Tartrazina: veneno legal

(Fuente)

Los edulcorantes y colorantes artificiales son muy utilizados en la industria alimentaria ya que le dan al alimento un sabor y color agradables y llamativos. Los colorantes artificiales son más utilizados que los naturales porque, en general, éstos tienen menor poder de coloración, son más delicados e inestables frente a otros compuestos y el ambiente y requieren una mayor dosificación, lo que aumenta el costo.
Sin embargo, es preocupante que en varios estudios científicos se evidencie la relación que tienen algunos colorantes artificiales con perjuicios en la salud de sus consumidores, como es el caso de la tartrazina [1]. Por ello es muy importante el control de calidad de los alimentos y la aplicación de la regulación de los colorantes artificiales en los alimentos que se consumen a diario puesto que la mayoría de etiquetas de alimentos y bebidas no registran su contenido exacto.
¿Qué es la tartrazina?
La tartrazina, también conocida como colorante amarillo no. 5 o E102, es un polvo naranja soluble en agua utilizado en productos alimenticios, cosméticos, drogas y fármacos. Pertenece al grupo de colorantes azoicos (doble enlace entre N) y su uso esta prohibido en Noruega. Su ingesta máxima debe ser de 7,5 mg / kg peso corporal.
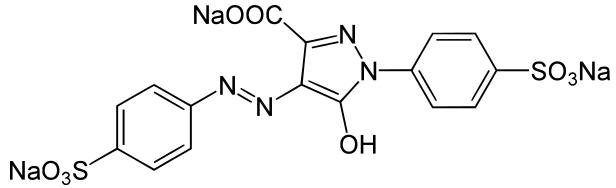
Estructura de la tartrazina (Fuente)

Este colorante presenta el reporte más alto de reacciones adversas a aditivos alimentarios en los primeros 10 años de vida del consumidor en Gran Bretaña y puede provocar asma en personas intolerantes al ácido acetil salicílico, el agente activo de la aspirina [2].

Productos en los que se encuentra la tartrazina

¿Cómo se identifica la tartrazina?
Como es importante determinar si un alimento tiene o no tartrazina y en caso de que sí, en qué cantidad, uno de los métodos para cuantificarla se basa en el uso de nanopartículas de plata (AgNPs) como catalizadores en la reacción de oxidación de la tartrazina por yodato de potasio.
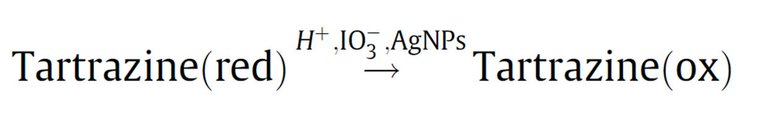
Reacción de la prueba de cuantificación
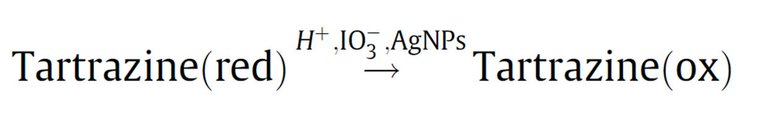
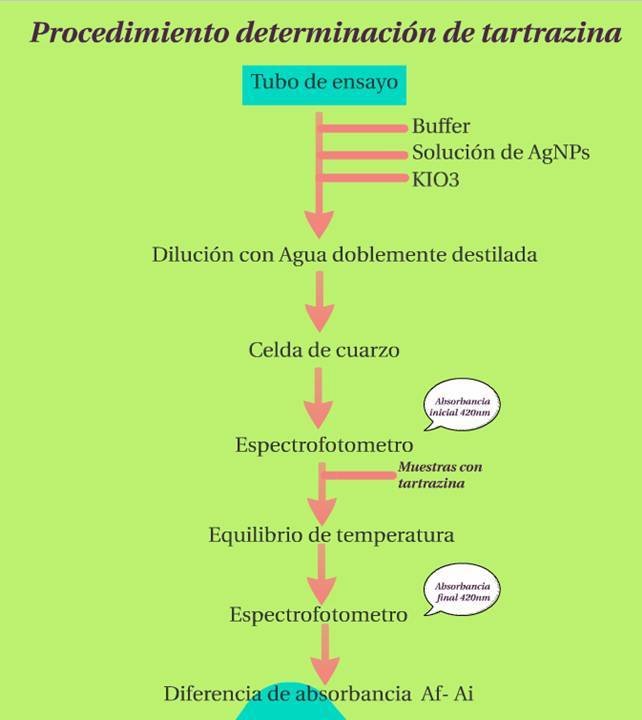
Procedimiento de identificación (Fuente propia)

Como se muestra en la imagen anterior, primero se somete una muestra de alimento o bebida a la reacción oxidativa, para luego cuantificar la tartrazina oxidada, ya que tiene una coloración café oscura y puede leerse a una longitud de onda de 420 nm. Al obtener el espectro se determina por medio de un software el área bajo la curva del patrón y de la muestra oxidada y con ayuda de una ecuación lineal calculada de una previa corrida en el espectrofotómetro de cantidades de tartrazina conocidas, se determina la cantidad de ésta en la muestra.
Cúrcuma como colorante natural alternativo

Tartrazina vs. Cúrcuma (Fuente)

