Hello everyone I'm back here again to explain you the basic concept about parasites which disturbs human immune system.
Introduction :-
At least 1/3rd of all animal species are estimated to be parasites according to one estimation. It is stated that the single most 'undiagnosed health challenge' in the history of the human race is 'parasites '. More than 130types of parasites are known to invade humans as hosts. Parasitism is described as a 'silent epidermic'. Most of the parasites tend to disturb the immunological system.
Diseases such as malaria, polio, plague, amoebiasis, dengue, filariasis, taeniasis, are more common in the tropical countries.

Parasitism and parasitic adaptations :-
An intimate association between two organisms of different species in which, 'one is benefited and the other one is often adversely affected' is called 'parasitism'.
The word parasitism was derived from a Greek word 'parasites' which means 'one eating at another one's table'.
The organism that obtains nourishment is called the 'parasite' the gainer and the organism from which the nourishment is obtained is called the 'host' the loser.
Types of parasites:-
Based on the interaction between the host and the parasite, various types of parasites are recognized. Some of them are listed below.
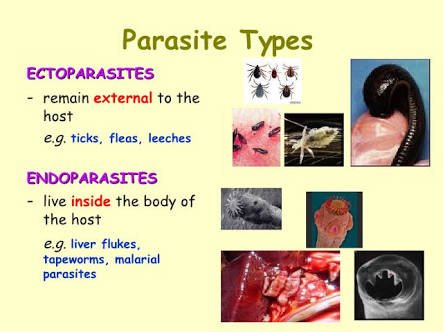
- Ectoparasite:-
A parasite that lives on the surface of the hosts body is called ectoparasite
Ex:- head lice and itch mites on human, ticks on dogs, copepods on marine fishes, etc
Source - Endoparasites:-
A parasite that lives inside the body of the host is called endoparasite.
Ex:- plasmodium vivax in man, wuchereria bancrofti, ascaris lumbricoides. - Hyperparasite:-
It is a parasite which lives in/on the body of another parasite.
Ex:- nosema notabilis lives in sphaerospora polymorpha which lives in the urinary bladder of toad fish. - Monogenetic parasite:-
It is a parasite which completes its life cycle in only one host.
Ex:- entamoeba histolytica, ascaris lumbricoides, etc - Digenetic parasite:-
It is a parasite which requires at least two hosts to complete its life cycle.
Ex:- plasmodium vivax, wuchereria bancrofti, etc .
Source
Types of hosts:-
- Primary host or definitive host:-
It is the host that harbours the adult stage or sexually mature stage of a parasite or the host in which the parasite undergoes sexual reproduction.
Ex:- man for wuchereria bancrofti - Intermediate host or secondary host:-
It is the host that harbours the developing 'larval or immature or asexual' stage of a parasite or the host in which the parasite undergoes asexual reproduction.
Ex:- man for plasmodium, female culex for wuchereria, etc. - Reservoir host:-
It is the host that lodges the infective stages of a parasite in its body when the human host is not available. In the reservoir host, the parasite neither undergoes development nor causes any disease.
Ex:- monkey for plasmodium, African antelope (gnu) for trypanosoma gambiense, etc.
Effects of parasites on hosts:-
In general, the parasites cause weakening of the body of their hosts by causing the deprivation of nutrients, fluids and metabolites as they complete with their hosts for the same. They may also cause pathological effects in their hosts such as
- Parasitic castration:-
Some parasites cause the degeneration of gonads of the host, making it sterile. This effect is called parasitic castration. - Neoplasia:-
Some cause an abnormal growth of the host cells in a tissue to form new structures. This effect is called neoplasia which leads to cancers. - Gigantism:-
Some parasites cause an abnormal increase in the size of the host. This effect is called gigantism. - Hyperplasia:-
Some parasites cause increase in the number of cells. This effect is called hyperplasia. - Hypertrophy:-
Some parasites cause an abnormal increase in the volume/size of the infected host cells. This effect is called hypertrophy.
Most of the parasites cause various types of diseases like
- African sleeping sickness by trypanosoma gambiense
- Delhi boils/ Tashkent ulcers/ oriental sores by leishmania tropica
- Kala azar/ dum dum fever/ visceral leishmaniasis by leishmania Donovani
- Malaria by plasmodium sps
- Elephantiasis by wuchereria bancrofti


Very Important An Article I like it very much. Will be useful in the future.