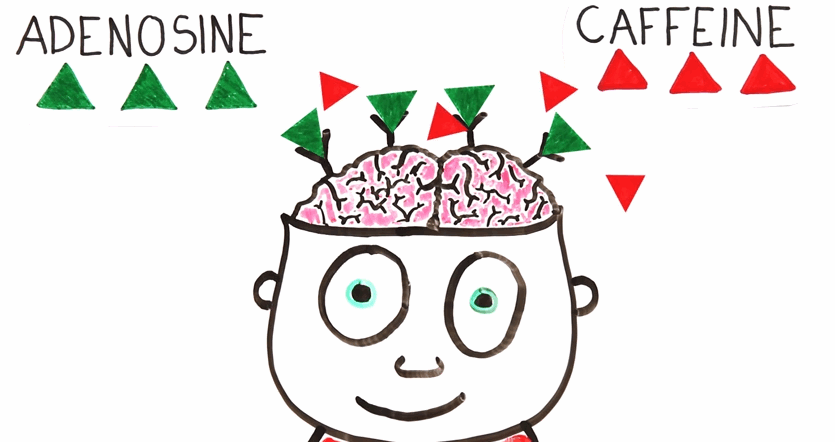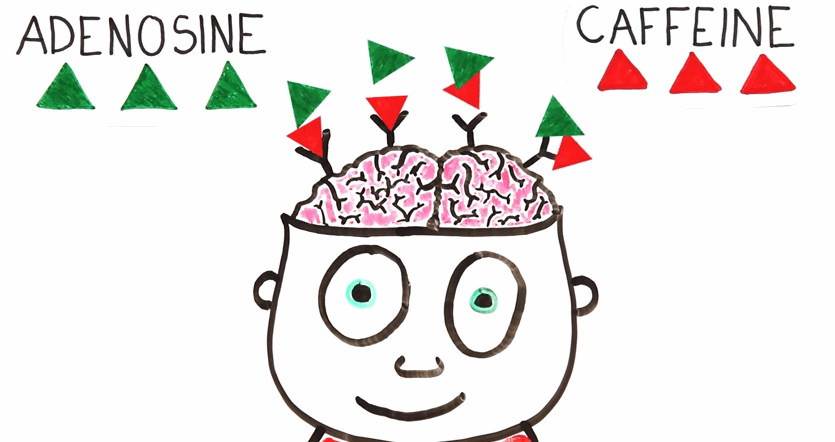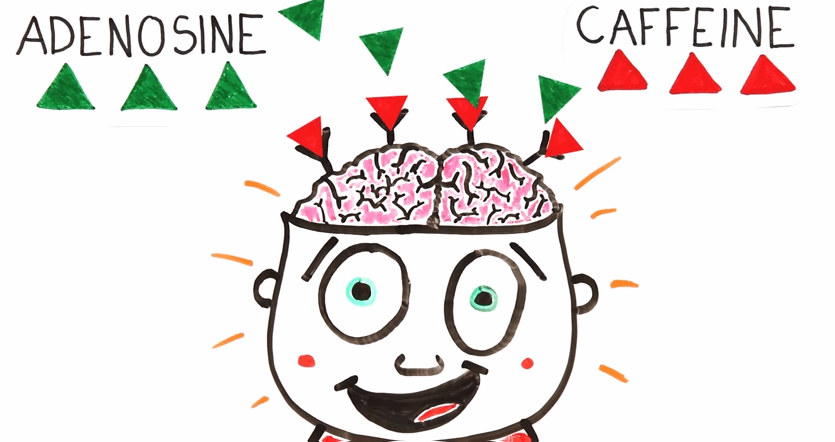
How Caffeine Works
Once this happens, stimulating brain chemicals such as dopamine (a.k.a "happy molecule") and serotonin (a.k.a "self-esteem molecule") are also released giving you a state of mental alertness and positive mindset. Research also indicates that caffeine improves learning by up to 10% and found to cure headaches and migraines. So yes, caffeine works like miracles.
What If You Drink Coffee Too Often?

With frequent and long-term consumption of caffeine, the body adapts by forming more adenosine receptors which translates to more caffeine molecules required to induce the same mental alertness as what it used to. Conversely, if you stop drinking coffee, you would tend to feel more tired and sleepy than what you used to known as withdrawal symptoms which essentially makes you "coffee-addict".
How Much Is Too Much Caffeine?

Researchers estimate the deadly dose of caffeine to be around 150 mg per kg of body weight. Since an average cup of coffee contains 150 mg, this means that if you weigh 60 kg, you need to drink 60 cups of coffee all at once would be enough to kill you. However, drinking such amount at once is quite not possible since it cannot physically fit inside your stomach. Hence, coffee overdose is highly unlikely but its long term effect may put you at risk of being dependent on caffeine to function normally throughout the day.
Summary
Coffee is the most consumed brain stimulant in the world and is known to enhance learning performance and productivity by up to 10%. The active stimulant in coffee called caffeine induces alertness by blocking adenosine from binding into the brain receptors. This process also stimulates the production of dopamine and serotonin which is responsible for "feel-good" sensations making coffee addictive if taken frequently for prolonged periods. Hence, drink moderately!
Image Sources
Sources
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/coffee-brain
https://www.cnet.com/news/this-is-your-brain-on-caffeine/
http://www.compoundchem.com/2014/01/30/why-is-coffee-bitter-the-chemistry-of-coffee/
https://www.chemistryworld.com/feature/chemistry-in-every-cup/3004537.article
https://lifehacker.com/5585217/what-caffeine-actually-does-to-your-brain
@originalworks
great content! I can't last a day without coffee. haha..
so you're a caffeine addict. haha
Great content. Keep it up!
me: goes to the pantry to get some coffee
Thanks. Just finished my coffee too.
We all know how much we love our coffee. It was a fun read.
Thank you. Cheers coffee lovers!
Es increíble como algo tan común y del día a día, realmente sea algo tan complejo.
Nuestro organismo no deja de sorprendernos y es bueno saber el porque de las cosas. Excelente post
De hecho, nuestro cuerpo es más complicado de lo que pensamos. Gracias por leer!
Peace, Abundance, and Liberty Network (PALnet) Discord Channel. It's a completely public and open space to all members of the Steemit community who voluntarily choose to be there.Congratulations! This post has been upvoted from the communal account, @minnowsupport, by ruel.cedeno from the Minnow Support Project. It's a witness project run by aggroed, ausbitbank, teamsteem, theprophet0, someguy123, neoxian, followbtcnews, and netuoso. The goal is to help Steemit grow by supporting Minnows. Please find us at the
If you would like to delegate to the Minnow Support Project you can do so by clicking on the following links: 50SP, 100SP, 250SP, 500SP, 1000SP, 5000SP.
Be sure to leave at least 50SP undelegated on your account.