La cúrcuma es una de las especias con más propiedades, beneficios o indicaciones medicinales. Es utilizada desde hace más de 4000 años como condimento y colorante y cuenta con numerosas propiedades beneficiosas para la salud como:
Antiinflamante: Alivia el dolor en personas con artritis, por ejemplo.
Anticoagulante: Previene la formación de coágulos en la sangre ya que limita la agregación plaquetaria mejorando así la circulación y previniendo la arterosclerosis.
Elimina toxinas: Favorece el buen funcionamiento del hígado ya que lo protege de toxinas, disminuye el colesterol, ayuda a que la bilis sea más fluida y puede colaborar, en algunos casos, en la lucha contra la hepatitis.
Anticancerígena: Se ha demostrado que es útil para hacer más efectivo el tratamiento de quimioterapia para eliminar el cáncer de ovarios e hígado.
Expectorante: Ideal para personas con asma y con mucha mucosidad bronquial.
Digestiva: Ayuda a aliviar la digestión lenta, la falta de apetito, los gases, el exceso o falta de ácidos gástricos, etc.
Son claros los beneficios de la cúrcuma frente a la aplicación de la tartrazina como colorante, sin embargo tiene algunas desventajas como su baja estabilidad y corta vida útil en el alimento o bebida. Aún así, la tartrazina es un colorante tóxico que debería tener una regulación más extricta, y mientras no la tenga opto por consumirla lo menos posible, ¿y ustedes? Gracias por leerme ☻
Tartrazine: legal poison

(Source)

Artificial sweeteners and colorants are widely used in the food industry as they give the food a pleasant and striking taste and color. Natural dyes are less used than artificial dyes because they have less coloring power, are more delicate and unstable when mixed with other compounds and with the environment and require a higher dosage, which increases the cost.
However, it is worrying that in several scientific studies some artificial colorants are related with detriments to the health of their consumers, as tartrazine is [1]. That is why it is very important to control the quality of food and the application of the regulation of artificial colors in foods that are consumed daily since most food labels and drinks do not record their exact content.
What is tartrazine?
Tartrazine, also known as yellow dye No. 5 or E102, is a water-soluble orange powder used in foodstuffs, cosmetics, drugs and pharmaceuticals. It belongs to the group of azo dyes (double bond between two N) and its use is prohibited in Norway. The maximum intake should be 7.5 mg / kg body weight.

Tartrazine structure (Source)

This dye has the highest reported adverse reactions to food additives in the first 10 life years of consumers in Britain and can cause asthma in people intolerant to acetylsalicylic acid, the active agent of aspirin [2].

Products found in the market that contain tartrazine

How is tartrazine identified?
As it is important to determine if a food has tartrazine or not, and if so, in what quantity, one of the methods to quantify it is based on the use of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) as catalysts in the oxidation reaction of tartrazine by potassium iodate.
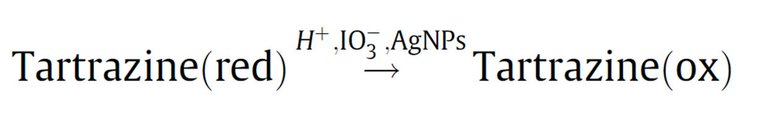
Quantification test reaction
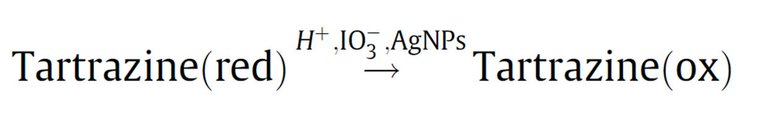

Identification process (Own source)

As shown in the above image, a sample of food or drink is first subjected to the oxidative reaction, then is quantified the oxidized tartrazine, as it has a dark brown coloration and can be read at a wavelength of 420 nm. When the spectrum is obtained, the area under the curve of the pattern and the oxidized sample is determined by means of a software and with the aid of a linear equation calculated from a previous run in the spectrophotometer of known quantities of tartrazine, the amount of tartrazine in the simple is determined.
Turmeric as an alternative natural colorant

Tartrazine vs. Turmeric (Source)

The turmeric is one of the spices with more properties, benefits and medicinal indications. It has been used for more than 4000 years as a seasoning and coloring and has many beneficial properties for health such as:
Anti-inflammatory: Relieves pain in people with arthritis, for example.
Anticoagulant: Prevents the formation of clots in the blood as it limits platelet aggregation thus improving circulation and preventing atherosclerosis.
It eliminates toxins: It favors the good functioning of the liver as it protects it from toxins, lowers cholesterol, helps the bile to be more fluid and can collaborate, in some cases, in the fight against hepatitis.
Anticancer: It has been shown to be useful in making chemotherapy treatment more effective in eliminating ovarian and liver cancer.
Expectorant: Ideal for people with asthma and a lot of bronchial mucus.
Digestive: Helps relieve slow digestion, lack of appetite, excess or lack of gastric acids, etc.
The benefits of turmeric are clear compared to tartrazine ones as a colorant, however it has some disadvantages such as its low stability and short useful life in food or drink products. Even so, tartrazine is a toxic dye that should have a more strict regulation, and as long as it is that way, I choose to consume it as little as posible… what about you? Thank you for reading me ☻
amazing
thanks!