These tattoos, considered the oldest in history in two Egyptian mummies, which are about five thousand years old.
With the use of infrared technology, researchers found a series of tattoos on two mummies at the British Museum in London.
For a preservation and research program, the mummies were analyzed with computerized tomographies and infrared technology in search of modifications in the body, it was then that they found tattoos in two of them: Gebelein Man A and Gebelein Woman, which are exhibited in the British Museum for almost 100 years.
The tattoos that were found in the mummy known as Gebelein Man A are in one of his arms and show three animals, which appear to be two long-tailed bulls with large horns and a sheep. Both species were known during the period in which the now mummified individuals lived.
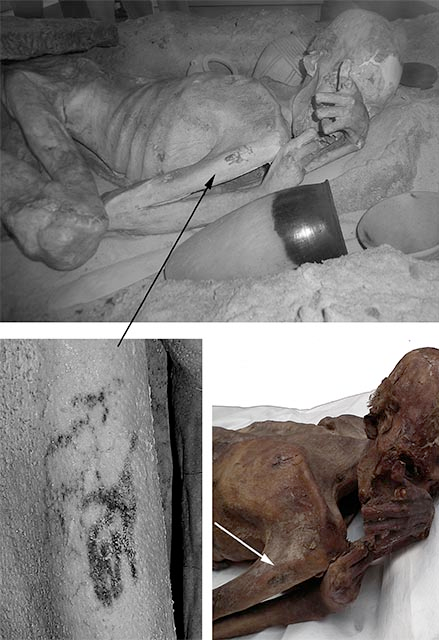
The tattoos of the second mummy, Gebelein Woman, are a series of four "S" shaped figures, placed vertically on the right shoulder. Below these, a mark was found in the form of a line, similar to objects that were used to decorate ceramic pieces.
The tattoos
The application of marks on the skin has been a cultural activity that have their origins in ancient societies. The tattoos on these mummies demonstrate the presence of this tradition in the predynastic period of Egypt, in the years 4000- 3100 BC.